Abstract
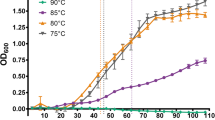
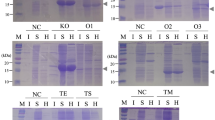
Thermotolerance in cultures of Chlorella zofingiensis was induced by heat shock treatment at supraoptimal temperatures (40and 45 °C for 30 min). Thermotolerance was assayed by two methods: the survival of the cells at 70 °C and the growth of diluted cultures at 35 and 45 °C. A culture without heat shock treatment was unable to grow at 45 °C. According to eletrophoretic analyses, the synthesis of proteins of 95, 73, 60, 43 and 27 kDa was induced by heat shock treatment. The large molecular weight proteins (95, 73, 60 and43 kDa) were present in non-heat treated cells, but the heat shock treatment increased their quantity in cells. The synthesis of a low molecular weight protein (27 kDa) was induced by heat shock treatment. The induced thermotolerance could be inhibited by the presence of an 80S ribosomal translation inhibitor, cycloheximide(CHI). The first 12 amino acid residues from the N-terminus of the27 kDa heat shock induced protein are Val-Glu-Trp-Try-Gly-Pro-Asn-Arg-Ala-Lys-Phe-Leu.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrov VYA (1979) Cell reparation of non-DNA injury. Int. Rev. Cytol. 60: 223–269
Hari V (1981) A method for the two dimensional electrophoresis of leaf proteins. Analyt. Biochem. 113: 332–335.
Kloppstech K, Ohad I, Schweiger A-G (1986) Evidence for an extranuclear coding site for a heat-shock protein in Acetabularia. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 42: 239–245.
Kruger NJ (1994) The Bradford method for protein quantitation. In Walker JM (ed.), Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 32: Basic Protein and Peptide Protocols. Humana Press Inc., Totowa: 17–26.
Larouche L, Tremblay C, Simard C, Bellemare G (1991) Chlorophyll A-B binding protein of LHCII type I precursor. Curr. Genet. 19: 285–288.
Lee YK, Choo CL (1989) The kinetics and mechanism of shear inactivation of lipase from Candida cylindracea. Biotech. Bioengng 33: 183–190.
Lee YK & Low CS (1992) Productivity of outdoor algal cultures in enclosed tubular photobioreactor. Biotech. Bioengng 40: 1119–1122.
Lee YK, Vonshak A (1988) The kinetics of photoinhibition and its recovery in the red alga Porphyridium cruentum. Arch. Microbiol. 150: 529–533.
Mastsudaira P (1987) Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted on to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J. biol. Chem. 262: 10035–10038.
Nover L (1991) Induced thermotolerance. In Nover L (ed.), Heat Shock Response. CRC Press, Florida: 410–412.
Nover L, Scharf KD (1991) Heat shock proteins. In Nover L (ed.), Heat Shock Response. CRC Press, Floride: 75–91.
Schuster, G, Even D, Kloppstech K, Ohad I (1988) Evidence for protection by heat shock proteins against photoinhibition during heat-shock. EMBO J. 7: 1–6.
Wollgiehn R, Neumann D, zur Nieden U, Musch A, Scharf KD, Nover L (1994) Intracellular distribution of small heat shock proteins in cultured cells of Lycopersicon peruvianum. J. Plant Physiol. 144: 491–499.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Lee, Y.K. Thermotolerance induced by heat shock in Chlorella. Journal of Applied Phycology 9, 471–475 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007956507345
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007956507345