Abstract
Purpose. Delivery of nasal powders of granulated β-cyclodextrin by insufflation was studied in order to find the relationship between powder properties and delivery behavior.
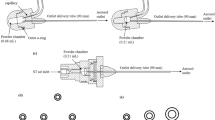
Methods. Three nasal powder formulations, prepared by granulating β-cyclodextrin with different binders, were delivered from a powder insufflation device, in which the dose to be emitted was loaded in a gelatin capsule. The delivery sequence of powder was recorded and characterized using an image analysis program.
Results. Particle size was the main parameter affecting nasal powder delivery, both as to the amount of dose sprayed and the aspect of cloud produced. Between 50–150 µm of particle size a substantial change in delivery behavior of powders was observed. Powder of around 100 µm in size showed useful insufflation characteristics for nasal delivery. Bioavailability of nasal formulations of progesterone/β-cyclodextrin powders was discussed in term of delivery behavior.
Conclusions. The formulation approaches for improving nasal delivery of powders require the use of size optimized carriers. Insufflation of powders over 50 µm can favour the particle deposition by impaction, whereas for powders below 50 µm, deposition by sedimentation is moved. β-cyclodextrin is a suitable carrier for achieving high systemic availability following nasal administration of powder formulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. H. L. Lee. Penetration and enzymatic barriers to peptide and protein absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 4:171–207 (1990).
S. Gizurarson. The relevance of nasal physiology to the design of drug absorption studies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rew. 11:329–347 (1993).
A. D. Chediak, A. Wanner. The circulation of the airways: anatomy, physiology and potential role in drug delivery to the respiratory tract. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rew. 5:11–18 (1990).
M. A. Sarkar. Drug metabolism in the nasal mucosa. Pharm. Res. 9:1–9 (1992).
M. A. H. Russell, M. J. Jarvis, C. Feyerabend. A new age for snuff?. Lancet 474–475 (1980).
S. P. Vyas, S. K. Goswami, R. Singh. Liposomes based nasal delivery system of nifedipine: development and characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 118:23–30 (1995).
L. Illum. Drug delivery systems for nasal application. S.T.P. Pharma 3:594–598 (1987).
J. C. Hardy, S. W. Lee, C. G. Wilson. Intranasal drug delivery by spray and drops. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 3:294–297 (1985).
N. G. M. Schipper, S. G. Romeijn, J. C. Verhoef, F. W. H. M. Merkus. Nasal insulin delivery with dimethyl-β-cyclodextrin as an absorption enhancer in rabbits: powders more effective than liquid formulations. Pharm. Res. 5:682–686 (1993).
P. Edman, E. Bjork, L. Ryden. Microspheres as a nasal delivery system for peptide drugs. J. Contr. Rel. 21:165–172 (1992).
T. Nagai, Y. Nishimoto, N. Nambu, Y. Suzuki, K. Sekine. Powder dosage form of insulin for nasal administration. J. Contr. Rel. 1:15–22 (1984).
J. M. Aiache. Les preparations pour inhalation. S.T.P. Pharma 6:753–761 (1990).
M. T. Vidgren, A. Karkkainen, P. Karjalainen, J. Nuutinen. Effect of powder inhaler design on drug deposition in respiratory tract. Int. J. Pharm. 42:221–216 (1988).
D. Provasi, A. De Ascentiis, P. Colombo. Powder delivery from a device for nasal application. 12th Pharmaceutical Techn. Conference (Elsinore) 3:98–111 (1993).
D. Provasi, A. De Ascentiis, A. Minutello, P. Colombo, P. L. Catellani. Nasal powders of Progesterone: manufacturing and bioavailability. Eur. J. Phar. Biopharm. 40:223–227 (1994).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Ascentiis, A., Bettini, R., Caponetti, G. et al. Delivery of Nasal Powders of β-Cyclodextrin by Insufflation. Pharm Res 13, 734–738 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016099516757
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016099516757