Abstract
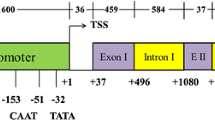
A 1420 bp genomic fragment (λ-horl-17) encompassing a Hor-1 gene encoding a C-hordein polypeptide is presented. The deduced amino acid sequence is 261 residues long. It comprises a 20 amino acid signal peptide, unique NH2- and COOH-terminal regions and a coding region comprised of pentapeptide (PQQPY) and octapeptide (PQQPFPQQ) repeat motifs. The 431 bp of 5′ non-coding region contains a ‘TATA box’ at −105, a ‘CACA box’ (−181 to −201) and a −300 prolamin element. In the 3′ noncoding region there are two putative polyadenylation signals located 88 and 142 bp downstream of the stop codon.
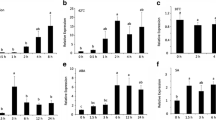
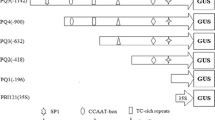
The structure of λ-hor1-17 is compared with that of another gene (λ-hor1-14) encoding a C-hordein polypeptide, which contains an amber codon interrupting the ORF. A functional assay in which the 5′ non-coding regions of the two genes were fused to the β-glucuronidase (GUS) gene demonstrated that both genes were transcriptionally active and that circa 430 bp of the C-hordein promoters were sufficient to drive the expression of the GUS gene in developing barley endosperms. It also demonstrated that both promoters had transcriptional efficiencies comparable with that of the 35S CaMV promoter. The in vitro translation of the coding region of λ-hor1-14 in the wheat germ system showed that the premature stop codon could be partially suppressed. The suppression was also demonstrated in a transient expression assay in vivo using isolated barley endosperms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b:
-
base
- CaMV:
-
cauliflower mosaic virus
- GUS:
-
β-glucuronidase
- HMW:
-
high molecular weight
- kb:
-
kilobase pair
- LMW:
-
low molecular weight
- Mabs:
-
monoclonal antibodies
- NOS:
-
nopaline synthase
- nt:
-
nucleotide
- ORF:
-
open reading frame
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- TMV:
-
tobacco mosaic virus
- Ψ:
-
pseudouridine
References
Anderson D, Blobel G: Immunoprecipitation of proteins from cell-free translations. Meth Enzymol 96: 111–120 (1983).
Angenon G, VanMontagu M, Depicker A: Analysis of the stop codon context in plant nuclear genes. FEBS Lett 271: 144–146 (1990).
Aviv H, Leder P: Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69: 1408–1411 (1972).
Beier H, Barciszewska M, Sickinger H-D: The molecular basis for the differential translation of TMV RNA in tobacco protoplasts and wheat germ extracts. EMBO J 3: 1091–1096 (1984).
Bossi L: Context effects: Translation of UAG codon by suppressor tRNA is affected by the sequence following UAG in the message. J Mol Biol 164: 73–87 (1983).
Brandt A, Ingversen J: Isolation and translation of hordein messenger RNA from wild type and mutant endosperms in barley. Carlsberg Res Commun 43: 451–469 (1978).
Brandt A, Montembault A, Cameron-Mills V, Rasmussen SK: Primary structure of a B1-hordein gene from barley. Carsberg Res Commun 50: 333–345 (1985).
Brett GM, Mills ENC, Parmar S, Tatham AS, Shewry PR, Morgan MRA: Monoclonal antibodies that recognise the repeat motif of the S-poor prolamins. J Cereal Sci 12: 245–255 (1990).
Callis J, Fromm M, Walbot V: Introns increase gene expression in cultured maize cells. Genes Devel 1: 1183–1200 (1987).
Cameron-Mills V: The structure and composition of protein bodies purified from barley endosperm by silica sol density gradients. Carlsberg Res Commun 45: 557–576 (1980).
Cameron-Mills V, Brandt A: A γ-hordein gene. Plant Mol Biol 11: 449–461 (1988).
Cameron-Mills V, Madrid SM: The signal peptide cleavage site of a B1 hordein determined by radiosequencing of the in vitro synthesized and processed polypeptide. Carlsberg Res Commun 54: 181–192 (1989).
Capone JP, Sharp PA, RajBhandary UL: Amber, ochre and opal suppressor tRNA genes derived from a human serine tRNA gene. EMBO J 4: 213–221 (1985).
Chamberlain JP: Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem 98: 132–135 (1979).
Colot V, Robert LS, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW, Thompson RD: Localization of sequences in wheat endosperm protein genes which confer tissue-specific expression in tobacco. EMBO J 6: 3559–3564 (1987).
Dierks-Ventling C, Cozens K: Immunochemical crossreactivity between zein, hordein and gliadin. FEBS Lett 142: 147–150 (1982).
Efstratiadis A, Posakony JW, Maniatis T, Lawn RM, O'Connell C, Spritz RA, DeRiel JK, Forget BG, Weissman SM, Slightom JL, Blechl AE, Smithies O, Baralle FE, Shoulders CC, Proudfoot NJ: The structure and evolution of the human β-globin gene family. Cell 21: 653–668 (1980).
Entwistle J: Primary structure of a C-hordein gene from barley. Carlsberg Res Commun 53: 247–258 (1988).
Forde BG, Kreis M, Williamson MS, Fry RP, Pywell J, Shewry PR, Bunce N, Miflin BJ: Short tandem repeats shared by B- and C-hordein cDNAs suggest a common evolutionary origin for two groups of cereal storage protein genes. EMBO J 4: 9–15 (1985).
Forde J, Malpica J-M, Halford NG, Shewry PR, Anderson OD, Greene FC, Miflin BJ: The nucleotide sequence of a HMW glutenin subunit gene located on chromosome 1A of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Nucl Acids Res 13: 6817–6832 (1985).
Forde BG, Heyworth A, Pywell J, Kreis M: Nucleotide sequence of a B1 hordein gene and the identification of possible upstream regulatory elements in endosperm storage protein genes from barley, wheat and maize. Nucl Acids Res 13: 7327–7339 (1985).
Giese H, Andersen B, Doll H: Synthesis of the major storage protein, hordein, in barley. Pulse-labeling study of grain filling in liquid-cultured detached spikes. Planta 159: 60–65 (1983).
Giese H, Hopp HE: Influence of nitrogen nutrition on the amount of hordein, protein Z and β-amylase messenger RNA in developing endosperms of barley. Carlsberg Res Commun 49: 365–383 (1984).
Graner A, Siedler H, Jahoor A, Wenzel G, Herrmann RG: Genome analysis in barley. VI. In: NATO Advanced Study Institute on Plant Molecular Biology, Schloss Elmau, Bavaria, Germany, 14–23 May 1990.
Halford NG, Forde J, Shewry PR, Kreis M: Functional analysis of the upstream regions of a silent and an expressed member of a family of wheat seed protein genes in transgenic tobacco. Plant Sci 62: 207–216 (1989).
Hanahan D: Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 166: 557–580 (1983).
Hänfler A, Kleuvers B, Göringer HU: The involvement of base 1054 in 16S rRNA for UGA stop codon dependent translation termination. Nucl Acids Res 18: 5625–5632 (1990).
Heijne Gvon: Analysis of the distribution of charged residues in the N-terminal region of signal sequences: implications for protein export in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. EMBO J 3: 2315–2318 (1984).
Heidecker G, Messing J: Structural analysis of plant genes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 37: 439–466 (1986).
Hill DE, Hope IA, Macke JP, Struhl K: Saturation mutagenesis of the yeast his3 regulatory site: Requirements for transcriptional induction and for binding by GCN4 activator protein. Science 234: 451–457 (1986).
Jefferson RA: Assaying chimeric genes in plants: The GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5: 387–405 (1987).
Jefferson RA: Plant reporter genes: the GUS fusion system. Genet Engng 10: 247–263 (1988).
Jensen J, Jørgensen JH, Jensen HP, Giese H, Doll H: Linkage of the hordein loci Hor1 and Hor2 with the powdery mildew resistance loci Ml-k and Ml-a on barley chromosome 5. Theor Appl Genet 58: 27–31 (1980).
Jofuku KD, Schipper RD, Goldberg RB: A frameshift mutation prevents Kunitz trypsin inhibitor mRNA accumulation in soybean embryos. Plant Cell 1: 427–435 (1989).
Klein TN, Gradziel T, Fromm ME, Sanford JC: Factors influencing gene delivery into Zea mays cells by high-velocity microprojectiles. Bio/technology 6: 559–563 (1988).
Knudsen S, Müller M: Transformation of the developing barley endosperm by particle bombardment. Planta (in press).
Kridl JC, Vieira J, Rubenstein I, Messing J: Nucleotide sequence analysis of a zein genomic clone with a short open reading frame. Gene 28: 113–118 (1984).
Kuchino Y, Beier H, Akita N, Nishimura S: Natural UAG suppressor glutamine tRNA is elevated in mouse cells infected with Molony murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 2668–2672 (1987).
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685 (1970).
Li W-H: Evolution of duplicated genes and pseudogenes In: Nei M, Koehn RK (eds) Evolution of Genes and Proteins, pp. 14–37. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA (1983).
Maier U-G, Brown JWS, Toloczyki C, Feix G: Binding of a nuclear factor to a consensus sequence in the 5′ flanking region of zein genes from maize. EMBO J 6: 17–22 (1987).
Marris C, Gallois P, Copley J, Kreis M: The 5′ flanking region of a barley B hordein gene controls tissue and developmental specific CAT expression in tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol 10: 359–366 (1988).
Matzke AJM, Stöger EM, Schernthaner JP, Matzke MA: Deletion analysis of a zein gene promoter in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol 14: 323–332 (1990).
O'Connor M, Gestleland RF, Atkins JF: tRNA hopping: enhancement by an expanded anticodon. EMBO J 8: 4315–4323 (1989).
Rafalski JA: Structure of wheat gamma-gliadin genes. Gene 43: 221–229 (1986).
Rahman S, Shewry PR, Miflin BJ: Differential protein accumulation during barley grain development. J Exp Bot 33: 717–728 (1982).
Rahman S, Kreis M, Forde BG, Shewry PR, Miflin BJ: Hordein gene expression during development of the barley (Hordeum vulgare) endosperm. Biochem J 223: 315–322 (1984).
Rasmussen SK, Brandt A: Nucleotide sequences of cDNA clones for C-hordein polypeptides. Carlsberg Res Commun 51: 371–379 (1986).
Reeves CD, Okita TW: Analyses of α/β-type gliadin genes from diploid and hexaploid wheats. Gene 52: 257–266 (1987).
Roberts BE, Patterson BM: Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70: 2330–2334 (1974).
Scallon BJ, Dickinson CD, Nielsen NC: Characterization of a null-allele for the Gy 4 glycinin gene from soybean. Mol Gen Genet 208: 107–113 (1987).
Schmitt JM: Purification of hordein polypeptides by column chromatography using volatile solvents. Carlsberg Res Commun 44: 431–438 (1979).
Schmitt JM, Svendsen I: Amino acid sequences of hordein polypeptides. Carlsberg Res Commun 45: 143–148 (1980).
Shewry PR, Faulks AJ, Pickering RA, Jones IT, Finch RA, Miflin BJ: The genetic analysis of barley storage proteins. Heredity 44: 383–389 (1980).
Shewry PR, Lew EJ-L, Kasarda DD: Structural homology of storage proteins coded by the Hor-1 locus of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Planta 153: 246–253 (1981).
Skuzeski JM, Nichols LM, Gesteland RF: Analysis of leaky viral translation termination codons in vivo by transient expression of improved β-glucuronidase vectors. Plant Mol Biol 15: 65–79 (1990).
Stueber D, Ibrahimi I, Cutler D, Dobberstein B, Bujard H: A novel in vitro transcription-translation system: accurate and efficient synthesis of single proteins from cloned DNA sequences. EMBO J 3: 3143–3148 (1984).
Sørensen MB, Cameron-Mills V, Brandt A: Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in developing barley endosperms. Mol Gen Genet 217: 195–201 (1989).
Tabor S, Richardson CC: DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 4767–4771 (1987).
Tatham AS, Drake AF, Shewry PR: Conformational studies of a synthetic peptide corresponding to the repeat motif of C-hordein. Biochem J 259: 471–476 (1989).
Thomas MS, Flavell RB: Identification of an enhancer element for the endosperm-specific expression of high molecular weight glutenin. Plant Cell 2: 1171–1180 (1990).
Valle RPC, Morch M-D: Stop making sense or regulation at the level of termination in eukaryotic protein synthesis. FEBS Lett 235: 1–15 (1988).
Valle RPC, Morch M-D, Haenni A-L: Novel amber suppressor tRNAs of mammalian origin. EMBO J 6: 3049–3055 (1987).
Viotti A, Cairo G, Vitale A, Sala E: Each zein gene class can produce polypeptides of different sizes. EMBO J 4: 1103–1110 (1985).
Voelker TA, Staswick P, Chrispeels MJ: Molecular analysis of two phytohemagglutinin genes and their expression in Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Pinto, a lectin-deficient cultivar of the bean. EMBO J 5: 3075–3082 (1986).
Voelker TA, Moreno J, Chrispeels MJ: Expression analysis of a pseudogene in transgenic tobacco: A frameshift mutation prevents mRNA accumulation. Plant Cell 2: 255–261 (1990).
Weiss RB, Dunn DM, Atkins JF, Gesteland RF: Slippery runs, shifty stops, backward steps, and forward hops: −2, −1, +1, +2, +5, and +6 ribosomal frame-shifting. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 52: 687–693 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Entwistle, J., Knudsen, S., Müller, M. et al. Amber codon suppression: the in vivo and in vitro analysis of two C-hordein genes from barley. Plant Mol Biol 17, 1217–1231 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028737
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028737