Abstract
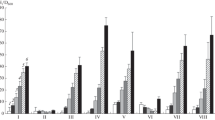
After addition of amino acids to a Bacillus subtilis glucose culture the intracellular guanosine triphosphate (GTP) concentration increased. The growth rate and the rate of RNA accumulation increased too. With mycophenolic acid, an inhibitor of inosinate dehydrogenase, it was possible to adjust the intracellular GTP concentration to values ranging between that of the glucose culture and that of the culture which had received amino acids. This led to intermediate growth rate values. Guanosine abolished the mycophenolic acid inhibition of GTP synthesis. It also counteracted the drug effects on growth rate and RNA accumulation. In cultures growing on Nutrient Sporulation Medium, in which the growth rate decreases as cell density increases, the GTP concentration did correlate with the growth rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ppGpp:
-
guanosine 5′-diphosphate 3′-diphosphate
- pppGpp:
-
guanosine 5-triphosphate 3′-diphosphate
References
Beck C, Ingraham J, Maaloe O, Neuhard J (1973) Relationship between the concentration of nucleoside triphosphates and the rate of synthesis of RNA. J Mol Biol 78:117–121
Biebricher CK, Druminski M (1980) Inhibition of RNA polymerase activity by the Escherichia coli protein biosynthesis elongation factor Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:866–869
Debenham PG, Pongs O, Travers AA (1980) Formylmethionyl-tRNA alters RNA polymerase specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:870–874
Erlich H, Gallant J, Lazzarini RA (1975) Synthesis and turnover of ribosomal ribonucleic acid in guanine-starved cells of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 250:3057–3061
Franzen JS, Binkley SB (1961) Comparison of acid-soluble nucleotides in Escherichia coli at different growth rates. J Biol Chem 236:515–519
Freese E, Heinze JE, Mitani T, Freese EB (1978) Limitation of nucleotides induces sporulation. In: Chambliss G, Vary JC (ds) Spores VII American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 277–285
Freese E, Heinze JE, Galliers EM (1979a) Partial purine deprivation causes sporulation of Bacillus subtilis in the presence of excess ammonia, glucose, and phosphate. J Gen Microbiol 115:193–205
Freese E, Lopez JM, Freese EB (1979b) Initiation of bacterial and yeast sporulation by partial deprivation of guanine nucleotides. In: Richter P, Koch G (eds) Regulation of Macromolecular Synthesis by low molecular weight mediators. Academic Press, New York, pp 127–143
Freese E, Lopez JM, Ochi K (1981) Role of guanine nucleotides and of the Stringent Response to amino acids deprivation in the initiation of bacterial sporulation. In: Schlesinger D (ed) Microbiology-1981. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 11–16
Gausing K (1976) Synthesis of rRNA and r-Protein mRNA in E. coli at different growth rates. In: Kjelgaard NO, Maaloe O (eds) Alfred Benzon symposium IX, control of ribosome synthesis. Munksgaard, Copenhagen, pp 292–303
Heinze JE, Mitani T, Rich KE, Freese EB (1978) Induction of sporulation by inhibitory purines and related compounds. Biochem Biophys Acta 521:16–26
Karl DM (1978) Occurrence and ecological significance of GTP in the ocean and in microbial cells. Appl Environm Microbiol 36:349–355
Karl DM (1980) Cellular nucleotide measurements and applications in microbial ecology. Microbiol Rev 44:739–796
Lopez JM, Marks CL, Freese E (1979) The decrease of guanine nucleotides initiates sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta 587:238–252
Lopez JM, Dromerick A, Freese E (1981a) Response of guanosine 5′-triphosphate concentration to nutritional changes and its significance for Bacillus subtilis sporulation. J Bacteriol 146:605–613
Lopez JM, Ochi K, Freese E (1981b) Initiation of Bacillus subtilis sporulation caused by the stringent response. In: Levinson HS, Sonenshein AL, Tipper DJ (eds) Sporulation and germination. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 128–136
Maaloe O (1969) An analysis of bacterial growth. Develop Biol Suppl 3:33–68
Mitani T, Heinze JE, Freese E (1977) Induction of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis by decoiynine or hadacidin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 77:1118–1125
Molin S (1976) Ribosomal RNA chain elongation rates in Escherichia coli. In: Kjelgaard NO, Maaloe O (eds) Alfred Benzon Symposium IX, control of ribosome synthesis. Munksgaard, Copenhagen, pp 333–339
Smith RC, Maaloe O (1964) Effect of growth rate on the acid-soluble nucleotide composition of Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta 86:229–234
Travers AA (1976) RNA polymerase specificity and the control of growth. Nature 263:641–646
Wilson A (1971) Miscellaneous Penicillum toxins. In: Ciegler A (ed) Microbial toxins, Vol. VI. Academic Press, New York, pp 460–470
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez, J.M. GTP pool expansion is necessary for the growth rate increase occurring in Bacillus subtilis after amino acids shift-up. Arch. Microbiol. 131, 247–251 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405887
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405887