Abstract
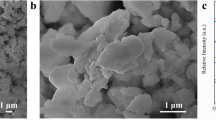
For the trace analysis of impurities in thick ceramic layers of a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) sensitive solid-state mass spectrometric methods, such as laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and radiofrequency glow discharge mass spectrometry (rf-GDMS) have been developed and used. In order to quantify the analytical results of LA-ICP-MS, the relative sensitivity coefficients of elements in a La0.6Sr0.35MnO3 matrix have been determined using synthetic standards. Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) – as a surface analytical method – has been used to characterize the element distribution and diffusion profiles of matrix elements on the interface of a perovskite/Y-stabilized ZrO2 layer. The application of different mass spectrometric methods for process control in the preparation of ceramic layers for the SOFC is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, J.S., Breuer, U., Westheide, J. et al. Trace and surface analysis of ceramic layers of solid oxide fuel cells by mass spectrometry. Fresenius J Anal Chem 355, 626–632 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s0021663550626
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s0021663550626