Abstract
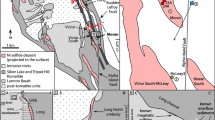
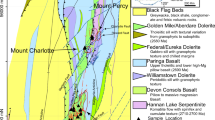
Kuroko-type massive sulfide deposits of the Eastern Black Sea province of Turkey are related to the Upper Cretaceous felsic lavas and pyroclastic rocks, and associated with clay and carbonate alteration zones in the footwall and hangingwall lithologies. A complete upward-vertical section of a typical orebody consists of a stringer-disseminated sulfide zone composed mainly of pyrite and chalcopyrite; a massive pyrite zone; a massive yellow ore consisting mainly of chalcopyrite and pyrite; a black ore made up mainly of galena and sphalerite with minor amounts of chalcopyrite, bornite, pyrite and various sulfosalts; and a barite zone. Most of the deposits in the province are associated with gypsum in the footwall or hangingwall. The paragenetic sequence in the massive ore is pyrite, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, bornite, galena and various sulfosalts, with some overlap between the mineral phases. Massive, stringer and disseminated sulfides from eight kuroko-type VMS deposits of the Eastern Black Sea province have a δ 34S range of 0–7 per mil, consistent with the δ 34S range of felsic igneous rocks. Sulfides in the massive ore at Madenköy (4.3–6.1 per mil) differ isotopically from sulfides in the stringer zone (6.3–7.2 per mil) suggesting a slightly increased input of H2S derived from marine sulfate with time. Barite and coarse-grained gypsum have a δ 34S range of 17.7–21.5 per mil, a few per mil higher than the δ 34S value of contemporaneous seawater sulfate. The deposits may, therefore, have formed in restricted basins in which bacterial reduction of sulfate was taking place. Fine-grained, disseminated gypsum at Kutlular and Tunca has δ 34S values (2.6–6.1 per mil) overlapping those of ore sulfides, indicating sulfide oxidation during waning stages of hydrothermal activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinci, O.T. (1980) Major copper metallogenic units and genetic igneous complexes of Turkey. In: Jankovic, S., Sillittoe, R.H. (eds.) European copper deposits. Belgrade, Yugoslavia, pp. 219–208
Altun, Y. (1984) Comparative ore mineralogy and genesis of the metallic deposits in the Giresun-Görele and Tirebolu areas (Eastern Black Sea Region). Unpubl. Ph.D. thesis, University of Istanbul (in Turkish)
Barton, P.B. (1978) Some ore textures involving sphalerite from Furutobe mine. Akita Prefecture, Japan. Mining Geol. 28:293–300
Bluth, G.J., Ohmoto, H. (1988) Sulfide-sulfate chimneys on the East Pacific Rise, 11° and 13° N latitudes, part II. Sulfur isotopes. Can. Mineralogist 26:505–515
Bowers, T.S. (1989) Stable isotope signatures of water-rock interaction in mid-ocean hydrothermal systems: sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen. Geophys. Res. 94:5775–5786
Brimhall, G.H., Crerar, D.A. (1989) Ore fluids: magmatic to supergene. In: Carmichael, I.S.E., Eugester, H.P. (eds.) Thermodynamic modelling of geological materials: minerals, fluids, and melts. Mineralogical Society of America, pp. 235–321
Brinkmann, R. (1974) Geologic relations between Black Sea and — Anatolia. In: Degens, E.T., Ross, D.A. (eds.) The Black Sea geology, chemistry, and biology. The American Assoc. Petrol. Geologists Memoir no. 20, pp. 63–76
Buser, S., Cvetic, S. (1973) Geology of the environs from the Murgul copper deposit, Turkey. Maden Tetkik ve Arama Enstitüsü (MTA) Bull. 81:22–45
Çagatay, M.N. (1981) Volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits of Turkey under the light of recent developments (in Turkish). In: First Scientific and Technical Congress of Chamber of the Turkish Geological Engineers 6:35–56
Çagatay, M.N. (1993) Hydrothermal alteration associated with volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits: Examples from Turkey. Econ. Geol. 88:606–621
Çagatay, M.N., Boyle, D.R. (1980) Geology, geochemistry, and hydrothermal alteration of the Madenköy massive sulfide deposit, Eastern Black Sea region, Turkey. In: Ridge, J.D. (ed.), IAGOD 5th Symposium Proc.: Schwaiserbart'sche Verlagbuchhandlung, Stuttgart, pp. 653–678
Claypool, G.E., Holser, W.T., Kaplan, I.R., Sakai, H., Zak, I. (1980) The age curves of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation. Chem. Geol. 28:199–260
Çogulu, H.E. (1970) Comparative petrological and geochronological study of the Gümüşhane and Rize plutons. Unpubl. Post-doctoral thesis, Technical University of Istanbul
Coleman, M., Moore, M.P. (1978) Direct reduction of sulfates to sulfur dioxide for isotopic analysis. Anal. Chem. 50:1594–1598
Davis, E.E., Goodfellow, W.D., Bornhold, B.D., Adshead, J., Blaise, B., Villinger, H., Le Cheminant, G. (1987) Massive sulfides in a sedimented rift valley, Northern Juan de Fuca Ridge. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 82:49–61
De Geoffroy, J. (1960) Geology and mineral deposits of Çayeli, Pazar, and Ardeşen districts. Maden Tetkik ve Arama Enstitüsü (MTA) Report no. 3073 (in Turkish)
Dixon, C.J., Pereira, J. (1974) Plate tectonics and mineralization in the Tethyan region. Mineral. Deposita 9:185–198
Eastoe, C.J., Nelson, S.E. (1988) A Permian kuroko-type hydrothermal system, Afterthought-Ingot area, Shasta County, California: lateral and vertical sections, and geochemical evolution. Econ. Geol. 83:588–605
Eastoe, C.J., Solomon, M., Garcia Palomero, F. (1986) A sulfur isotope study of the massive and stockwork pyrite deposits at Rio Tinto, Spain. Trans. Inst. Mining Metallurgy 95:B201-B207
Franklin, J.M. (1986) Volcanic-associated massive sulphide deposits — an update. In: Andrew, C.J., Crowe, R.W.A., Finlay, S., Pennell, W.M., Pyne, I.F. (eds.) Geology and genesis of Irish deposits: Irish Assoc. Econ. Geol., pp 49–69
Franklin, J.M., Lydon, J.W., Sangster, D.F. (1981) Volcanic-associated massive sulfide deposits. In: Skinner, B.J., Sims, P.K. (eds.) Econ. Geol. 75th Anniversary Volume, pp 485–627
Gemmell, J.B., Large, R.R. (1992) Stringer system and alteration zones underlying Hellyer volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit, Tasmania, Australia. Econ. Geol. 87:620–649
Goodfellow, W.D. (1987) Anoxic stratified oceans as a source of sulphur in sediment-hosted stratiform Zn-Pb deposits (Selwyn Basin, Yukon, Canada). Chem. Geol. (Isotope Geoscience Section) 65:359–382
Goodfellow, W.D., Biaise, B. (1988) Sulfide formation and hydrothermal alteration of hemipelagic sediment in Middle Valley, Northern Juan de Fuca Ridge. Can. Mineralogist 26:675–696
Green, G.R., Solomon, M., Walshe, J.L. (1981) The formation of the volcanic-hosted massive sulfide ore deposit at Rosebery, Tasmania. Econ. Geol. 76:304–338
Halbach, P., Nakamura, K., Wahsner, M., Lange, J., Kaselitz, L., Hansen, R.-D., Yamano, M., Post, J., Prause, B., Seifert, R., Michaelis, W., Teichmann, F., Kinoshita, M., Marten, A., Ishibashi, J., Czerwinski, S., Blum, N. (1989) Probable modern analogue of kuroko-type massive sulphide deposits in the Okinawa Trough back-arc basin. Nature 338:496–499
Holser, W.T. (1984) Gradual and abrupt shifts in ocean chemistry during Phanerozoic time. In: Holland, H.D., Trendall, A.F. (eds.) Patterns of change in earth evolution: Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 123–144
Ishihara, S., Sasaki, A. (1989) Sulfur isotope ratios of the magnetite-series and ilenite-series granitoids of the Sierra Nevada batholith — a reconnaisance study. Geology 17:788–791
Janecky, D.R., Shanks, W.C., III (1988) Computational modeling of chemical and sulfur isotopic reaction processes in seafloor hydrothermal systems: chimneys, massive sulfides and subjacent alteration zones. Can. Mineralogist 26:805–825
Kajiwara, Y. (1971) Sulfur isotope study of kuroko ores of Shakanai No. 1 deposits, Akita Prefecture, Japan. Geochem. J. 4:157–181
Kajiwara, Y., Date, J. (1971) Sulfur isotope study of Kuroko-type and Kieslager-type strata-bound massive sulfide deposits in Japan. Geochem. J. 5:133–150
Kraeff, A. (1963) Geology and mineral deposits of the Hopa-Murgul region western part of the province of Artvin, NE Turkey copper deposit, Turkey. Maden Tetkik ve Arama Enstitüsü (MTA) Bull. 60:45–60
Kronberg, P. (1970) Photogeological results on the tectonics of the Eastern Black Sea mountains (northeastern Turkey). Maden Tetkik ve Arama Enstitüsü (MTA) Bull. 74:57–65
Kusakabe, M., Chiba, H. (1983) Oxygen and sulfur isotope composition of barite and anhydrite from the Fukazawa deposit, Japan. In: Ohmoto, H., Skinner, B.J., (eds.) The Kuroko and related volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. Econ. Geol. Monogr. 5:292–301
Leitch, C.B.H. (1981) Mineralogy and textures of the Lahanos and Kizilkaya sulfide deposits, northeastern Turkey, and their similarity to Kuroko ores. Mineral. Deposita 16:241–257
Lusk, J. (1972) Examination of volcanic-exhalative and biogenic origins for sulfur in the stratiform massive sulfide deposits of New Brunswick, Canada. Econ Geol. 67:169–183
Mitsuno, C., Nakamura, T., Kanehira, K., Yamamoto, M., Sugita, M., Kase, K., Thadeu, D., de Carvalho, D., Arribas, A. (1986) Geological studies of the ‘Iberian Pyrite Belt’ with special reference to its genetic correlation of the Yanahara ore deposit and others of the inner zone of southwest Japan. Okayama Univ., Okayama, Japan., 206 pp
Moore, W.J., McKee, E., Akinci, O. (1980) Chemistry and chronology of plutonic rocks in the Pontid mountais, northern Turkey. In: Jankovic, S., Sillittoe, R.H. (eds.) European copper deposits: Belgrade, Yugoslavia, pp 209–215
Nebioglu, T.Y. (1975) Geological map of the Madenköy (1) area (1:1,000 scale) (in Turkish). Maden Tetkik ve Arama Enstitüsü (MTA) Map no. 31134
Ohmoto, H., Lasaga, A.C. (1982) Kinetics of reactions between aqueous sulfates and sulfides in hydrothermal systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 46:1727–1745
Ohmoto, H., Rye, R.O. (1979) Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In: Barnes, H.L., (ed.) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits. Wiley, New York, pp. 509–567
Robinson, B.W., Kusakabe, M. (1975) Quantitative preparation of SO2 for 34S/32S analyses from sulfides by combustion with cuprous oxide. Analyt. Chem. 47:1179–1181
Schneider, H.-J., Özgür, N., Palacios, C.M. (1988) Relationship between alteration, rare earth element distribution, and mineralization of the Murgul copper deposit, northeastern Turkey. Econ. Geol. 83:1238–1246
Sengör, A.M.C., Yilmaz, Y. (1981) Tethyan evolution of Turkey: a plate tectonic approach. Tectonophysics 75:181–241
Shanks, W.C., III, Seyfried, W.E., Jr. (1987) Stable isotope studies of vent fluids and chimney minerals, southern Juan de Fuca Ridge: sodium metasomatism and sea-water sulfate reduction. J. Geophys. Res. 92:11387–11399
Solomon, M., Eastoe, C.J., Walshe, J.L., Green, G.R. (1988) Mineral deposits and sulfur isotope abundances in the Mt. Read Volcanics between Que River and Mt. Darwin, Tasmania. Econ. Geol. 83:1307–1328
Solomon, M., Rafter, T.A., Jensen, M.N. (1969) Isotope studies on the Rosebery, Mount Farrell and Mount Lyell ores. Mineral. Deposita 4:172–199
Taner, M.F. (1976) Etude geologique et petrographique de la region de Guneyce-Ikizdere situee au sud de Rize (Pontides Orientales, Turquie): Unpubl. Ph. D. thesis, University of Genevre thesis no. 1788
Taylor, B.E., South, B.C. (1985) Regional stable isotope systematics of hydrothermal alteration and massive sulfide deposits in the West Shasta district, California. Econ. Geol. 80:2149–2163
Tokel, S. (1972) The stratigraphical and volcanic history of the Gümüshane area, northeast Anatolia. Unpubl. Ph.D. thesis, University of London
Tugal, H.T. (1969) Pyritic sulphide deposits of the Lahanos mine area, Eastern Black Sea Region, Turkey. Unpubl. Ph.D. thesis, University of Durham
Tupper, W.M. (1960) Sulfur isotopes and the origin of the sulfide deposits of the Bathurst-Newcastle area of northern New Brunswick. Econ. Geol. 55:1676–1707
Ueda, A., Sakai, H. (1984) Sulfur isotope study of Quaternary volcanic rocks from the Japanese Islands arc. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 48:1837–1848
Urabe, T. (1987) Kuroko deposit modeling based on magmatic hydrothermal theory. Mining Geology 37:159–176
Watanabe, M., Sakai, H. (1983) Stable isotope geochemistry of sulfates from the Neogene ore deposits in the Green Tuff region, Japan. In: Ohmoto, H., Skinner, B.J. (eds.) The Kuroko and related volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. Econ. Geol. Monogr. 5:282-291
Yilmaz, Y. (1972) The petrology and structure of the Gümüshane granite and the surrounding rocks, northeast Anatolia. Unpubl. Ph.D. thesis, University of London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çagatay, M.N., Eastoe, C.J. A sulfur isotope study of volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits of the Eastern Black Sea province, Turkey. Mineral. Deposita 30, 55–66 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208877
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208877