Abstract
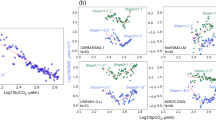
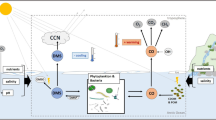
Simultaneous measurements of rain acidity and dimethyl sulfide (DMS) at the ocean surface and in the atmosphere were performed at Amsterdam Island over a 4 year period. During the last 2 years, measurements of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in the atmosphere and of methane sulfonic acid (MSA) and non-sea-salt-sulfate (nss-SO4 2-) in rainwater were also performed. Covariations are observed between the oceanic and atmospheric DMS concentrations, atmospheric SO2 concentrations, wet deposition of MSA, nss-SO4 2-, and rain acidity. A comparable summer to winter ratio of DMS and SO2 in the atmosphere and MSA in precipitation were also observed. From the chemical composition of precipitation we estimate that DMS oxidation products contribute approximately 40% of the rain acidity. If we consider the acidity in excess, then DMS oxidation products contribute about 55%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreae, M. O., 1986, The ocean as a source of atmospheric sulfur compounds, in P.Buat-Ménard (ed.), The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling, D. Reidel, Dordrecht, pp. 331–362.
Andreae, M. O. and Raemdock, H., 1983, Dimethyl sulfide in the surface ocean and the marine atmosphere: a global view, Science 221, 744–747.
Ayers, G. P., Ivey, J. P., and Gillett, R. W., 1990, Coherence between seasonal cycles of dimethyl sulphide, methanesulphonate and sulphate in marine air, Nature 349, 404–406.
Ayers, G. P., Ivey, J. P., and Goodman, H. S., 1986, Sulfate and methanesulfonate in the maritime aerosol at Cape Grim, Tasmania, J. Atmos. Chem. 4, 173–185.
Ayers, G. P. and Ivey, J. P., 1990, Methanesulfonate in rainwater at Cape Grim, Tasmania, Tellus 40B, 297–307.
Bates, T. M., Cline, J. D., Gammon, R. H., and Kelly-Hansen, S. R., 1987a, Regional and seasonal variation of the flux of oceanic dimethylsulfide to the atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 2930–2938.
Bates, T. M., Charlson, R. J., and Gammon, R. H., 1987b, Evidence for the climatic role of marine biogenic sulphur, Nature 329, 319–321.
Bates, T. S., Johnson, J. E., Quinn, P. K., Goldan, P. D., Kuster, W. C., Covert, D. C., and Hahn, C. J., 1990, The Biogeochemical sulfur cycle in the marine boundary layer over the northeast Pacific Ocean, J. Atmos. Chem. 10, 59–81.
Belviso, S., Kim, S. K., Rassoulzadegan, F., Krajka, B., Nguyen, B. C., Mihalopoulos, N., and Buat-Ménard, P., 1991, Production of dimethylsulfonium propionate (DMSP) and dimethylsulfide (DMS) by the microbial food web, Limnol. Oceanogr. 35, 1810–1821.
Berresheim, H., Andreae, M. O., Ayers, G. P., Gillett, R. W., Merrill, J. T., Davis, V. J., and Chameides, W. L., 1990, Airborne measurements of dimethylsulfide, sulfur dioxide, and aerosol ions over the Southern Ocean south of Australia, J. Atmos. Chem. 10, 341–370.
Bonsang, B., 1980, Cycle atmosphérique du soufre d'origine marine, PhD Thesis, Université de Picardie.
Bonsang, B., Nguyen, B. C., Gaudry, A., and Lambert, G., 1980, Sulfate enrichment in marine aerosols owing to biogenic gaseous sulfur compounds, J. Geophys. Res. 85, 7410–7416.
Charlson, R. J., Lovelock, J. E., Andreae, M. O., and Warren, S. G., 1987, Oceanic phytoplankton, atmospheric sulphur, cloud albedo and climate: a geophysiological feedback, Nature 326, 655–661.
Dacey, J. W. H. and Wakeham, S. G., 1986, Oceanic dimethylsulfide: production during zooplankton grazing on phytoplankton, Science 233, 1314–1316.
Erickson, D. J. and Duce, R. A., 1988, On the global flux of atmospheric sea salt, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 14079–14088.
Erickson, D. J., Ghan, S. J., and Penner, J. E., 1990, Global ocean to atmosphere dimethylsulfude flux, J. Geophys. Res. 95, 7543–7552.
Galloway, J. N. and Gaudry, A., 1984, The composition of precipitation on Amsterdam island, Indian Ocean, Amtos. Environ. 18, 2649–2656.
Gibson, J. A. E., Garrick, H. R. Burton, H. R., and McTaggart, A. R., 1990, The alga Phaeocystis poucheti and dimethylsulfide in Antarctic coastal waters, Marine Biol. 104, 339–346.
Keene, W. C., Pszenny, A. A. P., Galloway, J. N., and Hawley, M. E., 1986, Seasonal corrections and interpretation of constituent ratios in marine precipitation, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 6647–6658.
Likens, G. E., Keene, W. C., Miller, J. M., and Galloway, J. N., 1987, Chemistry of precipitation from a remote, terrestrial site in Australia, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 13299–13314.
Liss, P. S., 1973, Processes of gas exchange across an air-water interface, Deep Sea Res. 20, 221–238.
Liss, P. S. and Merlivat, L., 1986, in P.Buat-Ménard (ed.), The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling, D. Reidel, Dordrecht, pp. 113–127.
Lovelock, J. E., Maggs, R. J., and Rasmussen, R. A., 1972, Atmospheric dimethylsulfide and the global sulfur cycle, Nature 237, 452–453.
Mihalopoulos, N., Nguyen, B. C., and Belviso, S., 1988, Dimethyl sulfide in the Somali upwelling area, Chem. Geology 70(1/2), 95.
Moody, J. L., Pszenny, A. A. P., Gaudry, A., Keene, W. C., Galloway, J. N., and Polian, G., 1992, Precipitation composition and its variability in the southern Indian Ocean: Amsterdam Island, 1980–1987, J. Geophys. Res. (in press).
Nguyen, B. C., Bonsang, B., and Lambert, G., 1974, The atmospheric concentrations of sulfur dioxide and sulfate aerosols over Antarctica, Subantarctic areas and oceans, Tellus 26, 241–247.
Nguyen, B. C., Gaudry, A., Bonsang, B., and Lambert, G., 1978, Reevaluation of the role of dimethyl sulphide in the sulphur budget, Nature 275, 637–639.
Nguyen, B. C., Bonsang, B., and Gaudry, A., 1983, The role of the ocean in the global atmospheric sulfur cycle, J. Geophys. Res. 88, 10903–10914.
Nguyen, B. C., Belviso, S., Mihalopoulos, N., Gostan, J., and Nival, P., 1988, Dimethylsulfude production during natural phytoplankton blooms, Marine Chem. 24, 133–141.
Nguyen, B. C., Mihalopoulos, N., and Belviso, S., 1990, Seasonal variation of atmospheric dimethylsulfide at Amsterdam Island in the southern Indian Ocean, J. Atmos. Chem. 11, 123–143.
Polian, G., Lambert, G., Ardouin, B., and Jégou, A., 1986, Long range transport of continental radon in subantarctic areas, Tellus 38B, 178–189.
Putaud, J. P., Mihalopoulos, N., Nguyen, B. C., Campin, J. M., and Belviso, S., 1992, Seasonal variations of atmospheric sulfur dioxide and dimethylsulfide concentrations at Amsterdam Island in the Southern Indian Ocean, J. Atmos. Chem., in press.
Pszenny, A. A. P., MacIntyre, F., and Duce, A., 1982, Sea salt and acidity of marine rain on the windward coast of Samoa, Geophys. Res. Lett. 9, 751–754.
Pszenny, A. A. P., Castelle, A. J., Galloway, J. N., and Duce, R. A., 1989, A study of the sulfur cycle in the Antarctic marine boundary layer, J. Geophys. Res. 94, 9818–9830.
Pszenny, A. A. P., 1992, Particle size distributions for methanesulfonate in the tropical Pacific marine boundary layer, J. Atmos. Chem. (in press).
Saltzman, E. S., Savoie, D. L., Zika, R. G., and Prospero, J. M., 1983, Methanesulfonic acid in the marine atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res. 88, 10897–10902.
Shaw, 1983, Bio-controlled thermostasis involving the sulfur cycle, Climatic Change 5, 297–303.
Sievering, H., Boatman, J., Luria, M., and Van Valin, C. C., 1989, Sulfur dry deposition over the western North Atlantic: the role of coarse aerosol particles, Tellus 41B, 338–343.
Sievering, H., Boatman, J., Galloway, J., Keene, W., Kim, Y., Luria, M., and Ray, J., 1991, Heterogeneous sulfur conversion in sea-salt aerosol particles: The role of aerosol water content and size distribution, Atmos. Environ. 25A, 1479–1487.
Toon, O. B., Kasting, J. F., Turco, R. P., and Liu, M. S., 1987, The sulfur cycle in the marine atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 943–963.
Turner, S. M., Malin, G., Liss, P. S., Harbour, D. S., and Holligan, P. M., 1988, The seasonal variation of dimethyl sulfide and dimethylsulfoniumpropionate concentrations in nearshore waters, Limnol. Oceanogr. 33(3), 364–375.
Yu, T. W., 1988, A method for determining equivalent depths of the atmospheric boundary layer over the oceans, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 3655–3661.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, B.C., Mihalopoulos, N., Putaud, J.P. et al. Covariations in oceanic dimethyl sulfide, its oxidation products and rain acidity at Amsterdam Island in the Southern Indian Ocean. J Atmos Chem 15, 39–53 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00053608
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00053608