Abstract
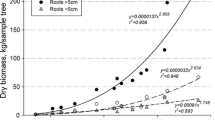
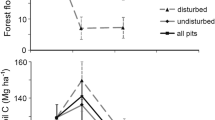
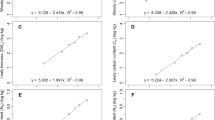
The combined effects of whole-tree harvesting (WTH) and soil leaching by both acid deposition and naturally-produced carbonic acid were evaluated in a mixed oak and a loblolly pine forest growing on similar soils in the Ridge and Valley province of eastern Tennessee. It was hypothesized that nutrient export via WTH would be greater in a mixed oak stand than in the loblolly pine stand because of greater nutrient concentrations in oak and hickory species than in pine. This hypothesis was true for N,P, and particularly Ca at the time of harvest, but not for K or Mg. When expressed on an annual basis, exports of N,P,K, and Mg were greater in the loblolly pine site and only Ca export was greater in the mixed oak site. It was also hypothesized that the large accumulation of Ca in the oak and hickory vegetation would cause lower exchangeable Ca2+ in soils, and, consequently, lower Ca2+ leaching in the mixed oak site than in the loblolly pine site. This hypothesis was supported by the data, which indicated 340–370% more exchangeable Ca and 100% more Ca2+ leaching in the loblolly pine site than in the mixed oak site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alban D H 1982. Effects of nutrient accumulation by aspen, spruce, and pine on soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46, 853–861.
Boyle J R, Phillips J J and Ek A R 1973 Whole-tree harvesting: nutrient budget evaluation. J. For. 71, 760–762.
Farmer R E, Bengston G W and Curlin J W 1970 Response of pine and mixed hardwood stands in the Tenessee Valley to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization. Forest Sci. 16, 130–136.
Gaines G L and Thomas H C 1953 Adsorption studies on clay minerals. II. A formulation of the thermodynamics of exchange adsorption. J. Chem. Phys. 21, 724.
Harris W F, Goldstein R A and Henderson G S 1973 Analysis of forest biomass pools, annual primary production, and turnover of biomass for a mixed deciduous forest watershed.In IUFRO Biomass Studies, Mensuration, Growth and Yield. University of Maine Press, Orono, Maine, USA.
Henderson G S, Swank W T, Waide J B and Grier C C 1978 Nutrient budgets of Appalachian and Cascade region watersheds: a comparison. For. Sci. 24(3), 385–397.
Johnson D W 1981 The natural acidity of some unpolluted waters in southeastern Alaska and potential impacts of acid rain. Water Air Soil Pollut. 16, 243–252.
Johnson D W, Henderson D S, Huff D D, Lindberg S E, Richter D D, Shriner D S, Todd D E and Turner J 1982a Cycling of organic and inorganic sulphur in a chestnut oak forest. Oecologia 54, 141–148.
Johnson D W, West D C, Todd D E and Mann L K 1982b Effects of sawlogvs whole-tree harvesting on the nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium budgets of an upland mixed oak forest. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46, 1304–1309.
Johnson F L and Risser P G 1974 Biomass, annual net primary production, and dynamics of six mineral elements in a post oak-blackjack oak forest. Ecology 55, 1246–1258.
Krug E C and Frink C R 1983 Acid rain on soil: a new perspective. Science 221, 520–525.
Lea R and Ballard R 1982 Relative effectiveness of nutrient concentrations in living foliage and needle fall at predicting response of loblolly pine to N and P fertilization. Can. J. For. Res. 12, 713–717.
Luxmoore R J 1983 Water budget of an eastern deciduous forest stand. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 47, 785–791.
Marion G K 1979 Biomass and nutrient removal in long-rotation stands.In Impact of Intensive harvesting on Forest Nutrient Cycling. Ed. A L Leaf. pp 98–110. State University of New York, Syracuse, New York, USA.
Olson S R and Dean L A 1965 Phosphorus.In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties. Eds. C A Black, D D Evans, J L White, L E Engsmiager and F E Clark. pp 1035–1049. American society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Rennie P J 1955 The uptake of nutrients by mature forest growth. Plant and Soil 7, 49–95.
Reuss J O, and Johnson D W 1986 Acid deposition and the acidification of soil and water. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA
Richter D D, Johnson D W and Todd D E 1983 Atmospheric sulfur deposition, neutralization, and ion leaching in two deciduous forest ecosystems. J. Environ. Qual. 12, 263–270.
Stone E L 1975 Effects of species on nutrient cycles and soil change. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B 271, 149–162.
Van Lear D H, Waide J B and Teuke M J 1984 Biomass and nutrient content of 41-year-old loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) plantation in South Carolina. For. Sci. 30, 395–410.
Wells C G 1967 Techniques and standards for foliar diagnosis of N deficiency in loblolly pineIn Forest Fertilization: Theory and Practice. Eds. G W Benston, W L Brendemuehl, W L Pritchett and W H Smith. pp 72–76. Tennessee Valley Authority, Muscle shoals, Alabama, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research sponsored by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency under Interagency Agreement No. 79-D-X0533 and Biofuels and Municipal Waste Technology Division, U.S. Department of Energy, under Contract No. De-AC05-84OR21400 with Martin Marietta Energy Systems, Inc.
Publication No. 2933, Environmental Sciences Division, ORNL.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, D.W., Todd, D.E. Nutrient export by leaching and whole-tree harvesting in a loblolly pine and mixed oak forest. Plant Soil 102, 99–109 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370907
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370907