Abstract
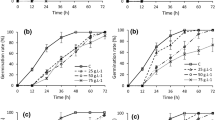
The allelopathic effects of vegetative and flowering plants of the annual/biennial pasture weed Senecio jacobaea L. (ragwort) against Lolium perenne L. (perennial ryegrass) and four pasture legumes were investigated using a range of bioassays. Bioassays based on shoot and root leachates demonstrated detectable, although usually slight, allelopathic effects, and these did not usually differ between the two developmental stages of S. jacobaea. However, aqueous extract and tissue decomposition bioassays demonstrated stronger allelopathic effects, particularly for flowering plants, and this was in general agreement with toxicity assessments of soil collected from under S. jacobaea plants in the field. According to our study, flowering plants have the potential to weaken pasture through allelopathy, and decomposition of above-ground litter appears as the most likely mechanism facilitating this. The aqueous extract and tissue decomposition bioassays also revealed that L. perenne was less susceptible to S. jacobaea allelopathy than were the legumes, suggesting that encouraging a strong L. perenne component in pastures has potential for reducing the overall inhibitory ef S. jacobaea on pasture production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, J P and Putnam, A R 1987 Role of benzoxazinones in allelopathy by rye (Secale cereale L.). J. Chem. Ecol. 13, 889–906.
Clapham, A R, Tutin, T G and Warburg, E F 1962 Flora of the British Isles. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 1269 p.
DeJong, T J and Klinkhamer, P G L 1985 The negative effect of litter of parent plants of Cirsium vulgare to their offsprings. Autotoxicity or immobilisation. Oecologia 65, 153–166.
DelMoral, C L and Muller, C M 1969 Fogdrip: a mechanism of toxin transport from Eucalyptus globulus. Bull. Torrey Botan. Club 96, 467–475.
Facelli, J M and Pickett, S T A 1991 Plant litter: its dynamics and effects on plant community structure. Bot. Rev. 57, 1–32.
Harper, J L 1958 The ecology of ragwort (Senecio jacobaea L) with special reference to control. Herbage Abstr. 28, 151–157.
Harper, J L 1977 Population Biology of Plants. Academic Press, London. 892 p.
Heisey, R M 1990 Evidence for allelopathy by Tree-of-Heaven (Alanthus altissima) J. Chem. Ecol. 6, 2039–2054.
Khandakar, A L and Bradbeer, J W 1983 Jute Seed Quality. Bangladesh Agricultural Research Council, Dhaka.
Kitanaka, S and Takido, M 1986 Studies on the constituents in the roots of Cassia oftusifolia L. and the antimicrobial activities of constituents of the roots and the seed. Yakugaku Zasski 106, 302–306.
Leather, G R and Einhellig, F A 1986 Bioassays in the study of allelopathy. In The Science of Allelopathy. Eds. A RPutanam and C STang. pp 133–145. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Lovett J V 1990. Chemicals in plant protection: is there a natural alternative? Alternatives to Chemical Control of Weeds—Proceedings of an International Conference on Biological Control at FRI, Rotorua, pp 57–65.
May, F E and Ash, J E 1990 An assessment of the allelopathic potential of Eucalyptus. Aust. J. Bot. 38, 245–254.
McEvoy, P B 1984 Seedling dispersion and the persistence of ragwort Senecio jacobaea (Compositae) in a grassland dominated by perennial species. Oikos 42, 138–143.
McEvoy, P B, Rudd, N T, Cox, C S and Huso, M 1993 Disturbance, competition and herbivory effects on ragwort Senecio jacobaea populations. Ecol. Monogr. 63, 55–75.
McPherson, J K, Chou, C-H and Muller, C M 1971 Allelopathic constituents of the chaparral shrub Adenostema fascicalatum. Phytochem. 10, 2925–2933.
Panetta, F D and Wardle, D A 1992 Gap size and regeneration in a New Zealand dairy pasture. Aust. J. Ecol. 17, 169–175.
Poole, A L and Cairns, D 1940 Biological aspects of ragwort (Senecio jacobaea L.) control. Department of Scientific and Industrial Research Bulletin No. 82, Government Printer, Wellington.
Purvis, C F 1990 Allelopathy: a new direction in weed control. Plant Prot. Quart. 5, 55–59.
Putnam, A R and Tang, C S 1986 Allelopathy: state of the science. In The Science of Allelopathy. Eds. A RPutnam and C STang. pp 1–19. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Rice, E L 1984 Allelopathy. 2nd Edn. Academic Press, London. 424 p.
Rice, E L 1986 Allelopathic growth stimulation. In The Science of Allelopathy. Eds. A RPutnam and C STang. pp 23–42. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Rovira, A D 1969 Plant root exudates. Bot. Rev. 35, 35–59.
Shafer, W E and Garrison, S A 1986 Allelopathic effects of soil incorporated asparagus roots on lettuce, tomato and asparagus seedling emergence. Hortscience 21, 82–84.
Singh, R and Bawa, R 1982 Effect of leaf leachates from Eucalyptus globulus Labill and Aesculus indica Colebr. on germination of Glaucium flavum Crantz. Ind. J. For. 9, 21–28.
Stowe, L G 1979 Allelopathy and its influence on the distribution of plants in an Illinois old field. J. Ecol. 67, 1065–1085.
Thompson A, Saunders A E and Martin P 1987 The effect of nodding thistle (Carduus nutans) on pasture production. Proc. 40th N Z Weed and Pest Control Conf, 222–225.
Tukey, H BJr 1969 Implications of allelopathy in agricultural plant science. Bot. Rev. 35, 1–16.
Wardle, D A 1987 The ecology of ragwort (Senecio jacobaea L.)-a review. N. Z. J. Ecol. 10, 67–76.
Wardle, D A 1992 A comparative assessment of factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soils. Biol. Rev. 67, 321–358.
Wardle, D A, Ahmed, M and Nicholson, K S 1991 Allelopathic influence of nodding thistle (Carduus nutans L.) seeds on germination and radical growth of pasture plants. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 34, 185–191.
Wardle, D A, Nicholson, K S and Ahmed, M 1992 Comparison of osmotic and allelopathic effects of grass leaf extracts on grass seed germination and radicle elongation. Plant and Soil 140, 315–319.
Wardle, D A, Nicholson, K S and Rahman, A 1993 Influence of plant age on the allelopathic potential of nodding thistle (Carduus nutans L.) against pasture grasses and legumes. Weed Res. 33, 69–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, M., Wardle, D.A. Allelopathic potential of vegetative and flowering ragwort (Senecio jacobaea L.) plants against associated pasture species. Plant Soil 164, 61–68 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010111
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010111