Abstract
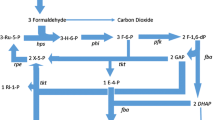
Elevated values of molar growth yield (Yx/s = 14–26 g mol–1) were obtained during exponential growth (μ > 0.4 h–1) of Zymomonas mobilis ATCC 29191 by using reduced concentrations of glucose (6.25–100 mM) and increased oxygen supply (E h > 300 mV) in the growth medium, as compared to the Yx/s of anaerobic exponential growth (8–10 g mol–1). Aerobically grown cells showed an increased maximum growth rate (μmax), and a reduced specific glucose consumption rate (qs), and specific ethanol formation rate (qp), thus demonstrating a more pronounced energy-coupling growth under oxic conditions. These results can be neither explained by the concept of a solely operating Entner-Doudoroff pathway as an ATP source in aerobically growing cultures of Z. mobilis nor considered to be consistent with existing data on the lack of the Pasteur effect in this bacterium. Therefore, the results rather give evidence for the essential contribution of aerobic ATP generation under the reported conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 September 1996 / Accepted: 9 December 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zikmanis, P., Krúče, R. & Auzin¸a, L. An elevation of the molar growth yield of Zymomonas mobilis during aerobic exponential growth. Arch Microbiol 167, 167–171 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050430
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050430