Summary
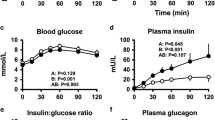
1. Six healthy male volunteers received equivalent intravenous beta-blocking doses of propranolol, practolol and betaxolol (SL75212) or saline at weekly intervals Sixty minutes later 0.1 unit/kg insulin was given intravenously. 2. In all studies, maximum hypoglycaemia (mean 1.2 mmol/l) was reached thirty minutes after insulin. Recovery from hypoglycaemia was delayed with propranolol but practolol and betaxolol had no effect. 3. Propranolol blocked the tachycardia and widening of pulse pressure seen in saline treated subjects. It also blocked the rebound rise in free fatty acids (FFA) and glycerol concentrations that followed the nadir of hypoglycaemia. 4. Neither practolol nor betaxolol had significant effects on pulse rate or blood pressure but betaxolol resembled propranolol in blocking the rebound rise in FFA and glycerol, while practolol blocked the rise in glycerol alone. 5. The magnitude of the rise in growth hormone following hypoglycaemia was similar in all groups, but the peak was earlier after practolol and betaxolol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablad B, Borg KC, Carlsson E, Ek L, Johnsson J, Malmfors T and Regardh CG. (1975). A survey of the pharmacological properties of metroprolol in animals and man. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 36: (suppl V): 7–23
Abramson EA, Arky RA, Woeber KA (1966). Effects of propranolol on the hormonal and metabolic responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Lancet 2: 1386–1388
Antonis A, Clark ML, Hodge RL, Moloney M, Pilkington TRE (1967). Receptor mechanisms in the hyperglycaemic response to adrenaline in man. Lancet 1: 1135–1137
Bianchetti G, Cadigan PJ, Gomeni R, Kilborn JR, London DR, Morselli PL, Pentecost BL (1979). Cardiovascular effects of single oral doses of the new beta adrenoceptor antagonist SL 75212 in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2: 403 P
Blackard WG, Heidingsfelder SA (1968). Adrenergic receptor control mechanism for growth hormone secretion. J Clin Invest 47: 1407–1414
Boudot JP, Cavero I, Fenard S, Lefevre-Borg F, Manoury P, Roach AG (1981). Preliminary studies on SL 75212, a new potent, cardioselective beta-adrenoceptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol (in press)
Breviere GM, Rey C, Pernot C, Dupuis C (1978). Accidents hypoglycemiques majeurs chez les enfants traités par des betabloquants. Arch Mal Coeur 71: 525–588
Cadigan PJ, London DR, Pentecost BL, Bianchetti G, Gomeni R, Kilborn JR, Morselli PL (1980). Cardiovascular effects of single oral doses of the newβ-adrenoceptor blocking agent betaxolol (SL 75212) in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 9: 569–575
Carruthers M, Young DAB (1973). Free fatty acid estimation by a semi-automated fluorimetric method. Clin Chem Acta 49: 341–348
Christensen NJ, Alberti KGMM, Brandsborg O (1975). Plasma catecholamines and blood substrate concentrations: studies in insulin induced hypoglycaemia and after adrenaline infusion. Eur J Clin Invest 5: 415–423
Conolly ME, Kersting F, Dollery CT (1976). The clinical pharmacology of beta adrenoceptor blocking drugs. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 19: 203–234
Davidson NM, Corrall RJM, Shaw TRD, French EB (1977). Observations in man of hypoglycaemia during selective and non-selective beta blockade. Scott Med J 22: 69–72
Davis BJ, Turner P (1979). The spectrofluorimetric estimation and buccal absorption of SL 75212, a novelβ-adrenoceptor antagonist. Br J Clin Pharmacol 8: 408 P
Deacon SP (1978). The effects of atenolol and propranolol upon lipolysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 5: 123–126
Deacon SP, Karunanayake A, Barnett D (1977). Acebutolol, atenolol and propranolol and metabolic responses to acute hypoglycaemia in diabetes. Br Med J 2: 1255–1257
Deacon SP, Barnett D (1976). Comparison of atenolol and propranolol during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Br Med J 2: 272–273
Gibbons DC, Lant AP, Ashford A, Collins RF, Pinder S (1976). Comparative effects of acebutolol and practolol on the lipolytic response to isoprenaline. Br J Clin Pharmacol 3: 177–184
Gomeni C, Gomeni R (1978). IGPHARM: interactive graphic package for pharmacokinetic analysis. Comput Biomed Res 11: 345–361
Gomeni C, Gomeni R (1980). Multivariate statistical methods in pharmacokinetics. In: Endrenyi L (ed) Design and analysis of enzyme and pharmacokinetic experiments. Plenum Press, New York
Gundogdu S, Brown PM, Juul S, Sachs L, Sönksen PH (1979). Comparison of hormonal and metabolic effects of salbutamol infusion in normal subjects and insulin-requiring diabetics. Lancet 2: 1317–1321
Harms HH, Gooren L, Spoelstra AJG, Hesse C, Verschoor L (1978). Blockade of isoprenaline-induced changes in plasma free fatty acids, immunoreactive insulin levels and plasma renin activity in healthy human subjects, by propranolol, pindolol, atenolol, metoprolol and acebutolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol 5: 19–26
Harms HH, van der Meer J (1975). Isoprenaline antagonism of cardioselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents on human and rat adipocytes. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2: 311–315
Hökfelt B, Hansson B, Heding LG, Nilsson KO (1978). Effect of insulin induced hypoglycaemia on the blood levels of catecholamines, glucagon, growth hormone, cortisol, C-peptide and proinsulin before and during medication with the cardioselective beta-receptor blocking agent metoprolol in man. Acta Endocrinol 87: 659–667
Imura L, Kato Y, Ikeda M, Morimoto M, Yawata M (1971). Effect of adrenergic-blocking or stimulating agents on plasma growth hormone, immunoreactive insulin and blood free fatty acid levels in man. J Clin Invest 50: 1069–1079
Kotler MN, Berman L, Rubenstein AH (1966). Hypoglycaemia precipitated by propranolol. Lancet 2: 1389–1390
Kreutz FH (1962). Enzymatische Glyzerin-Bestimmung. Klin Wochenschr 40: 362–363
Lager I, Blohme G, Smith V (1979). Effect of cardioselective and non-selectiveβblockade on the hypoglycaemic response in insulin-dependent diabetics. Lancet 1: 458–462
Lands A, Arnold A, McAuliff J, Luduena F, Brown T (1967). Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature 214: 597–598
Lloyd-Mostyn RH, Oram S (1975). Modification by propranolol of cardiovascular effects on induced hypoglycaemia. Lancet 1: 1312–1215
Newman RJ (1976). Comparison of propranolol, metoprolol and acebutolol on insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Br Med J 2: 447–449
Newman RJ (1977). Comparison of the antilipolytic effect of metoprolol, acebutolol and propranolol in man. Br Med J 2: 601–603
Nilsson A, Hansson BG, Hökfelt B (1978). Effect of metoprolol on blood glycerol, free fatty acids, triglycerides and glucose in relation to plasma catecholamines in hypertensive patients at rest and following submaximal work. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 13: 5–8
Nilsson OR, Anderberg B, Karlberg BE, Kagedal B (1980). Cortisol, growth hormone and prolactin responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in hyperthyroid patients before and duringβ-adrenoceptor blockade. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 12: 581–588
Oh VMS, Kaye CM, Warrington SJ, Taylor EA, Wadsworth J (1978). Studies of cardioselectivity and partial agonist activity inβ-adrenoceptor blockade comparing effects on heart rate and peak expiratory flow rate during exercise. Br J Clin Pharmacol 5: 107–120
Porte D, Robertson RP (1973). Control of insulin secretion by catecholamines, stress and the sympathetic nervous system. Fed Proc 32: 1792–1796
Robertson RP, Porte D (1973). Adrenergic modulation of basal insulin secretion in man. Diabetes 22: 1–8
Rowe MJ, Neilson JMM, Oliver MF (1975). Control of ventricular arrhythmias during myocardial infarction by antilipolytic treatment using a nicotinic acid analogue. Lancet 1: 295–300
Sönksen PH (1976). Double-antibody technique for the simultaneous assay of insulin and growth hormone. In: Antoniades HN (ed) Hormones in human blood: detection and assay. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Tarazi RC, Dustan HP (1972). Beta adrenergic blockade in hypertension: practical and theoretical implications of long-term haemodynamic variation. Am J Cardiol 29: 633–640
Taylor EA, Trembath PW, Warrington SJ (1981). Influence of environmental temperature and humidity on bronchial responses during assessment of selectivity ofβ-adrenoceptor antagonists in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol (in press)
Van Herwaarden CLA, Fennis JFM, Binkhorst RA, Van't Laar A (1977). Haemodynamic effects of adrenaline during treatment of hypertensive patients with propranolol and metoprolol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 12: 397–402
Warrington SJ, Turner P, Kilborn JR, Bianchetti G, Morselli PL (1980). Blood concentrations and pharmacodynamic effects of betaxolol (SL 75212) a newβ-adrenoceptor antagonist after oral and intravenous administration. Br J Clin Pharmacol 10: 449–452
West TET, Sönksen PH (1977). Is growth hormone response to insulin due to hypoglycaemia, hyperinsulinaemia or a fall in plasma free fatty acids? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 7: 283–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saunders, J., Gomeni, R., Kilborn, J.R. et al. A comparison between propranolol, practolol and betaxolol (SL75212) on the circulatory and metabolic responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 21, 177–184 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00627917
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00627917