Abstract
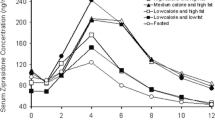
The GI transit of radiolabeled sustained-release ibuprofen 800-mg tablets in eight healthy, fed volunteers was monitored using external gamma scintigraphy. Ibuprofen serum concentrations were determined from blood samples drawn over 36 hr following dosing. Sustained-release ibuprofen tablets containing 0.18% of 170Er2O3 (>96% 170Er) in the bulk formulation were manufactured under pilot-scale conditions and were radiolabeled utilizing a neutron activation procedure which converted stable 170Er to radioactive 171Er (t 1/2 = 7.5 hr). At the time of dosing, each tablet contained 50 µCi of 171Er. Dosage form position was reported at various time intervals. In five subjects the sustained-release tablet remained in the stomach and eroded slowly over 7–12 hr, resulting in gradual increases in small bowel radioactivity. In the remaining three subjects, the intact tablet was ejected from the stomach and a gastric residence time of approximately 4 hr was measured. This is in marked contrast to a previous study conducted in fasted volunteers in which gastric retention time ranged from 10 to 60 min. Differences in GI transit between fed and fasted volunteers had little effect on ibuprofen bioavailability. AUC and T max were unaltered and C max was increased by 24%, which is in agreement with results from a previous, crossover-design food effect study.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. L. Casey, R. M. Beihn, G. A. Digenis, and M. D. Shambu. J. Pharm. Sci. 65:1412–1413 (1976).
L. C. Kaus, J. T. Fell, H. Sharma, and D. C. Taylor. Int. J. Pharm. 20:315–323 (1984).
A. Parr, M. Jay, G. A. Digenis, and R. M. Beihn. J. Pharm. Sci. 74:590–591 (1985).
A. Parr, R. M. Beihn, and M. Jay. Int. J. Pharm. 32:251–256 (1986).
F. Parr, R. M. Beihn, R. M. Franz, G. J. Szpunar, and M. Jay. Pharm. Res. 4:486–489 (1987).
G. J. Szpunar, J. H. Shepard, and K. S. Albert. Pharm. Res. 4 (Suppl.):592 (1987).
P. G. Welling. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:291–334 (1977).
R. D. Toothaker and P. G. Welling. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 20:173–199 (1980).
L. Vaughan, G. Milavetz, M. Hill, M. Weinberger, and L. Hendeles. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 18:510 (1984).
M. Lagas and J. H. G. Jonkman. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 24:761–767 (1983).
G. F. Lockwood and J. G. Wagner. J. Chromatogr. 232:335–343 (1982).
A. Rubinstein, V. Hon Kin Li, P. Gruber, and J. R. Robinson. In A. Yacobi and E. Halperin-Walega (eds.), Oral Sustained Release Formulations: Design and Evaluation, Pergamon Books, New York, 1987, pp. 124–156.
A. Karim. Am. Pharm. NS25:4–5 (1985).
A. Karim, T. Burns, L. Wearley, J. Streicher, and M. Palmer. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 38:77–83 (1985).
A. Karim, T. Burns, D. Janky, and A. Hurwitz. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 38:642–647 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borin, M.T., Khare, S., Beihn, R.M. et al. The Effect of Food on Gastrointestinal (GI) Transit of Sustained-Release Ibuprofen Tablets as Evaluated by Gamma Scintigraphy. Pharm Res 7, 304–307 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015842600189
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015842600189