Summary
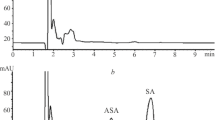
A high-pressure liquid chromatographic technique was developed which allowed concurrent measurement of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and salicylic acid (SA) in plasma. ASA was extensively deacetylated to SA not only in vivo but also in vitro, even in frozen plasma. The in vitro conversion could be prevented by physostigmine. In vivo, ASA was eliminated within few hours, whereas SA was continuously present following daily administration of conventional doses of ASA. A slight modification of a similar method, originally developed for naproxen determination [9], was found appropriate for measurement of the SA derivative diflunisal, of two non-SA antiinflammatory agents, indomethacin and indoprofen, and of a related anti-platelet agent, indobufen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew A, Rodda B, Verhaest L, van Winzum C (1977) Diflunisal: six-month experience in osteoarthritis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 4 (Suppl 1) 45S-52S
Ekdahl C, Håkansson E, Lindholm L, Melander A, Olsson S, Svensson B, Wåhlin-Boll E (1981) Comparison of diflunisal and acetylsalicylic acid in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol (in press)
Tempero KF, Cirillo VJ, Steelman SL (1979) Diflunisal. New Perspectives in Analgesia. Royal Society of Medicine International Congress and Symposium Series No.6. Royal Society of Medicine, London, pp 1–20
Harris PA, Riegelman S (1967) Acetylsalicylic acid hydrolysis in human blood and plasma I. Methodology and in vitro studies. J Pharm Sci 56: 713–716
Levy G (1979) Pharmacokinetics of salicylate in man, Drug Metab Rev 9: 3–19
Brodie DA, Hooke KF (1971) Effects of route of administration on the production of gastric hemorrhage in the rat by aspirin and sodium salicylate. Am J Dig Dis 16: 985–989
Quick AJ (1966) Salicylates and bleeding: The aspirin tolerance test. Am J Med Sci 252: 265–269
Wilson JT, Bocchini J, Dixon J, Hunter J, Brown DR (1980) Pharmacodynamics of acetyl salicylic acid (ASA) and acetaminophen (APAP) in febrile children. World Conference on Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, London 1980. Abstract no. 0356.
Westerlund D, Theodorsen A, Jaksch Y (1979) Bioanalysis of naproxen by high performance reversed phase liquid chromatography with photometric and fluorimetric detection. J Liquid Chromatogr 2: 969–1001
Peng GW, Gadalla MAF, Smith V, Peng A, Chiou WL (1978) Simple and rapid high-pressure liquid chromatographic simultaneous determination of aspirin, salicylic acid and salicyluric acid in plasma. J Pharm Sci 67: 710–712
Menguy R, Desbaillets L, Masters Y, Okabe S (1972) Evidence for a sex-linked difference in aspirin metabolism. Nature 239: 102–103
Mandelli M, Tognoni G (1980) Monitoring plasma concentrations of salicylate. Clin Pharmacokinet 5: 424–440
Rowland M, Riegelman S (1967) Determination of acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid in plasma. J Pharm Sci 56: 717–720
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wåhlin-Boll, E., Brantmark, B., Hanson, A. et al. High-pressure liquid chromatographic determination of acetylsalicylic acid, salicylic acid, diflunisal, indomethacin, indoprofen and indobufen. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 20, 375–378 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00615408
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00615408