Abstract
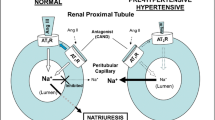
Purpose. To study the relationship between angiotensin II (All) receptor occupancy ex vivo in tissues plasma concentration and hypotensive effect of a novel All receptor antagonist, TH-142177 and losartan in rats.
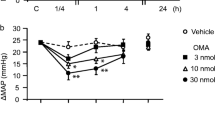
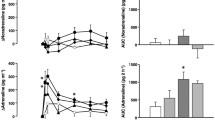
Methods. At 2, 8 and 24 hr after oral administration of TH-142177 and losartan in rats, All receptors in myocardium, adrenal cortex and cerebral cortex were determined by radioligand binding assay using [125I]Sar1,Ile8-AII. Plasma concentrations of both drugs and metabolite in rats were also measured using validated HPLC assays. Further, systolic blood pressure (SBP) in conscious renal hypertensive rats treated orally with TH-142177 and losartan were measured by using a tail cuff plethysmographic method.
Results. Oral administration of TH-142177 (1.8 and 5.5 μmol/kg) and losartan (6.5 and 21.7 μmol/kg) in rats brought about dose-dependent decreases in [125I]Sar1,Ile8-AII binding sites (Bmax) in myocardium and adrenal cortex. The extent of receptor occupancy by both drugs in adrenal cortex was maximal at 2 hr later but that in myocardium at 8 hr later. Further, the receptor occupancy was more sustained in myocardium than adrenal cortex. The ex vivo binding affinity of TH-142177 for All receptors in these tissues was roughly three times higher than that of losartan. Also, cerebral cortical [125I]Sar1,Ile8-AII binding was significantly reduced by oral administration of losartan but not by TH-142177. The time course of All receptor occupancy by both drugs in adrenal cortex appeared to be in parallel with that of their plasma concentrations, while the time course in myocardium correlated with that of their hypotensive effects rather than plasma concentrations.
Conclusions. TH-142177 produced a relatively selective and sustained occupancy ex vivo of All receptors in myocardium and adrenal cortex of rats with approximately three times greater potency than losartan. Its time course of myocardial receptor occupancy was in parallel with that of hypotensive effect rather than plasma concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. B. Vallotton. The renin angiotensin system. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 8:69-74 (1987).
H. G. Williams. Converting enzyme inhibitors in the treatment of hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 319:1517-1525 (1988).
H. R. Brunner, Y. Christen, A. Munafo, R. J. Lee, B. Waeber, and J. Nussberger. Clinical experience with angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Am. J. Hypertens. 12: 243S-246S (1992).
Y. Nozawa, H. Miyake, S. Yamada, S. Uchida, T. Ohkura, and R. Kimura. Pharmacological profile of TH-142177, a novel orally active AT1 receptor antagonist. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 11:395-401 (1997).
H. T. Beauchamp, R. S. L. Chang, P. K. S. Siegl, and R. E. Gibson. In vivo receptor occupancy of the angiotensin II receptor by nonpeptide antagonists: Relationship to in vitro affinities and in vivo pharmacologic potency. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 272:612-618 (1995).
S. Uchida, S. Yamada, T. Ohkura, M. Heshikiri, A. Yoshimi, H. Shirahase, and R. Kimura. The receptor occupation and plasma concentration of NKY-722, a water-soluble dihydropyridine-type calcium antagonist, in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 114:217-223 (1995).
S. Yamada, Y. Matsuoka, Y. Kato, R. Kimura, and O. Inagaki. A sustained occupancy in vivo of cardiovascular calcium antagonist receptors by mepirodipine and its relation to pharmacodynamic effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 262:589-594 (1992).
S. Yamada, N. Sugimoto, S. Uchida, Y. Deguchi, and R. Kimura. Pharmacokinetics of amlodipine and its occupancy of calcium antagonist receptors. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 23:466-472 (1994).
Y. Igari, Y. Sugiyama, Y. Sawada, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Kinetics of receptor occupation and anticonvulsive effects of diazepam in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 13:102-106 (1985).
H. Ishizuka, Y. Sawada, K. Ito, Y. Sugiyama, H. Suzuki, T. Iga, and M. Hanano, Nonlinear relationship between benzodiazepine receptor occupancy and glucose metabolic response in the conscious mouse brain in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 251:362-367 (1989).
M. M. Bradford. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254 (1976).
L. A. Sechi, C. A. Griffin, E. F. Grady, J. E. Kalinyak, and M. Schambelan. Characterization of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in rat heart. Circ. Res. 71:1482-1489 (1992).
Y. Nozawa, A. Haruno, N. Oda, Y. Yamasaki, N. Matsuura, S. Yamada, K. Inabe, R. Kimura, H. Suzuki, and T. Hoshino, Angiotensin II receptor subtypes in bovine and human ventricular myocardium. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 270:566-571 (1994).
S. Yamada, H. I. Yamamura, and W. R. Roeske. Characterization of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart using [3H]WB4101: effect of 6-hydroxydopamine treatment. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 215:176-185 (1980).
J. W. Regan, W. R. Roeske, J. B. Malick, S. H. Yamamura, and H. I. Yamamura. γ-Aminobutyric acid enhancement of CL 218,872 affinity and evidence of benzodiazepine receptor heterogeneity. Mol. Pharmacol. 20:477-483 (1981).
P. B. M. W. M. Timmermans, P. C. Wong, A. T. Chiu, W. F. Herblin, P. Benfield, D. J. Carini, R. J. Lee, R. R. Wexler, J. A. M. Saye, and R. D. Smith. Angiotensin II receptors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Pharmacol. Rev. 45:205-251 (1993).
F. H. Marshall, S. A. Clark, A. D. Michel, and J. C. Barnes. Binding of angiotensin antagonists to rat liver and brain membranes measured ex vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 109:760-764 (1993).
R. P. Dennes, J. C. Barnes, A. D. Michel, and M. B. Tyers. The effect of the AT1 receptor antagonist, losartan (DuP 753) on cognitive performance in the radial maze and in a delayed nonmatching to position task in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 105:88P(1992).
P. C. Wong, J. R. Price, A. T. Chiu, J. V. Duncia, D. J. Carini, R. R. Wexler, A. L. Johnson, and P. B. W. M. Timmermans. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. IX. Pharmacology of EXP3174: an active metabolite of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 255:211-217 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nozawa, Y., Miyake, H., Yamada, S. et al. Receptor Occupancy in Myocardium, Adrenal Cortex, and Brain by TH-142177, a Novel AT1 Receptor Antagonist in Rats, in Relation to Its Plasma Concentration and Hypotensive Effect. Pharm Res 15, 911–917 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011932800729
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011932800729