Abstract
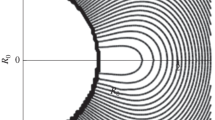
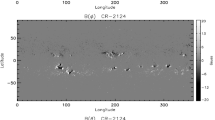
An analytical solution is presented for linear force fields within a spherical shell, representing the solar corona. Allowing for a global magnetic helicity, we find magnetic fields over the entire corona with realistic inner boundary conditions obtained from transformation and extrapolation of photospheric magnetograms and considering alternative outer boundary conditions. Such fields are found for the well known coronal hole extension event of August 1996.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clegg, J. R., Bromage, B. J. I., and Browning, P. K.: 1999, “Modelling the coronal magnetic field with a new method for obtaining boundary conditions on the far side of sun, ” JGR, in press.
Vibert, D., Lamy, P., and Llebaria, A.: 1997, “Streamer belt at solar min: simulation & comparison with LASCO C2 images, ” Proc. 5th SOHO Workshop, Oslo, p. 713.
Wang, Y.-M., and Sheeley, N. R., Jr.: 1992, “On potential field models of the solar corona, ” Ap.J., 392, 310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clegg, J.R., Bromage, B.J.I. & Browning, P.K. The Solar Magnetic Field as a Coronal Hole Extension Forms: Effects of Magnetic Helicity and Boundary Conditions. Space Science Reviews 87, 145–148 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005190821498
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005190821498