Abstract
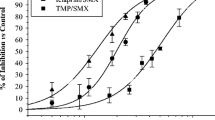
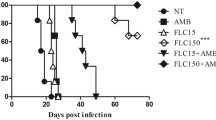
Patients with severe and complicated paracoccidioidomycosis are treated with amphotericin B by the intravenous route. Fluconazole is active in vitro against Paracoccidioides brasiliensis and can also be administered intravenously, but few clinical or experimental data are available about its action against the infection caused by this fungus. In the present study, the efficacy of fluconazole andamphotericin B was assessed comparatively in rats inoculated parenterally with P. brasiliensis. The treatment was performed 3 times a week for 4 weeks starting one week after infection. Fluconazole administered intraperitoneally (14 mg/kg bodyweight/dose) was more effective (P > 0.001)than amphotericin B (2 mg/kg body weight/dose) in reducing the number of colony forming units in the lungs and spleen. When administered intravenously at the dose of 3 mg/kg body weight, fluconazole was as effective as amphotericin B (0.8 mg/kg body weight) in reducing the pulmonary fungal burden. Under these conditions, the rats treated with fluconazole had a smaller number of colony forming units than untreated animals (P > 0.001), but amphotericin B was more effective than fluconazole in reducing spleen infection (P > 0.005). Except for this result obtained with a low dose, fluconazole showed an antifungal action equal to or higher than that of amphotericin B. The activity of fluconazole at doses equivalent to those used for human treatment suggests that this antifungal agent may be an alternative to amphotericin B for the early intravenous treatment of patients with paracoccidioidomycosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Espinel-Ingroff A, Kerkering TM, Negroni R, Restrepo A. Susceptibilities of the yeast and mycelial phase of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis to five antifungal agents. Rev Argent Micol 1992; 15: 30 (Abstract).
Negroni R, Elias Costa MRI, Finquelievich JL, Iovannitti C, Agorio IL, Tiraboschi IN. Three triazoles in the treatment of experimental paracoccidioidomycosis. Rev Iberoamer Micol 1991; 8: 8–12.
Brummer E, Castaneda E, Restrepo A. Paracoccidioidomycosis: an update. Clin Microbiol Rev 1993; 6: 89–117.
Mendes RP, Negroni R, Arechavala A. Treatment and control of cure. In: Franco M, Lacaz CS, Restrepo-Moreno A, Del Negro G, eds. Paracoccidioidomycosis. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1994: 373–392.
Negroni R, Robles AM, Arechavala A, Taborda A. Experiencia terapeutica con el fluconazol en las micosis profundas. Rev Argent Micol 1990; 13: 26–32.
Diaz M, Negroni R, Montero-Gei F, Castro LMG, Sampaio SAP, Borelli D, Restrepo A, Franco L, Bran JL, Arathoon EG, Stevens DA, and other investigators of the Fluconazole PanAmerican Study Group. A Pan-American 5-year study of fluconazole therapy for deep mycoses in the immunocompetent host. Clin Infect Dis 1992; 14: S68–S76.
Singer-Vermes LM, Ciavaglia MC, Kashino SS, Burger E, Calich VLG. The source of the growth-promoting factor(s) affects the plating efficiency of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Med Vet Mycol 1992; 30: 261–264.
Stevens DA, Brummer E, McEwen JG, Perlman A. Efficacy of fluconazole, a new oral triazole, in blastomycosis and paracoccidioidomycosis and in comparison with ketoconazole. Rev Iber Micol 1988; 5 (suppl 1): 26 (Abstract).
Louie A, Drusano GL, Banerjee P, Liu Q-F, Kaw P, Shayegani M, Taber H, Miller MH. Pharmacodynamics of fluconazole in a murine model of systemic candidiasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1998; 42: 1105–1109.
Sanati H, Ramos CF, Bayer AS, Ghannoum MA. Combination therapy with amphotericin B and fluconazole against invasive candidiasis in neutropenic-mouse and infective-endocarditis rabbit models. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1997; 41: 1345–1348.
Kobayashi GS, Travis SJ, Medoff G. Comparison of fluconazole with amphotericin B in treatment of histoplasmosis in normal and immunosuppressed mice. Rev Infect Dis 1990; 12: S291–S293.
Patterson TF, Miniter P, Andriole VT. Efficacy of fluconazole in experimental invasive aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis 1990; S281–S285.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez, R., Malta, M.H.B., Verceze, A.V. et al. Comparative efficacy of fluconazole and amphotericin B in the parenteral treatment of experimental paracoccidioidomycosis in the rat. Mycopathologia 146, 131–134 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007013808797
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007013808797