Abstract
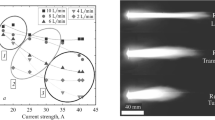
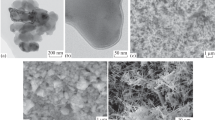
A study was carried out of the induction plasma melting of alumina powders (particle mean diameter, ¯d p=24.5 μm), (Ar/H2 or Ar/N2 plasma, plate power, 40 kW) under reduced pressure conditions (400 torr). The results reveal that in the process, partial vaporization of the alumina powders takes place in the hot region of the discharge. As the molten particles cool down and solidify, the deposits from the vapour phase was formed with the spheroidized particles. In all treatments with the Ar/H2 and Ar/N2 plasmas, a condensate of ultrafine alumina fume (d p<200 nm) was obtained. The fine particles consisted essentially of metastable γ-, δ- and θ-phases. Needle-like crystals(0.1–0.3 μm diameter, by 5–15 μm long) were observed when operating with an Ar/N2 plasma at powder feed rates exceeding 10 g min−1. Electron diffraction analysis revealed that the needles were whiskers, whose structure was very similar to κ- or χ-aluminas with an hexagonal close-packed oxygen lattice. The change of morphology is related to the degree of supersaturation in the vapour phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Ishigaki and M. I. Boulos, Ceram. Trans. 22 (Ceram. Powder Sci. IV), (1991) 139.
P. Proulx, J. Mostaghimi and M. I. Boulos, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 28 (1985) 1327.
Idem Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 7 (1987) 29.
B. Lewis, in “Crystal Growth”, 2nd. Edn edited by B. R. Pamplin (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1980) p. 23.
J. Harvey, H. I. Matthews and H. Wilman, Discuss. Faraday Soc. 30 (1960) 113.
T. I. Barry, R. K. Bayliss and L. A. Lay, J. Mater. Sci. 3 (1968) 229.
M. Kagawa, F. Honda, H. Onodera and T. Nagae, Mater. Res. Bull. 18 (1983) 1081.
K. Wafers and G. M. Bell, “Oxides and Hydroxides of Aluminium”, Technical Paper 19 (Alcoa Research Laboratories, Alcoa Center, PA, 1972).
M. Suzuki, M. Kagawa, Y. Syono and T. Hirai, Ceram. Trans. 22 (Ceram. Powder Sci. IV) (1991) 147.
S. Iijima, Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 23 (1984) L347.
G. Lantagne, B. Marcos and B. Cayrol, Comput. Chem. Eng. 12 (1988) 589.
J. Lothe and G. M. Pound, in “Nucleation”, edited by A. C. Zettlemoyer, (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1969) p. 109.
R. McPherson, J. Mater. Sci. 8 (1973) 851.
ASTM Powder Diffraction File, 10-173 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA).
H. C. Stumpf, A. S. Russerll, J. W. Newsome and C. M. Tucker, Ind. Eng. Chem. 42 (1950) 1398.
H. Saalfeld, N. Jb. Miner. Abh. 95 (1960) 1.
G. W. Brindley and J. O. Choe, Am. Mineral. 46 (1961) 771.
M. Okumiya, G. Yamaguchi, O. Yamada and S. Ono, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 44 (1971) 418.
P. Liu and J. Skogsmo, Acta Crystallogr. B47 (1991) 425.
G. Yamaguchi, H. Yanagida and S. Ono, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 37 (1964) 1555.
G. W. Sears, Acta Metall. 3 (1955) 361.
R. S. Wagner and W. C. Ellis, Appl. Phys. Lett. 4 (1964) 89.
R. S. Wagner and R. G. Treuting, J. Appl. Phys. 33 (1961) 2490.
L. E. Murr, in “Electron Optical Applications in Materials Science” (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1970) pp. 254, 293.
P. B. Hirsch, A. Howie, R. B. Nicholson and D. W. Pashley and M. J. Whwlan, in “Electron Microscopy of Thin Crystals” (Butterworths, London, 1965) p. 98.
S. Vuorinen and J. Skogsmo, Thin Solid Films 193/194 (1990) 536.
J. D. Snow and A. H. Heuer, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 56 (1973) 154.
R. C. DeVries and G. W. Sears, J. Chem. Phys. 31 (1959) 1256.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishigaki, T., Bando, Y., Moriyoshi, Y. et al. Deposition from the vapour phase during induction plasma treatment of alumina powders. JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 28, 4223–4228 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351258
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351258