Abstract
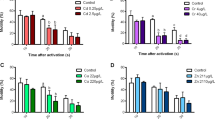
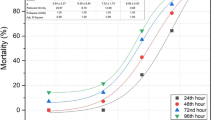
The action of various concentrations of zinc on different phases of development of Arbacia lixula L. has been observed. The following concentrations were used in the experiment: 0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 mg l-1; these concentrations were tested on unfertilized eggs, sperms, fertilized eggs and adult individuals. It was found that after 96 h a 0.01 mg l-1 concentration reduces the mobile sperm percentage compared with the control group. At concentrations of 0.1, 1 and 10 mg l-1 no mobile sperm were found after 96 h. Compared with the control group, the action of zinc on unfertilized eggs was to increase the percentage of eggs showing signs of cytolisis after 12, 36 and 60 h. In the case of fertilized eggs it was found that with a concentration of 0.01 mg l-1 the P5 pluteus stage was attainable; the percentage of forms reaching that stage was less than in the control group. At 0.1 mg l-1 only a very low percentage of eggs could reach the P5 pluteus stage; concentrations of 1 and 10 mg l-1 are incompatible with the normal development of an egg. Adult individuals kept in aquaria with 1 mg l-1 zinc showed no signs of suffering after 20 d. Gametes are proposed as the appropriate material for carrying out bioassays.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Barber, R. T., J. Barret, J. A. McGowen, J. G. Quinn, L. Pomeray and L. Provasoli: The effects on marine organisms. Marine environmental quality. National Acad. of Science, Wash. D.C. 63–81, 1971
Bernhard, N. and A. Zattera: Valutazione per alcuni polluenti delle concentrazioni tollerabili nell'ambiente marino e della ingestione limite per l'uomo. Ecologia, Acqua, Aria, Suolo, 8, 612–620 (1975)
Bryan, G. W.: Zinc regulation in the lobster Homarus vulgaris. 1: Tissue zinc and copper concentrations. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 44, 549–563 (1964)
Bryan, G. W.: The metabolism of zinc in crabs, lobster and freshwater crayfish, pp 1005–1016. Ed. by B. Alberg and F. P. Ungate. Radioecological concentration process. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1967
Goldberg, E. D.: Minor elements in sea water in chemical oceanography, pp 163–196. Ed. by J. P. Riley and G. Skirrow. New York: Academic Press 1965
Kinoshita, S.: The mode of action of metal chelating substances on sperm motility in some marine forms as shown by glyceral extracted sperm models. J. Fac. Sci. Tokyo Univ. Sec. IV, Zool. 8, 219–228 (1958)
Kinoshita, S.: On the identity of the motility-inducing factor of flagellum and the relaxing factor of muscle. J. Fac. Sci. Tokyo Univ. Sec. IV, Zool. 8, 427–437 (1959)
Kobayashi, N.: Fertilised sea urchin eggs as an indicator material for marine pollution bioassay, preliminary experiments. Publ. Seto mar. biol. Lab. XVIII (6), 379–406 (1971)
Kobayashi, N., H. Nagami and K. Doi: Marine pollution bioassay by using sea urchin eggs in the inland sea of Japan (the seto-Naikai). Publ. Seto mar. biol. Lab. XIX (6), 359–381 (1972)
Kobayashi, N.: Studies on the effects of some agents on fertilised sea urchin eggs, as a part of the bases for marine pollution bioassay I. Publ. Set mar. biol. Lab. XXI (2), 109–114 (1973)
Kobayashi, N.: Marine pollution bioassay by sea urchin eggs, an attempt to enhance accuracy. Publ. Seto. mar. biol. Lab. XXI (5/6) 377–391 (1974)
Lallier, R.: Effects des ions zinc et cadmium sur le développement de l'oeuf de l'oursin Paracentrotus lividus. Arch. Biol. (Liège) 66, 75–102 (1955)
Lallier, R.: Recherches sur la détermination embryonnaire chez les Echinodermes. L'action des oxydants et de l'acide p-cloro-mercuribenzoique sur le développement de l'oeuf de l'oursin Paracentrotus lividus. Arch. Biol. 67, 181–209 (1956a)
Lallier, R.: Les ions des metaux lourds et le problème de la détermination embryonnaire chez les Echinodermes. J. Embryol. exp. Morphol. 4, 265–278 (1956b)
Lallier, R.: Recherches sur l'animalization de l'oeuf d'oursin par les ions zinc. J. Embryol. exp. Morphol. 7, 540–548 (1959)
Mateyko, C.M.: Developmental modifications in Arbacia punctulata by various metabolic substances. Biol. Bull., mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 130, 184–228 (1967)
Metz, C. B. and C. W. Birky: The action of some metal ions and some metal chelating agents on the motility and respiration of the starfish sperm. Biol. Bull., mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 109, 365–366 (1955)
Okubo, K. and T. Okubo: Study on the bioassay method for evaluation of water pollution. II: Use of fertilised eggs of sea urchins and bivalves. Bulletin, Tokai Regional Fisheries Research Laboratory 32, 131–140 (1962)
Pirrone, A. M., G. Scanzo, V. Mutalo and G. Giudice: Effect of chemical animalization and vegetalization on the synthesis of ribosomial RNA in sea urchin embryos. Wilhelm Roux Arch. Entwicklungsmech. Organismen 164, 222–225 (1970)
Ranzi, S. and P. Citterio: Sulle proteine dell'Arbacia lixula nello sviluppo embrionale e postembrionale. Rend. Ist. lombardo Sci. 90, 515–521 (1956)
Ranzi, S.: Early determination in development under normal and experimental conditions, pp 291–318 In: The beginnings of embryonic development. Washington. Am. Assoc. Advanc. Science 1957
Ranzi, S.: On the stability of the structures of animalized and vegetalized sea urchin embryos. Biol. Bull., mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 171, 436–437 (1959)
Slater, J. P., A. S. Mildvan and L. A. Loeb: Zinc in DNA polymerase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 44, 37–43 (1971)
Steele, J. H., A. D. McIntyre, R. Johnston, J. G. Baxter, G. Topping and H. D. Dooley: Pollution studies in the Clyde sea area. Mar. Poll. Bull. 4, 153–157 (1973)
Sugiyama, M.: Polyspermy in the sea urchin eggs induced by CuSO4. Zool. Magz. 50, 11–12 (1950)
Waterman, A. J.: Effects of salts of heavy metals on development of the sea urchin, Arbacia punctulata. Biol. Bull., mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 73, 401–420 (1937)
WQC: Water quality criteria 1972. Report of the Committee on water quality criteria pp 1–594. Nat. Acad. Engineering Superint. Dac. U.S. Govern. Print. Office, Washington D.C. Stock. No. 5501-00520 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by B. Battaglia, Padova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castagna, A., Sinatra, F., Scalia, M. et al. Observations of the effect of zinc on the gametes and various development phases of Arbacia lixula . Mar. Biol. 64, 285–289 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393628
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393628