Abstract
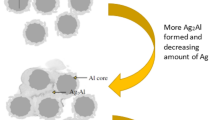
Silver-palladium alloy films were made by a thick-film technique using several metal powders prepared by the spray-pyrolysis method. Two types of powders were used: silver-palladium alloy powders (15 mol % Pd and 30 mol % Pd) and mixtures of silver and palladium powders. The fired films were about 2–3 Μm in thickness. The alloy particles sintered uniformly in firing, whereas, in the case of the powder mixtures, the alloying of silver and palladium particles caused uneven particle growth and large voids were formed in the fired films. For this reason the films made from the alloy powders had better conductive properties than those made from the powder mixtures. The resistivities of the films made from the alloy powders were close to the intrinsic value for silver-palladium alloys. Further, the oxidation of palladium during heating in air was significantly suppressed in the alloy powders when the palladium content was lower than 30 mol % in accordance with thermodynamic considerations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Kato, A. Takayama andY. Morimitsu,Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 1985 (1985) 2342.
K. Nagashima, Y. Morimitsu andA. Kato,Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 1987 (1987) 2293.
K. Nagashima, T. Iwaida, H. Sasaki, Y. Katatae andA. Kato,Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 1990 (1990) 17.
K. Nagashima, Y. Katatae andA. Kato,Funtai Oyobi Funmatsuyakin 36 (1989) 278.
B. R. Coles,J. Inst. Met. 84 (1955–56) 346.
B. Svensson,Annalen der Physik 5 (1932) 699.
G. Yamaguchi, in “Seramikku Kiban to sono Oyo”, edited by T. Ohno (Gakkensha, Tokyo, 1988) p. 247.
Dowa Mining Co. Ltd, andDaiichi Kogyo Seiyaku Co. Ltd, Jpn Kokai Tokkyo Koho Japanese Patent 61 203 503 (1986),Chem. Abstr. 106, 112173x (1987).
Showa Denko K. K., Jpn Kokai Tokkyo Koho Japanese Patent 61 245 405 (1986);Chem. Abstr. 106, 130174c (1987).
S. S. Cole, Jr,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 68 (1985) C-106.
H. Saito, in “Sekiso Seramikku Kondensa”, edited by H. Igarashi (Gakkensha, Tokyo, 1988) p. 60.
R. Hultgren, R. L. Orr, P. D. Anderson andK. K. Kelley, in “Selected Values of Thermodynamic Properties of Metals and Alloys” (John Wiley, New York, 1963) p. 382.
O. Kubaschewski, E. Ll. Evans andC. B. Alcock, in “Metallurgical Thermochemistry”, 4th Edn (Pergamon Press, New York, 1967) p. 427.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagashima, K., Himeda, T. & Kato, A. Properties of conductive films made from fine spherical silver-palladium alloy particles. J Mater Sci 26, 2477–2482 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01130198
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01130198