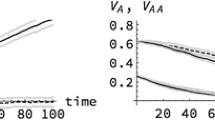
Summary
Theoretical predictions of changes in variance with disruptive selection have used models of infinitely many genes so the increase in variance was necessarily due to linkage disequilibrium. With small numbers of loci, the disequilibrium is shown still to comprise the major part of the changes in variance.
In a replicated experiment with Drosophila melanogaster, disruptive selection was practised for three generations, and this was followed by 5 or 7 generations of random mating. The heritability, as estimated from regression of progeny on parent, rose from 37% to 68% on selection, and subsequently declined to 45% on random mating. Changes of variance can be interpreted invoking the build up of linkage disequilibrium during selection followed by its breakdown upon relaxation. The results agree well with those obtained from Monte Carlo simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker, JSF, Cummins LJ (1969) Disruptive selection for sternopleural bristle number in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 21:697–712
Bulmer MG (1971) The effect of selection on genetic variability. Am Nat 105:201–211
Bulmer MG (1974) Linkage disequilibrium and genetic variability. Genet Res 23:281–289
Bulmer MG (1976) The effect of selection on genetic variability: a simulation study. Genet Res 28:101–117
Bulmer MG (1980) The mathematical theory of quantitative genetics. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Clayton GA, Morris JA, Robertson A (1957) An experimental check on quantitative genetical theory. 1. Short-term responses to selection. J Genet 55:131–151
Crow JF, Morton NE (1955) Measurement of gene frequency drift in small populations. Evaluation 9:202–214
Gibson JB, Thoday JM (1963) Effects of disruptive selection. 8. Imposed quasi-random mating. Heredity 18:513–524
Mather K (1955) Polymorphism as an outcome of disruptive selection. Evolution 9:52–61
Maynard, Smith J (1979) The effect of normalizing and disruptive selection on genes for recombination. Genet Res 33:121–128
Robertson A (1956) The effect of selection against extreme deviants based on deviation or on homozygosis. J Genet 54:236–248
Robertson A (1970a) A theory of limits in artificial selection with many linked loci. In: Kojima KI (ed) Mathematical topics in population genetics. Springer, Berlin, pp 246–288
Robertson A (1970b) A note on disruptive selection experiments in Drosophila. Am Nat 104:561–569
Robertson A (1977) The effect of selection on the estimation of genetic parameters. Z Tierz Züchtungsbiol 94:131–135
Scharloo W (1964) The effect of disruptive and stabilizing selection on the expression of a cubitus interruptus mutant in Drosophila. Genetics 50:553–562
Scharloo W, Hoogmoed MS, Ter Kulle A (1967) Stabilizing and disruptive selection on a mutant character in Drosophila. 1. The phenotypic variance and its components. Genetics 56:709–726
Simpson GG (1944) Tempo and mode in evolution. Columbia University Press, New York
Thoday JM (1959) Effects of disruptive selection. 1. Genetic flexibility. Heredity 13:187–203
Thoday JM (1972) Review lecture: disruptive selection. Proc R Soc London Ser B 182:109–143
Thoday JM, Gibson JB (1962) Isolation by disruptive selection. Nature 193:1164–1166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. Riley
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorensen, D.A., Hill, W.G. Effects of disruptive selection on genetic variance. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 65, 173–180 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00264888
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00264888