Abstract
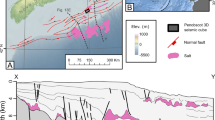
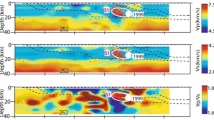
Two seismic refraction and gravity lines were obtained along and normal to the axis of the Aegir Rift, an extinct spreading centre in the Norway Basin. Velocity-depth solutions and crustal structure models are derived from ocean-bottom records using two-dimensional ray tracing and synthetic seismogram modelling techniques. Gravity data are used to generate models consistent with the lateral variations in thickness of the layers in the crustal models. The resulting models require considerable degree of lateral inhomogeneity along and perpendicular to the rift axis. Crust within the extinct spreading centre is found to be thinner and of low P-wave velocity when compared with the crust sampled off-axis. To explain reduced velocities of the lower crust we suggest that, due to the relationship between fracturing and seismic velocity, the decreasing spreading rate leading up to extinction let the mechanically strong layer thicken, so that faulting and fracturing extended to greater depths . Low velocities are also observed in the uppermost mantle underlying the extinct spreading ridge. This zone is attributed to hydrothermal alteration of upper mantle peridotites. Furthermore, after spreading ceased 32-26 my ago, ongoing passive hydrothermal circulation was accompanied by the precipitation of alteration products in open void spaces, thereby decreasing the porosity and increasing the velocity. Consequently the typical low velocities of layer 2 found at active mid-ocean ridges have been replaced by values typical of mature oceanic crust.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avedik, F., 1986, Sea-Floor Seismology: Mobile Ocean Bottom Vertical Seismic Array for Controlled Source Experiments, in T. Akal and J. M. Berkson (eds.), Ocean Seismo-Acoustics, NATO Conference Series IV: Marine Series, 863–870.
Avery, O. E., Burton, G. D., Heirtzler, J. R., 1968, An Aeromagnetic Survey of the Norwegian Sea, J. Geophys. Res. 73, 4583–4600.
Bott, M. H. P., 1985, Plate Tectonic Evolution of the Icelandic Transverse Ridge and Adjacent Regions, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 9953–9960.
Bown, J. W. and White, R. S., 1994, Variation with Spreading Rate of Oceanic Crustal Thickness and Geochemistry, Earth and Planet Sci. Lett. 121, 435–449.
Cerveny, V., Molotkov, I. A. and Psencik, I., 1977, Ray Method in Seismology. Charles Univ., Prague, 214 pp.
Cerveny, V. and Psencik, I., 1981, 2-D Seismic Ray Package. Charles Univ., Prague, 1981.
Christensen, N. I., 1966, Elasticity of Ultrabasic Rocks, J. Geophys. Res. 71, 5921–5931.
Dietrich, G., 1969, Atlas of the Hydrography of the Northern Atlantic Ocean. Conseil International pour l'Exploration de la Mer, 140 pp.
Ewing, J., 1963, Elementary Theory of Seismic Refraction and Reflection Measurements, in M. N. Hill (ed.), The Sea, 3, Wiley Interscience, New York, pp. 1–19.
Goff, J. A., Tucholke, B. E., Lin, J., Jaroslow, G. E. and Kleinrock, M. C., 1995, Quantitative Analysis of Abyssal Hills in the Atlantic Ocean: A Correlation between Inferred Crustal Thickness and Extensional Faulting, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 22,509–22,522.
Goldschmidt-Rokita, A. et al., 1989, Fahrtbericht über die FS Valdi-via-Expedition Nr. 84. Inst. f. Geophys., Univ. Hamburg.
Grevemeyer, I. and Weigel, W., 1995, A Seismic Image of the Great Meteor Tablemount (Abstract), Ann. Geophys. 13 (Suppl.), EGS Meeting 1995, 130 pp.
Grevemeyer, I. and Weigel, W., 1996, SeismicVelocities of the Upper-most Igneous Crust Versus Age, Geophys. J. Int. 124, 631–635.
Grevemeyer, I., 1996, Hotspot-Ridge Interaction in the Indian Ocean: Constraints from Geosat/ERM Altimetry, Geophys. J. Int. 126, 796–804.
Gronlie, G. and Talwani, M., 1978, Geophysical Atlas Norwegian-Greenland Sea, Vema Research Series 4, Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory, New York.
Herber, R., Nuppenau, V. and Snoek, M., 1981, An OBS System for Marine Seismic Investigations, Basic Requirements and Options: The Hamburg OBS, Bollettino Di Geofisica Teorica Ed Applicata 23, 233–242.
Herber, R. and Snoek, M., 1984, Increased Efficiency of Chemical Charges in Refraction Seismic Experiments at Sea, Mar. Geophys. Res. 6, 433–446.
Hess, H., 1964, Seismic Anisotropy of the Uppermost Mantle under Oceans, Nature 203, 629–631.
Hinz, K. and Moe, A., 1971, Crustal Structure in the Norwegian Sea, Nature Phys. Sci. 232, 187–190.
Hinz, K., 1972, Der Krustenaufbau des Norwegischen Kontinental-randes und der Norwegischen Tiefsee zwischen 66º und 68º N nach seismischenUntersuchungen, Meteor. Forsch.Ergebnisse C10, 1–16.
Hinz, K., 1981, A Hypothesis on Terrestrial Catastrophes: Wedges of Very Thick Oceanward Dipping Layers Beneath Passive Continental Margins - Their Origin and Paleoenvironment Significance, Geol. Jahrb. Ser. E 22, 3–28.
Hinz, K., Weber, J. and Hanisch, J., 1984, Structural Elements of the Norwegian Continental Margin, Geol. Jahrb. Ser. A 75, 193–221.
Houtz, R. and Ewing, J., 1976, Upper Crustal Structure as a Function of Plate Age, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 2490–2498.
Huang, P. Y. and Solomon, S. C., 1988, Centroid Depths of Mid-Ocean Ridge Earthquakes: Dependence on Spreading Rate, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 13,445–13,477.
Jacobson, R. S., 1992, Impact of Crustal Evolution on Changes of the Seismic Properties of the Uppermost Ocean Crust, Rev.Geophys. 30, 23–42.
Johnson, G. L. and Heezen, B. C., 1967, Morphology and Evolution of the Norwegian-Greenland Sea, Deep Sea Res. 13, 755–771.
Kirk, R. E., Whitmarsh, R. B. and Langford, J. J., 1982, A Three Component Ocean-Bottom Seismograph for Controlled Source and Earthquake Seismology, Mar. Geophys. Res. 5, 327–341.
Klitgord, K. D. and Mammerickx, J., 1982, Northern East Pacific Rise: Magnetic Anomaly and Bathymetric Framework, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 6725–6750.
Kristoffersen, Y. and Talwani, M, 1977, Extinct Triple Junction South of Greenland and the Tertiary Motion of Greenland Relative to North America, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 88, 1037–1049.
Kusznir, N. J., 1980, Thermal Evolution of the Oceanic Crust: Its Dependence on Spreading Rate and Effect on Crustal Structure, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 61, 167–181.
Lewis, B. T. R. and Snydsman, W. E., 1979, Fine Structure of the Lower Crust on the Cocos Plate, in J. Francheteau (ed), Processes at Mid-Ocean Ridges, Tectonophysics 55, 87–105.
Lin, J. and Phipps Morgan, J., 1992, The Spreading Rate Dependence of Three-Dimensional Mid-Ocean Ridge Gravity Structure, Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 13–16.
Mammerickx, J, Herron, E. and Dorman, L., 1980, Evidence for Two Fossile Spreading Ridges in the Southeast Pacific, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 91, 263–271.
Mutter, J. C., Talwani, M. and Stoffa, P. L., 1984, Evidence for a Thick Oceanic Crust Adjacent to the Norwegian Margin, J. Geophys. Res. 89, 483–502.
Nafe, J. E. and Drake, C. L., 1963, Physical Properties of Marine Sediments, in M. N. Hill (ed.), The Sea, 3, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 794–815.
Nunns, A.G., Talwani, M., Lorentzen, P. R., Vogt, P. R., Sigurgeirson, T., Kristjansson, L., Larsen, H. C. and Voppel, D. 1983, Magnetic Anomalies Over Iceland and Surrounding Seas, in H. M. P. Bott, S. Saxov, M. Talwani and J. Thiede (eds.) Structure and Development of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge: New Methods and Concepts, Plenum, New York, 661–678.
Nunns, A.G., 1983,The Structure and Evolution of the Jan Mayen Ridge and Surrounding Regions, in J.S. Watkins and C. L. Drake (eds.), Continental Margin Geology, Mem. Assoc. Pet. Geol. 34, 193–208.
Osler, J. C. and Louden, K. E., 1992, Crustal Structure of an Extinct Rift Axis in the Labrador Sea: Preliminary Results from a Seismic Refraction Survey, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 108, 243–258.
Osler, J. C. and Louden, K. E., 1995, Extinct Spreading Center in the Labrador Sea: Crustal Structure from a 2-D Seismic Refraction Velocity Model, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 2261–2278.
Phipps Morgan, J., Morgan, W. J., Zhang, Y.-S. and Smith, W. H. F., 1995, Observational Hints, for a Plume-Fed, Suboceanic Asthenosphere and its Role in Mantle Convection, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 12,753–12,767.
Purdy, G. M., 1983, The Seismic Structure of 140 my Old Crust in the Western Central Atlantic Ocean, Geophys. J.R. Astr. Soc. 72, 115–137.
Purdy, G. M. and Detrick, R. S., 1986, Crustal Structure of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 23º N from Seismic Refraction Studies, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 3739–3762.
Purdy, G. M., 1987, New Observations of the Shallow Seismic Structure of Young Oceanic Crust, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 9351–9362.
Reid, I. and Jackson, H. R., 1981, Ocean Spreading Rate and Crustal Thickness, Mar. Geophys. Res. 5, 165–172.
Schilling, J.-G., Thompson, G., Kingsley, R. and Humphris, S., 1985, Hotspot-Migrating Ridge Interaction in the South Atlantic, Nature 313, 187–191.
Sinton, J. M. and Detrick, R. S., 1992, Mid-Ocean Ridge Magma Chambers, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 197–216.
Skogseid, J. and Eldholm, O., 1987, Early Cenozoic Crust at the Norwegian Continental Margin and the Conjugate Jan Mayen Ridge, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 11,471–11,491.
Smith, D. K. and Cann, J. R., 1992, The Role of Seamount Volcanism in Crustal Construction at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge (24º - 30º N), J. Geophys. Res. 97, 1645–1658.
Smith, D. K. and Cann, J. R. 1993, Building the Crust at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Nature 365, 707–715.
Talwani, M. and Eldholm, O., 1977, Evolution of the Norwegian-Greenland Sea, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 88, 969–999.
Talwani, M., Worzel, J. L. and Landisman, M., 1959, Rapid Gravity Compution for Two-Dimensional Bodies with Application to the Mendocines Submarine Fracture Zone, J. Geophys. Res. 64, 49–59.
Uenzelmann-Neben, G., Jokat, W., Miller, H., Steinmetz, S., 1992, The Aegir Ridge-Structure of an Extinct Spreading Axis, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 9203–9218.
Vera, E. E., Buhl, P., Mutter, J. C., Harding, A. J., Orcutt, J. A. and Detrick, R. S., 1990, The Structure of 0- 0.2 my Old Oceanic Crust at 9º N in the East Pacific Rise from Expanded Spread Profiles, J. Geophys. Res. 95, 15,529–15,556.
Vogt, P. R., Ostenso, N. A. and Johnson, G. L., 1970, Magnetic and Bathymetric Data Bearing on Sea-Floor Spreading North of Iceland, J. Geophys. Res. 75, 903–920.
Vogt, P. R., Johnson, G. L. and Kristjansson, L., 1980, Morphology and Magnetic Anomalies North of Iceland, J. Geophys. 47, 67–80.
Weigel, W., 1989, Valdivia-Fahrt Nr. 59: Projekt JAMNORT. Berichte über die Fahrten des Hamburger Forschungsschiffes Valdivia. Univ. Hamburg, 173–237
Weigel, W. 1988, Bericht über die Polarstern-Expedition ARK V/3b, DFG-Projekt GRÖ KORT, Inst. f. Geophys., Univ. Hamburg, 139 pp.
Weigel, W., Gebhardt, V., Whitmarsh, R. B., Dehghani, G. A. and Hillermann, E., 1992, Abschlussbericht des DFG-Projekts JAMNORT. Inst. f. Geophys., Univ. Hamburg, 153 pp.
White, R. S. and McKenzie, D. P., 1989, Magmatism at Rift Zones: The Generation of Volcanic Continental Margins and Flood Basalts, J. Geophys. Res. 94, 7685–7729.
White, R. S., McKenzie, D. P. and O'Nions, R. K., 1992, Oceanic Crustal Thickness from Seismic Measurements and Rare Earth Element Inversions, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 19,683–19,715.
Whitmarsh, R. B., 1978, Seismic Refraction Studies of the Upper Igneous Crust in the North Atlantic and Porosity Estimates for Layer 2, Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett. 37, 451–464.
Wood, R., 1994, Geophysical Aspects of the Opening of the Tasman Sea Basin, in van der Lingen, G. J., Swanson, K. M., Muir, R. J. and Balkema, A. A. (eds.), Evolution of the Tasman Sea Basin, Rotterdam, 261 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grevemeyer, I., Weigel, W., Dehghani, G.A. et al. The Aegir Rift: Crustal Structure of an Extinct Spreading Axis. Marine Geophysical Researches 19, 1–23 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004288815129
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004288815129