Summary
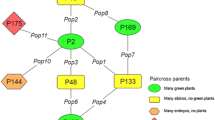
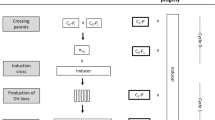
The effect of genotype on maternal haploid plant production in maize was studied. The frequency of gynogenetic plants when “Stock 6” was used as pollinator varied according to the female parent genotype. No simple relation was observed between genotypic aptitudes for gynogenetic and androgenetic development, which occured after pollination of “W23” plant carrying the “indeterminate gametophyte” gene. Furthermore, the population NS, a favorably responsive genotype to anther culture, does not exhibit exceptional ability for in vivo gynogenesis. The effect of inbreeding and the influence of maternal haploid origin suggest that specific genes control maternal haploid initiation and development. However, gynogenetic development is not limited to a particular genotype. The frequency of maternal haploids may be increased by using specific pollen parents. Attempts were made to select for a high haploidyinducing trait and the present study reports the successful development of lines that can be utilized as pollen parents to induce haploids for experimental purposes and breeding programmes. When an inbred line “WS14”, derived from the cross W23 x Stock 6, was used as pollen parent, 2%–5% maternal haploids were obtained according to the female parent genotype. A high haploidy-inducing potential is a heritable trait and may be controlled by a limited number of genes. Genetic determination of the haploidy-inducing character was examined in relation to the efficiency of the selecting method and the mechanisms involved in the origin of maternal haploids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aman MA, Sarkar KR (1978) Selection for haploidy inducing potential in maize. Indian J Genet 38:452–457
Chase SS (1952) Production of homozygous diploids of maize from monoploids. Agron J 44:263–267
Chase SS (1969) Monoploids and monoploid-derivatives of maize. Bot Rev 35:117–167
Chase SS (1974) Utilisation of haploids in plant breeding: breeding diploid species. Proc. 1st Int Symp Haploids, University of Guelph, Canada, pp 211–230
Coe EH (1959) A line of maize with high haploid frequency. Am Nat 93:381–382
Dieu P, Beckert M (1986) Further studies of androgenetic embryo production and plant regeneration from in vitro cultured anthers in maize (Zea mays L.). Maydica 31:245–259
Kermicle JL (1969) Androgenesis conditioned by a mutation in maize. Science 166:1422–1424
Kimber G, Riley R (1963) Haploid angiosperms. Bot Rev 29:480–531
Lashermes P (1987) Gynogénèse et androgénèse in vivo chez le maîs (Zea mays L.): études génétique et physiologique, utilisation en sélection. Thèse de l'université de Clermont II, France (no. d'ordre 58), 183 pp
Magoon ML, Khanna KR (1963) Haploids. Caryologia 16:191–235
Mathur DS, Sachan JKS, Sarkar KR (1976) Radiation induced haploidy and heterofertilization in maize. J Nucl Agric Biol 5:76–77
Mathur DS, Aman MA, Sarkar KR (1980) Induction of maternal haploids in maize through heat treatment of pollen. Curr Sci 49:744–746
Randolph LF (1932) Some effects of high temperature on polyploidy and other variations in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci 18:222–229
Sarkar KR, Coe EH (1966) A genetic analysis of the origin of maternal haploids in maize. Genetics 54:453–464
Sarkar KR, Sudha Panke, Sachan JKS (1972) Development of maternal-haploidy-inducer lines in maize. Indian J Agric Sci 42:781–786
Zuoyo Z, Mingguang G (1984) Production of diploid pure lines of maize through parthenogenesis induced by chemicals. Acta Genet Sin 11:39–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lashermes, P., Beckert, M. Genetic control of maternal haploidy in maize (Zea mays L.) and selection of haploid inducing lines. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 76, 405–410 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265341
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265341