Abstract
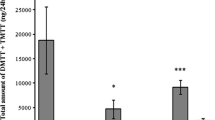
Electroantennogram techniques were used to elucidate antennal olfactory response of male and female boll weevils to a dilution series of grandlure, its components, and some vicinal dimethyl analogs. At higher concentrations, response to the mixture of the two aldehyde components of grandlure was significantly higher than to the two alcohol components. Only one vicinal dimethyl analog elicited a significantly higher response than the control. There were no significant differences in response due to sex over all compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dickens, J.C., andPayne, T.L. 1977. Bark beetle olfaction: Pheromone receptor system inDendroctonus frontalis.J. Insect Physiol. 23:481–489.
Hardee, D.D. 1972. A review of literature on the pheromone of the boll weevil,Anthonomus grandis Boheman (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). U.S. Department of Agriculture Cooperative Economy Ins. Report 22:200–207.
Hardee, D.D., Mckibben, G.H., Rummel, D.R., Huddlestone, P.M., andCoppedge, J.R. 1974. Response of boll weevils to component ratios and doses of the pheromone, grandlure.Environ. Entomol. 3:135–138.
Helwig, J.T., andCouncil, K.A. (ed.). 1979.SAS User's Guide, pp. 237–244. SAS Institute, Raleigh, North Carolina.
Ott, L. 1977. An Introduction to Statistical Methods and Data Analysis, 730 pp. Duxbury Press, North Scituate, Massachusetts.
Payne, T.L. 1970. Electrophysiological investigations on response to pheromones in bark beetles.Contrib. Boyce Thompson Inst. 24:275–282.
Payne, T.L. 1975. Bark beetle olfaction. III. Antennal olfactory responsiveness ofDendroctonus frontalis Zimmerman andD. brevicomis LeConte (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) to aggregation pheromones and host tree terpene hydrocarbons.J. Chem. Ecol. 1:233–242.
Payne, T.L., andDickens, J.C. 1976. Adaptation to determine receptor system specificity in insect olfactory communication.J. Insect Physiol. 22:1569–1572.
Perkins, J.H. 1980. Boll weevil eradication.Science 207:1044–1050.
Schneider, D. 1957. Elektrophysiologische Untersuchungen von Chemo- und Mechanorezeptoren der Antenne des SeidenspinnersBombyx mori.Z. Vergl. Physiol. 40:8–41.
Tumlinson, J.H., Hardee, D.D., Gueldner, R.C., Thompson, A.C., Hedin, P.A., andMinyard, J.P. 1969. Sex pheromones produced by the male boll weevil: Isolation, identification and synthesis.Science 166:1010–1012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Texas Agricultural Experiment Station paper number 16382. Research supported by McIntire-Stennis project 1525. All programs of the Texas Agricultural Experiment Station are available without regard to race, sex, color or religion.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutmann, A., Payne, T.L., Roberts, E.A. et al. Antennal olfactory response of boll weevil to grandlure and vicinal dimethyl analogs. J Chem Ecol 7, 919–926 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00987617
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00987617