Abstract
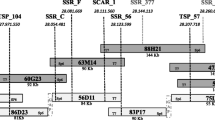
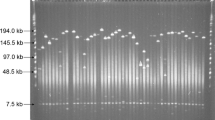
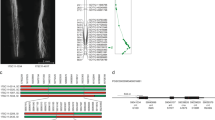
A yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) library was constructed from high-molecular-weight DNA of potato (Solanum tuberosum). Potato DNA fragments obtained after complete digestion with four different rare-cutter restriction enzymes were cloned using the pYAC-RC vector. The library consists of 21 408 YAC clones with an average insertion size of 140 kb. The frequency of YAC clones having insertions of chloroplast or mitochondrial DNA was estimated to be 0.5% and 0.3%, respectively. The YAC library was screened by PCR with 11 DNA markers detecting single genes or small gene families in the potato genome. YACs for 8 of the 11 markers were detected in the library. Using 2 markers that are linked to the resistance genes R1 and Gro1 of potato, we isolated two individual YAC clones. One of these YAC clones was found to harbour one member of a small family of candidate genes for the nematode resistance gene Gro1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received : 5 May 1997 / Accepted : 20 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leister, D., Berger, A., Thelen, H. et al. Construction of a potato YAC library and identification of clones linked to the disease resistance loci R1 and Gro1. Theor Appl Genet 95, 954–960 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050647
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050647