Abstract
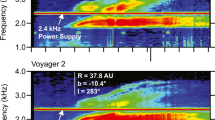
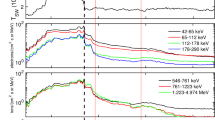
An overview of the solar wind termination shock is presented including: its place in the heliosphere and its origin; its structure including the role of interstellar pickup ions and galactic and anomalous cosmic rays; its inferred location based on Lyman-α backscatter, Voyager radio signals, and anomalous cosmic rays; its shape and movement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axford, W.I.: 1972, in C.P. Sonett, PJ. Coleman Jr., and J.M. Wilcox (eds.). ‘The Interaction of the Solar Wind with the Interstellar Medium’, Solar Wind, NASA SP 308, p. 609.
Barnes, A.: 1993, ‘Motion of the Heliospheric Termination Shock: A Gasdynamic Model’, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 15137.
Fisk, L.A., Kozlovsky, B., and Ramaty, R.: 1974, ‘An Interpretation of the Observed Oxygen and Nitrogen Enhancements in Low-energy Cosmic Rays’, Astrophys. J. 190, L35.
Gurnett, D.A., Kurth, W.S., Allendorf, S.C., and Poynter, R.L.: 1993, ‘Radio Emission from the Heliopause Triggered by an Interplanetary Shock’, Science 262, 199.
Grzedzielski, S.: 1993, ‘The Heliospheric Boundary Regions’, Adv. Space Res. 13 (6), 147.
Hall, D.T., Shemansky, D.E., Judge, D.L., Gangopadhyay, P., and Gruntman, M.A.: 1993, ‘Heliospheric Hydrogen Beyond 15 AU: Evidence for a Termination Shock’, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 15185.
Holzer, T.E.: 1989, ‘Interaction Between the Solar Wind and the Interstellar Medium’, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 27, 199.
Jokipii, J.R.: 1986, 'Particle Acceleration at a Termination Shock, 1, Application to the Solar Wind and the Anomalous Component, J. Geophys. Res., 91, 2929.
Jokipii, J.R., and McDonald, F.B.: 1995, ‘Quests for the Limits of the Heliosphere’, Scientific American 272, 62.
Landau, L.D., and Lifshitz, E.M.: 1959, Fluid Mechanics, Pergamon Press, New York, p. 332.
Lee, M.A., Shapiro, V.D., and Sagdeev, R.Z.: 1996, ‘Pickup Ion Energization by Shock Surfing’, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 4777.
Lee, M.A.: 1990, in S. Grzedzielski and D.E. Page (eds.), ‘Ion Acceleration to Cosmic Ray Energies’, Physics of the Outer Heliosphere, COSPAR, Pergamon Press, New York, p. 157.
Lee, M.A., and Axford, W.I.: 1988, ‘Model Structure of a Cosmic-ray Mediated Stellar or Solar Wind’, Astron. Astrophys. 194, 297.
Parker, E.N.: 1963, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, Wiley-Interscience, New York, pp. 113–128.
Pesses, M.E., Jokipii, J.R., and Eichler, D.: 1981, ‘Cosmic Ray Drift, Shock Wave Acceleration, and the Anomalous Component of Cosmic Rays’, Astrophys. J. 246, L85.
Phillips, J.L. et al.: 1995, ‘Ulysses Solar Wind Plasma Observations From Pole to Pole’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 3301.
Sagdeev, R.Z.: 1966, in M.A. Leontovich (ed.), ‘Cooperative Phenomena and Shock Waves in Collisionless Plasmas’, Reviews of Plasma Physics 4, Consultants Bur., New York, p. 23.
Stone, E.C., Cummings, A.C., and Webber, W.R.: 1996, ‘The Distance to the Solar Wind Termination Shock in 1993 and 1994 from Observations of Anomalous Cosmic Rays’, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 11017.
Suess, S.T.: 1993, ‘Temporal Variations in the Termination Shock Distance’, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 15147.
Whitham, G.B.: 1974, Linear and Nonlinear Waves, John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 458.
Zank, G.P., Pauls, H.L., Cairns, I.H., and Webb, G.M.: 1996, ‘Interstellar Pickup Ions and Quasi-Perpendicular Shocks: Implications for the Termination Shock and Interplanetary Shocks’, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.A. The termination shock of the solar wind. Space Sci Rev 78, 109–116 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170797
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170797