Abstract
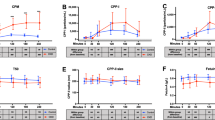
The alteration of regucalcin concentrations in the liver and serum of rats administered orally calcium is investigated. Rats received a single oral administration of calcium chloride solution (25, 50 and 75 mg Ca/100 g body weight). The administration of calcium (50 mg/100 g) produced a significant increase in liver regucalcin concentration between 30 and 180 min after the administration, while serum regucalcin concentration was not altered appreciably. The effect of calcium administration increasing liver regucalcin concentration was also seen with the dose of 25 mg/100 g. When liver cytosol prepared from normal rats was incubated for 6 h in the presence of 10 μM Ca2+, the cytosolic regucalcin concentration at 3 and 6 h of incubation was decreased about 20% (p<0.05) as compared with the value at zero time point, indicating that the presence of Ca2+ does not inhibit the decomposition of liver cytosolic regucalcin. Moreover, serum regucalcin concentration was not significantly altered by the incubation for 6 h at 37°C, indicating a stability of regucalcin in rat serum. This suggests that the calcium administration-induced in liver regucalcin concentration is not based on the inhibition of regucalcin release from liver to serum. The present study demonstrates that regucalcin in the liver is clearly increased by calcium administration, presumably due to stimulating the protein synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williamson JR, Cooper RK, Hoek JB: Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 639: 243–295, 1981
Reinhart PH, Taylor WM, Bygrave FL: The role of calcium ions in the mechanisms of action of α-adrenergic agonists in rat liver. Biochem J 223: 1–13, 1984
Cheung WY: Calmodulin plays a pirotol role in cellular regulation. Science 202: 18–27, 1980
Nishizuka Y: Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science 233: 305–312, 1986
Yamaguchi M, Sugii K: Properties of calcium-binding protein isolated from the soluble fraction of normal rat liver. Chem Pharm Bull 29: 567–570, 1981
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Molecular cloning and sequencing of the cDNA coding for a calcium-binding protein regucalcin from rat liver. FEBS Lett 327: 251–255, 1993
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Calcium administration stimulates the expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in rat liver. FEBS Lett 305: 151–154, 1992
Yamaguchi M, Tai H: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity in rat liver cytosol. Mol Cell Biochem 106: 25–30, 1991
Yamaguchi M, Mori S: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on protein kinase C activity in rat liver cytosol. Biochem Med Metab Biol 43: 140–146, 1990
Yamaguchi M, Sakurai T: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett 279: 281–284, 1991
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Expression of hepatic calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA is mediated through Ca2+/calmodulin in rat liver. FEBS Lett 316: 79–84, 1993
Yamaguchi M, Kanayama Y, Shimokawa N: Expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in rat liver is stimulated by calcitonin: the hormonal effect is mediated through calcium. Mol Cell Biochem 136: 43–48, 1994
Yamaguchi M, Isogai M: Tissue concentration of calcium-binding protein regucalcin in rats by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Mol Cell Biochem 122: 65–68, 1993
Yamaguchi M, Yamamoto T: Purification of calcium binding substance from soluble fraction of normal rat liver. Chem Pharm Bull 26: 1915–1918, 1978
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NH, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 263–273, 1951
Yamaguchi M, Sugii K: Movement of subcellular calcium in bile pool of hepatocyte in rats: Effect of thyroparathyroidectomy. Endocrinol Jpn 27: 613–618, 1980
Yamaguchi M, Imase M: Hormonal regulation of billiary calcium excretion in rats: Inhibition of calcitonin action by α1-adrenergic stimulation. Horm metab Res 20: 221–224, 1988
Yamaguchi M, Sakurai T: Reversible effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on the Ca2+-induced inhibition of deoxyuridine 5′-triphosphatase activity in rat liver cytosol. Mol Cell Biochem 110: 25–29, 1992
Farber JL: The role of calcium in cell death. Life Sci 29: 1289–1295, 1981
Ishiura S: Calcium-dependent proteolysis in living cells. Life Sci 29: 1079–1087, 1981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isogai, M., Yamaguchi, M. Calcium administration increases calcium-binding protein regucalcin concentration in the liver of rats. Mol Cell Biochem 143, 53–58 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925926
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925926