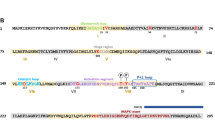
Abstract
Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinases and their target ribosomal protein S6 (RSK) kinases have been recognized as shared components in the intracellular signaling pathways of many diverse cytokines. Recent studies have extended this protein kinase cascade by identifying the major activator of vertebrate MAP kinases as a serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase called MEK, which is related to yeast mating factor-regulated protein kinases encoded by the STE7 and byr1 genes. MEK, in turn, may be activated following its phosphorylation on serine by either of the kinases encoded by proto-oncogenesraf1 ormos, as well as by p78mekk, which is related to the yeast STE11 and byr2 gene products. Isoforms of all of these protein kinases may specifically combine to assemble distinct modules for intracellular signal transmission. However, the fundamental architecture of these protein kinase cascades has been highly conserved during eukaryotic evolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunter T: A thousand and one kinases. Cell 50: 823–829, 1987
Pelech SL, Sanghera JS, Daya-Makin M: Protein kinase cascades in meiotic and mitotic cell cycle control. Biochem Cell Biol 68: 1297–1330, 1990
Cobb MH, Boulton TG, Robbins DJ: Extracellular signal regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul 2: 965–978, 1991
Pelech SL, Sanghera JS: Mitogen-activated protein kinases, versatile transducers in cell signalling. Trends Biochem Sci 17: 233–238, 1992
Anderson N: MAP kinases-Ubiquitous signal transducers and potentially important components of the cell cycling machinery in eukaryotes. Cellular Signaling 4: 239–246, 1992
Ray LB, Sturgill TW: Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 1502–1506, 1987
Hoshi M, Nishida E, Sakai H: Activation of a Ca2+-inhibitable protein kinase that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2in vitro by growth factors, phorbol esters, and serum in quiescent cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 263: 5396–5401, 1988
Cicirelli M, Pelech SL, Krebs EG: Activation of multiple kinases during the burst in protein phosphorylation that precedes the first meiotic division inXenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem 263: 2009–2019, 1988
Pelech SL, Tombes RM, Meijer L, Krebs EG: Activation of myelin basic protein kinases during echinoderm oocyte mutaration and egg fertilization. Dev Biol 130: 28–36, 1988
Cooper JA, Bowen-Pope DF, Raines E, Ross R, Hunter T: Similar effects of platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor on the phosphorylation of tyrosine in cellular proteins. Cell 31: 263–273, 1982
Kohno M: Diverse mitogenic agents induce rapid phosphorylation of a common set of cellular proteins at tyrosine in quiescent mammalian fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 260: 1771–1779, 1985
Ray LB, Sturgill TW: Insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine and threoninein vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 3753–3757, 1988
Anderson NG, Maller JL, Tonks NK, Sturgill TW: Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature 343: 651–653, 1990
Payne DM, Rossomando AJ, Martino P, Erikson AK, Her J-H, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Weber MJ, Sturgill TW: Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J 10: 885–892, 1991
Wu J, Rossomando AJ, Her J-H, Del Vecchio R, Weber MJ, Sturgill TW: Autophosphorylationin vitro of recombinant 42-kilodalton mitogen-activated protein kinase on tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9508–9512, 1991
Rossomando AJ, Wu J, Michel H, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Weber MJ, Sturgill TW: Identification of Tyr-185 as site of tyrosine autophosphorylation of recombinant mitogen-activated protein kinase p42mapk. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 5779–5783, 1992
Seger R, Ahn NG, Boulton TG, Yancopoulos GD, Panayotatos N, Radziejewska E, Ericsson L, Bratlien RL, Cobb MH, Krebs EG: Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases, ERK1 and ERK2, undergo autophosphorylation on both tyrosine and threonine residues: Implications for their mechanism of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 6142–6146, 1991
L'Allemain G, Her J-H, Wu J, Sturgill TW, Weber MJ: Growth factor-induced activation of a kinase activity which causes regulatory phosphorylation of p42/microtubule-associated protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol 12: 2222–2229, 1992
Rossomando AJ, Wu J, Weber MJ, Sturgill TW: The phorbolester-dependent activator of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p42mapk is a kinase with specificity for the threonine and tyrosine regulatory sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 5221–5225, 1992
Nakielny S, Cohen P, Wu J, Sturgill TW: MAP kinase activator from insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle is a protein threonine/tyrosine kinase. EMBO J 11: 2123–2129, 1992
Alessandrini A, Crews CM, Erikson RL: Phorbol ester stimulates a protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates and activates theErk-1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 8200–8204, 1992
Kosako H, Gotoh Y, Matsuda S, Ishikaa M, Nishida E:Xenopus MAP kinase activator is a serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activated by threonine phosphorylation. EMBO J 11: 2903–2908, 1992
Matsuda S, Kosako H, Takenaka K, Moriyama K, Sakai H, Akiyama T, Gotoh Y, Nishida E:Xenopus MAP kinase activator: identification and function as a key intermediate in the phosphorylation cascade. EMBO J 11: 973–982, 1992
Crews CM, Erikson RL: Purification of a murine protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates and activates the Erk-1 gene product: Relationship to the fission yeast byr1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 8205–8209, 1992
Nakielny S, Cohen P, Wu J, Sturgill T: MAP kinase activator from insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle is a protein threonine/tyrosine kinase. EMBO J 11: 2123–2129, 1992
Wu J, Michel H, Rossomando A, Haystead T, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Sturgill TW: Renaturation and partial peptide sequencing of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase) activator from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J 285: 701–705, 1992
Seger R, Ahn NG, Posada J, Munar ES, Jensen AM, Cooper JA, Cobb MH, Krebs EG: Purification and characterization of mitogen-activated protein kinase activator(s) from epidermal growth factor-stimulated A431 cells. J Biol Chem 267: 14373–14381, 1992
Crews CM, Alessandrini A, Erikson RL: The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science 258: 478–480, 1992
Seger R, Seger D, Lozeman FJ, Ahn NG, Graves LM, Campbell JS, Ericsson L, Harrylock M, Jensen AM, Krebs EG: Human T-cell mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases are related to yeast signal transduction kinases. J Biol Chem 267: 25628–25631, 1992
Ashworth A, Nakielny S, Cohen P, Marshall C: The amino acid sequence of a mammalian MAP kinase kinase. Oncogene 7: 2555–2556, 1992
Wu J, Harrison JK, Vincent LA, Haystead C, Haystead TAJ, Michel H, Hunt DF, Lynch KR, Sturgill TW: Molecular structure of a protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase activating p42 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase: MAP kinase kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 173–177, 1993
Kosako H, Nishida E, Gotoh Y: cDNA cloning of MAP kinase kinase reveals kinase cascade pathways in yeast to vertebrates. EMBO J 12: 787–794, 1993
Tsuda L, Inoue YH, Yoo M-A, Mizuno M, Hata M, Lim Y-M, Adachi-Yamada T, Ryo H, Masamune Y, Nishida Y: A protein kinase similar to MAP kinase acivator acts downstream of the raf kinase inDrosophila. Cell 72: 407–414, 1993
Kosako H, Gotoh Y, Matsuda S, Ishikawa M, Nishida E:Xenopus MAP kinase activator is a serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activated by threonine phosphorylation. EMBO J 11: 2903–2908, 1992
Nakielny S, Campbell DG, Cohen P: MAP kinase activator from insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle; a novel dual specificity enzyme showing homology to yeast protein kinases involved in pheromone-dependent signal transduction. FEBS Lett 308: 183–189, 1992
Kyriakis JM, App H, Zhang X-F, Banerjee P, Brautigan DL, Rapp UR, Avruch J: Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature 358: 417–421, 1992
Dent P, Haser W, Haystead TAJ, Vincent LA, Roberts TM, Sturgill TW: Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells andin vitro. Science 257: 1404–1407, 1992
Howe LR, Leevers SJ, Gomez N, Nakielny S, Cohen P, Marshall CJ: Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell 71:335–342, 1992
Gomez N, Traverse S, Cohen P: Identification of a MAP kinase kinase in phaeochromocytoma (PC12) cells. FEBS Lett 314:461–465, 1992
Matsuda S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E: Phosphorylation ofXenopus mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase by MAP kinase kinase kinase and MAP kinase. J Biol Chem 268:3277–3281, 1993
Qiu M-S, Green SH: PC12 cell neuronal differentiation is associated with prolonged p21ras activity and consequent prolonged ERK activity. Neuron 9:705–717, 1992
Kolch W, Heidecker G, Lloyd P, Rapp UR: Raf-1 protein kinase is required for growth of induced NIH/3T3 cells. Nature 349: 426–428, 1991
Wood KW, Sarnecki C, Roberts TM, Blenis J: Ras mediates nerve growth factor modulation of three signal transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Rafl and RSK. Cell 68:1041–1050, 1992
Troppmair J, Bruder JT, App H, Cai H, Liptak L, Szeberenyi J, Cooper GM, Rapp UR: Ras controls coupling of growth factor receptors and protein kinase C in the membrane to Raf-1 and B-Raf protein serine kinases in the cytosol. Oncogene 7:1867–1873, 1992
Morrison DK, Kaplan DR, Rapp U, Roberts TM: Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8855–8859, 1988
Thomas SM, DeMarco M, D'Arcangelo G, Halegoua S, Brugge JS: Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell 68:1031–1040, 1992
Nori M, L'Allemain G, Weber MJ: Regulation of tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-induced responses in NIH 3T3 cells by GAP, the GTPase-activating protein associated with p21c-ras. Mol Cell Biol 12:936–945, 1992
de Vries-Smits AMM, Burgering BMT, Leevers SJ, Marshall CJ, Bos JL: Involvement of p21ras in activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. Nature 357:602–604, 1992
Williams NG, Paradis H, Agarwal S, Charest DL, Pelech SL, Roberts TM: Raf-1 and p21v-ras cooperate in the activation of MAP kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5772–5776, 1993
Gupta SK, Gallego C, Johnson GL, Heasley LE: MAP kinase is constitutively activated ingip2 andsrc transformed rat 1a fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 267:7987–7990, 1992
Qureshi SA, Alexandropoulos K, Rim M, Joseph CK, Breder JT, Rapp UR, Foster DA: Evidence that Ha-Ras mediates two distinguishable intracellular signals activated by v-src. J Biol Chem 267:17635–17639, 1992
Gallego C, Gupta SK, Heasley LE, Quian N-X, Johnson GL: Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation resulting from selective oncogene expression in NIH 3T3 and Rat 1a cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:7355–7359, 1992
Ettehadieh E, Sanghera JS, Pelech SL, Hess-Bienz D, Watts J, Shastri N, Aebersold R: Tyosyl phosphorylation and activation of MAP kinases by p56lck. Science 255:853–855, 1992
Charest DL, Mordret G, Jirik F, Harder K, Pelech SL: Molecular cloning expression and characterization of human MAP kinase p44erkl. Mol Cell Biol 13:4679–4690, 1993
Nishizuka Y: Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science 258:607–613, 1992
Rhee SG, Choi KD: Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem 267:12393–12396, 1992
Sternweis PC, Smrcka AV: Regulation of phospholipase C by G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 17:502–506, 1992
Sozeri O, Voller K, Liyanage M, Frith D, Kour G, Mark GE III, Stabel S: Activation of c-Raf protein kinase by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Oncogene 7:2259–2262, 1992
Song J, Pfeffer LM, Foster DA: v-Src increases diacylglycerol levels via a type D phospholipase-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine. Mol Cell Biol 11:4903–4908, 1991
Duronio V. Welham M, Abraham S, Dryden P, Schrader JW: p21ras activation via haemopoietin receptors and c-kit requires tryosine kinase activity but not tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1587–1591, 1992
Satoh T, Endo M, Nakafuku M, Nakamura S, Kaziro Y: PLatelet-derived growth factor stimulates formation of active p21ras GTP complex in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 5993–5997, 1990
Nakanishi H, Brewer KA, Exton JH: Activation of the ξ isozyme of protein kinase C by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate. J Biol Chem 268:13–16, 1993
Downes CP, Carter AN: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase: a new effector in signal transduction? Cellular Signalling 3:501–513, 1991
Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Matsuda S, Shiina N, Kosako H, Shiokawa K, Akiyama T, Ohta K, Sakai H:In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purifiedXenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature 349:251–254, 1991
Gotoh Y, Moriyama K, Matsuda S, Okumura E, Kishimoto T, Kawasaki H, Sukuzi K, Yahara I, Sakai H, Nishida E:Xenopus M phase MAP kinase isolation of its cDNA and activation by MPF. EMBO J 10:2661–2668, 1991
MacNicol AM, Muslin AJ, Williams LT: Raf-1 kinase is essential for earlyXenopus development and mediates the induction of mesoderm by FGF. Cell 1993, in press
Muslin AJ, MacNicol AM, Williams LT: Raf-1 protein kinase activity is important in progesterone-inducedXenopus oocyte maturation and is downstream of Mos activity. Mol Cell Biol 13: 4197–4202, 1993
Pomerance M, Schweighoffer F, Tocque B, Pieree M: Stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by oncogenic Ras p21 inXenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem 267:16155–16160, 1992
Shibuya EK, Polverino AJ, Chang E, Wigler M, Ruderman JV: Oncogenic Ras triggers the activation of 42-kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase in extracts of quiescentXenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9831–9835, 1992
Hattori S, Fukuda M, Yamashita T, Nakamura S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E: Activation of MAP kinase activator byras in intact cells and in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem 267:20346–20351, 1992
Nebreda AR, Porras A, Santos E: p21ras-induced meiotic maturation ofXenopus oocytes in the absence of protein synthesis: MPF activation is preceded by activation of MAP and S6 kinases. Oncogene 8:467–477, 1993
Itoh T, Kaibuchi K, Masuda T, Yamamoto T, Matsuura Y, Maeda A, Shimizu K, Takai Y: The post-translational processing ofras p21 is critical for its stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 268:3025–3028, 1993
Korn LJ, Siebel CW, McCormick F, Roth RA: Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action inXenopus oocytes. Science 236: 840–843, 1987
Deshpande AK, Kung H-F: Insulin induction ofXenopus laevis oocyte maturation is inhibited by monoclonal antibodies against p21ras proteins. Mol Cell Biol 7:1285–1288, 1987
Posada J, Yew N, Ahn NG, Vande Woude GF, Cooper JA: Mos stimulates MAP kinase inXenopus oocytes and activates MAP kinase kinasein vitro. Mol Cell Biol 13:2546–2553, 1993
Sanghera JS, Paddon HB, Bader SA, Pelech SL: Purification and characterization of a maturation-activated myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem 265:52–57, 1990
Posada J, Sanghera J, Pelech S, Aebersold R, Cooper JA: Tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of homologous protein kinases during oocyte maturation and mitogenic activation of fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 11:2517–2528, 1991
Sanghera J, Paddon HB, Pelech SL: Role of protein phosphorylation in the maturation-induced activation of a myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem 266:6700–6707, 1991
Sanghera J, McNabb C, Tonks N, Pelech S: Tyrosyl phosphorylation and activation of the myelin basic protein kinase p44mpk during sea star oocyte maturation. Biochem Biophys Acta 1095:153–160, 1991
Elion EA, Brill JA, Fink GR: FUS 3 represses CLN1 and CLN2 and in concert with KSS1 promotes signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9392–9396, 1991
Courchesne WE, Kunisawa R, Thorner J: A putative protein kinase overcomes pheromone-induced arrest of cell cycling inS. cerevisae. Cell 58:1107–1119, 1989
Elion EA, Grisafi PL, Fink GR: FUS3 encodes a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase required for the transition from mitosis into conjugation. Cell 60:649–664, 1990
Gartner A, Nasmyth K, Ammerer G: Signal transduction inSaccharomyces cerevisiae requires tyrosine and threonine phosphorylation of FUS3 and KSS1. Genes & Dev 6:1280–1292, 1992
Marsh L, Neiman AM, Herskowitz I: Signal transduction during pheromone response in yeast. Ann Rev Cell Biol 7:699–728, 1991
Sprague GF Jr: Signal transduction in yeast mating: receptors, transcription factors, and the kinase connection. Trends Genetics 7:393–398, 1991
Leberer E, Dignard D, Harcus D, Thomas DY, Whiteway M: The protein kinase homologue Ste20p is required to link the yeast pheromone response G-protein γ subunits to downstream signalling components. EMBO J 11:4815–4824, 1992
Rhodes N, Connell L, Errede B: STE11 is a protein kinase required for cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast. Genes Dev 4:1862–1874, 1990
Teague MA, Chaleff DT, Errede B: Nucleotide sequence of the yeast regulatory gene STE7 predicts a protein homologous to protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7371–7375, 1986
Errede B, Gartner A, Zhou Z, Nasmyth K, Ammerer G: A pheromone induced kinase cascade inS. cerevisiae: activation of the FUS3 kinase by the STE7 kinasein vitro. Nature 362:261–264, 1993
Zhou Z, Gartner A, Cade R, Ammerer G, Errede B: Pheromone induced signal transduction inS. cerevisiae requires the sequential function of three protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol 13:2069–2080, 1993
Stevenson BJ, Rhodes N, Errede B, Sprague GF Jr: Constitutive mutants of the protein kinase STE11 activate the yeast pheromone response pathway in the absence of the G protein. Genes & Dev 6:1293–1304, 1992
Cairns BR, Ramer SW, Kornberg RD: Order of action of components in the yeast pheromone response pathway revealed with a dominant allele of the STE11 kinase and the multiple phosphorylation of the STE7 kinase. Genes & Dev 6:1305–1318, 1992
Lange-Carter CA, Plelman CM, Gardner AM, Blumer KJ, Johnson GL: A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science 260:315–319, 1993
Nadin-Davis SA, Nasim A, Beach D: Involvement of ras in sexual differentiation but not in growth control in fission yeast. EMBO J 5:2963–2971, 1986
Fukui Y, Kozasa T, Kaziro Y, Takeda T, Yamamoto M: Role of aras homolog in the life cycle ofSchizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell 44:329–336, 1986
Nadin-Davis SA, Nasim A: A gene which encodes a predicted protein kinase can restore some functions of theras gene in fission yeast. EMBO J 7:985–993, 1988
Wang Y, Xu H-P, Riggs M, Rodgers L, Wigler M: byr2, aSchizosaccharomyces pombe gene encoding a protein kinase capable of partial suppression of theras1 mutant phenotype. Mol Cell Biol 11:3554–3563, 1991
Toda T, Shimanuki M, Yanagida M: Fission yeast genes that confer resistance to staurosporine encode and AP1-like transcription factor and a protein kinase related to the mammalian ERK1/MAP2 and budding yeast FUS3 and KSS1 kinases. Genes Dev 5: 60–73, 1991
Neiman AM, Stevenson BJ, Xu H-P, Sprague GF Jr, Herskowitz I, Wigler M, Marcus S: Functional homology of protein kinases required for sexual differentiation inSchizosaccharomyces pombe andSaccharomyces cerevisiae suggests a conserved signal transduction module in eukaryotic organisms. Molecular Biology Cell 4:107–120, 1993
Levin DE, Fields FD, Kunisawa R, Bishop JM, Thorner JA: A candidate protein kinase C gene, PKC1, is required for theS. cerevisiae cell cycle. Cell 62:213–224, 1990
Levin DE, Bartlett-Heubusch E: Mutants in theS. cervisiae PKC1 display a cell cycle-specific osmotic stability defect. J Cell Biol 116:1221–1229, 1992
Paravicini G, Cooper M, Fiedli L, Smith DJ, Carpentier J-L, Klig LS, Payton MA: The osmotic integrity of the yeast cell requires a functional PKC1 gene product. Mol Cell Biol 12:4396–4905, 1992
Lee KS, Levin DE: Dominant mutations in a gene encoding a putative protein kinase (BCK1) bypass the requirement for aSaccharomyces cerevisiae protein kinase C homolog. Mol Cell Biol 12:172–182, 1992
Irie K, Takase M, Araki H, Matsumoto K, Oshima Y: MKk1 and MKK2, encodingSaccharomyces cerevisiae MAP kinase-kinase homologs, function in the pathway mediated by protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol 13:3076–3083, 1993
Lee KS, Irie K, Gotoh Y, Watanabe Y, Nishida E, Matsumoto K, Levin DE: A yeast MAP kinase homolog (MPK1) mediates signalling by protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol 13:3067–3075, 1993
Brewster JL, de Valoir T, Dwyer ND, Winter E, Gustin MC: An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in yeast. Science 259: 1760–1763, 1993
Boguslawski G, Polazzi JO: Complete nucleotide sequence of a gene conferring polymyxin B resistance on yeast: similarity of the predicted polypeptide to protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5848–5842, 1987
Boguslawski G: PBS2, a yeast gene encoding a putative protein kinase, interacts with the RAS2 pathway and affects osmotic sensitivity ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiology 138: 2425–2432, 1992
Anderson NG, Li P, Marsden LA, Williams N, Roberts TM, Sturgill TW: Raf-1 is a potential substrate for mitogen-activated protein kinasein vivo. Biochem J 277:573–576, 1991
Lee R, Cobb MH, Blackshear PJ: Evidence that extracellular signal-regulated kinases are the insulin-activated Raf-1 kinase kinases. J Biol Chem 267:1088–1092, 1992
Watts JD, Sanghera JS, Pelech SL, Aebersold R: Phosphorylation of serine-59 of p56lck in activated T cells. J Biol Chem 1993, in press
Northwood IC, Gonzalez FA, Wartmann M, Raden DL, Davis RJ: Isolation and characterization of two growth factor-stimulated protein kinases that phosphorylate the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 669. Biol Chem 266:15266–15276, 1991
Sanghera JS, Hall FL, Warburton D, Campbell D, Pelech SL: Identification of epidermal growth factor Thr-669 phosphorylation site peptide kinases as distinct MAP kinases and p34cdc2. Biochim Biophys Acta 1135:335–342, 1992
Williams R, Sanghera J, Wu F, Carbonaro-Hall D, Warburton D, Campbell D, Pelech SL, Hall F: Identification of a human EGF-receptor associated (HERA) protein kinase as a new member of the MAPK/ERK family. J Biol Chem 268:18213–18217, 1993
Loeb DM, Tsao H, Cobb MH, Greene LA: NGF and other growth factors induce an association between ERK1 and the NGF receptor, gp140prototrk. Neuron 9:1053–1065, 1992
Clark-Lewis I, Sanghera JS, Pelech SL: Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem 266: 15180–15184, 1991
Mukhopadhyay NK, Price DJ, Kyriakis JM, Pelech S, Sanghera JS, Avruch J: An array of insulin-activated, proline-directed serine/threonine protein kinases phosphorylate the p70 S6 kinase. J Biol Chem 267:3325–3335, 1992
Chung J, Kuo CJ, Crabtree GR, Blenis J: Rapamycin-FKBP specifically blocks growth-dependent activation of and signalling by the 70kd S6 protein kinases. Cell 69:1227–1236, 1992
Lane HA, Morley SJ, Doree M, Kozma SC, Thomas G: Identification and early activation of aXenopus laevis p70S6K following progesterone-induced meiotic maturation. EMBO J 11:1743–1749, 1992
Sturgill TW, Wu J: Recent progress in characterization of protein kinase cascades for phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Biochim Biophys Acta 1092:350–357, 1991
Blenis J: Growth-regulated signal transduction by the MAP kinases and RSK's. Cancer Cells 3:445–449, 1991
Chung J, Pelech SL, Blenis J: Mitogen-activated Swiss mouse 3T3 RSK kinases I and II are related to pp44mpk from sea star oocytes and participate in the regulation of pp90rsk activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4981–4985, 1991
Sturgill TW, Ray LB, Erikson E, Maller JL: Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature 334:715–718, 1988
L'Allemain G, Sturgill TW, Weber MJ: Defective regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in a 3T3 cell variant mitogenically nonresponsive to tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate. Mol Cell Biol 11:1002–1008, 1991
Meier KE, Licciardi KA, Haystead TAJ, Krebs EG: Activation of messenger-independent protein kinases in wild-type and phorbol ester-resistant EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem 266: 1914–1920, 1991
Leevers SL, Marshall CJ: Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J 11:569–574, 1992
Ballou LM, Luther H, Thomas G: MAP2 kinase and 70K S6 kinase lie on distinct signalling pathways. Nature 349:348–350, 1991
Stokoe D, Campbell DG, Nakielny S, Hidaka H, Leevers SJ, Marshall C, Cohen P: MAPKAP kinase-2; a novel protein kinase activated by mitogen-activated protein kinase. EMBO J 11: 3985–3994, 1992
Stokoe D, Engel K, Campbell DG, Cohen P, Gaestel M: Identification of MAPKAP kinase 2 as a major enzyme responsible for the phosphorylation of the small mammalian heat shock proteins. FEBS Lett 313:307–313, 1992
Campbell DL, Sanghera JS, Stewart J, Walsh MP, Pelech SL: Phosphorylation and inhibition of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by MAP kinase and cyclin-dependent kinase-1. J Biochem J 1993, submitted
Chen R-H, Sarnecki C, Blenis J: Nuclear localization and regulation of ERK- and RSK-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol 12:915–927, 1992
Sanghera JS, Peter M, Nigg EA, Pelech SL: Immunological characterization of avian MAP kinases: Evidence for nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol 3:775–787, 1992
Alvarez E, Northwood IC, Gonzalez FA, Latour DA, Seth A, Abate C, Curran T, Davis RJ: Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 266:15277–15285, 1991
Pulverer BJ, Kyriakis JM, Avruch J, Nikolakaki E, Woodgett JR: Phosphorylation ofc-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature 353: 670–674, 1991
Seth A, Alvarez E, Gupta S, Davis RJ: A phosphorylation site located in the NH2-terminal domain of c-Myc increases transactivation of gene expression. J Biol Chem 266:23521–23524, 1991
Cheng J-T, Cobb MH, Baer R: Phosphorylation of the TAL1 oncoprotein by the extracellular-signal-regulated protein kinase ERK1. Mol Cell Biol 13:801–808, 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelech, S.L., Charest, D.L., Mordret, G.P. et al. Networking with mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Cell Biochem 127, 157–169 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01076767
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01076767