Abstract
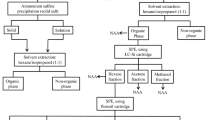
Thermal and epithermal neutron activation analysis has been applied to determine the concentrations of magnesium, aluminium, phosphorus, copper and manganese in two biological fluids: blood serum and market milk. Both epithermal neutron irradiation and radiochemical separation (a chromatographic column of HAP) were used to get rid of the interferences from 24-Na. Strongly acidic solutions of the irradiated samples were passed through the columns of HAP, where sodium was completely adsorbed while, Al, Cu, Mg and Mn were eluted with an efficiency of 99±1%. Since both Al and P were determined through the formation of28Al (2.24 min) thermal and epithermal neutron activation have been applied in order to determine the contribution of each radionuclide to28Al activity. The determination of Mg, Al and P in milk samples was done instrumentally, whereas in the case of blood serum with higher concentration of Na, a radiochemical separation is essential in both cases. The concentrations of Al, Cu, Mg, Mn and P in blood serum and market milk were found to be 0.24±0.02 and 1.85±0.09 μg Al/ml, 1.35±0.04 and 0.068±0.005 μg Cu/ml, 22.9±1 and 98.9±8.6 μg Mg/ml, 22±3 and 16±2 ng Mn/ml and 167±13 and 865±32 μg P/ml, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. S. PRASAD (Ed.), Trace Elements in Human Health and Disease, Vol. 1 and 2, Academic Press, New York, 1976.
E. J. UNDERWOOD, Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, 4th ed., Academic Press, New York, 1977.
D. BEHNE, F. DIEL, Nuclear Activation Techniques in the Life Sciences, Rept. IAEA-SM-157, 1972, p. 41.
E. S. GLADNEY, J. W. OWENS, J. W. STERNER, Anal. Chim. Acta, 104 (1979) 121.
C. Y. LIN, S. C. WU, Radiochem. Radioanal. Lett., 53 (1982) 203.
Z. B. ALFASSI, N. LAVI, Analyst, 109 (1984) 959.
F. GIRARDI, E. SABBIONI, J. Radioanal. Chem., 1 (1968) 169.
S. KNOBL, F. LUX, T. BEREZNAI, G. BLUMEL, H. REACHL, 9th Intern. Symp. on Microchemical Techniques, Amsterdam, August 28, 1983.
G. V. IYENGAR, W. E. KOLLMER, H. I. M. BOWEN, The Elemental Composition of Human Tissues and Body Fluids, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, New York, 1978, p. 22.
G. V. IYENGAR, Elemental Composition of Human and Animal Milk, IAEA-TECDOC-269.
L. A. CURRIE, Anal. Chem., 40 (1968) 586.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lavi, N., Lux, F. & Alfassi, Z.B. Determination of Mg, Al, P, Cu and Mn in biological fluids by neutron activation analysis. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Articles 129, 93–101 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037572
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037572