Abstract
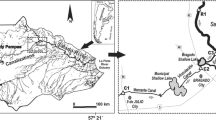
The floodplain of the river Ill in the Alsace Rhine valley is used as a model to study river-groundwater exchange process. Groundwater-fed streams located in the Ill floodplain are analysed using three methods: an analytical method based on hydrochemical variables (Cl− NO3 −, PO 3−4 and NH4 +), a phytosociological one based on surveys of aquatic macrophyte communities and a biological method based on the accumulation of mercury in the moss Fontinalis antipyretica. The results show that the eutrophicated and polluted river Ill (660 µg l−1 N-NH4 +, 500 µg l−1 P-PO 3−4 , 0.3–0.4 mg Hg kg− dry weight of moss) has a negative effect on the groundwater via the bed, depending on the level of the river bed in relation to the groundwater table level. Upstream of Colmar in the south of the Alsace floodplain, the Ill waters infiltrate and contaminate the groundwater, but this is not the case further downstream. Along a stretch of the Ill (40 km) annual floods provide eutrophicated and polluted waters to the aquifer. However these waters are purified during their transfer through the soil-vegetation system. Thus in the groundwater-fed streams the water is characterised by a low level of phosphate, ammonium nitrogen and mercury (10–20 µg l−1 N-NH4 + and P-PO 3−4 , < 0.05 mg Hg kg−1 dry weight of moss). We demonstrate the importance of a functional floodplain in replenishing the aquifer with poor-nutrient waters. The aquatic vegetation of groundwater-fed streams reflects the water quality and thus can be used as a bioindicator and descriptor of river-groundwater exchange process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoros, C, A. L. Roux, J. L. Reygrobellet, J. P. Bravard & G. Pautou, 1987. A method applied ecological studies of fluvial hydrosystems. Regulated rivers 1: 17–36.
Barko, J. W. & M. Smart, 1980. Mobilization of sediment phosphorus by submersed freshwater macrophytes. Freshwat. Biol. 10: 229–238.
Bernard, C., R. Carbiener, A. R. Cloots, R. Froehlicher, C. Schenck & L. Zilliox, 1992. Nitrate pollution of groundwater in the alsatian plain (France) — A multidisciplinary study of an agricultural area: the central Ried of the Ill river. Envir. Geol. Wat. Sci. 20: 125–137.
Bornette, G. & C. Amoros, 1991. Aquatic vegetation and hydrology of a braided river floodplain. J. Vegetat. Sci. 2: 497–512.
Bourg, A. C. M., D. Darmendrail & J. Ricour, 1989. Geochemical filtration of riverbank and migration of heavy metals between the Deûle river and the Ansereuilles alluvion-chalk aquifer (nord, France). Geoderma 44: 229–244.
Bournaud, M. & C. Amoros, 1984. Des indicateurs biologiques aux descripteurs de fonctionnement: quelques exemples dans un système fluvial. Bull. Ecol. 15: 57–66.
Braun-Blanquet, J., 1964. Pflanzensoziologie. Grundzüge der Vegetationskunde, 3rd edn. Springer Verlag, Wien, New York, 543 pp.
Carbiener, R. & W. Krause, 1975. Die Chloridkonzentration in den Gewässern der Oberrheinebene und ihrer Randgebirge. Erdkunde, Archiv für wissenschaftliche Geographie, 29: 267–277.
Carbiener, R. & A. Ortscheit, 1987. Wasserpflanzengesellschaften als Hilfe zur Qualitätsüberwachung eines der grössten Grundwasservorkommen Europas. In A. Miyawaki, A. Bogenrieder, S. Okuda & J. White (eds), Proc. Int. Symp. IAVS, Tokyo-Yokohama, 1984, Tokai University Press: 283–312.
Carbiener, R., M. Trémolières, A. Ortscheit & J. P. Klein, 1988. Les associations végétales biorévélatrices des échanges hydrologiques eaux de surface-eaux souterraines. In H. Kobus & L. Zilliox (eds), ‘Contamination des eaux souterraines par les nitrates, incidences de l'agriculture sur la qualité des eaux souterraines et mesures de protection’, Deutsch-französisches Kolloquium 6 Okt. 1988, Universität Stuttgart et Université Louis Pasteur Strasbourg, 71 Veröff. des Institut für Wasserbau, Universität Stuttgart: 171–200.
Carbiener, R., M. Trémolières, J. L. Mercier & A. Ortscheit, 1990. Aquatic macrophyte communities as bioindicators of eutrophication in calcareous oligosaprobe stream waters (Upper Rhine plain, Alsace). Vegetatio 86: 71–88.
Carbiener, R. & M. Trémolières, 1990. The Rhine rift valley groundwater-river interactions: evolution of their susceptibility to pollution. Regulated rivers: Res. & Mgmt 5: 375–389.
Castella, C. & C. Amoros, 1984. Répartition des Characées dans les bras morts du Haut-Rhône et de l'Ain et signification écologique. Cryptogamie, Algologie 2–3: 127–139.
Castella, E. & C. Amoros, 1988. Freshwater macroinvertebrates as functional describers of the dynamics of former river beds. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol., 23: 1299–1305.
Cloots-Hirsch, A. R., 1987. Echanges nappe-rivières et genèse des inodations dans le Ried central de l'Ill (Alsace): premiers résultats. Actes du colloque ‘crues et inodations’, 16–18 oct. 1986. Strasbourg, Comité national français de géographie, commission d'hydrologie continentale: 47–60.
Décamps, H. & R. J. Naiman, 1989. L'écologie des grands fleuves. La recherche 208: 310–319.
Dister, E., D. Gomer, P. Oberdlik, P. Petermann & E. Schneider, 1990. Water management and ecological perspectives of the upper Rhine's floodplains. Regulated rivers: Res. & Mgmt 5: 1–15.
Esteves, M., 1989. Etude et modélisation des relations aquifère-rivière dans le Ried de Colmar (Haut-Rhin, France). Thèse Université Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, 233 p.
Klein, J. P. & R. Carbiener, 1988. Effects des crues de l'Ill sur les phytocénoses aquatiques de deux rivières phréatiques du secteur de Benfeld et d'Erstein: la Lutter et le Bronnwasser. Intérêt des plantes aquatiques comme bioindicateurs d'eutrophisation. Bull. Ass. Phil. Alsace et Lorraine 24: 3–34.
Klimo, E. & F. Vasicek, 1991. Cycling of elements and some ecological effects of water management measures in the region of floodplain forests of southern Moravia. Laufener Seminarbeiträge, Akad. Natursch. Landschaftpflege (ANL) 4: 93–100.
Klosowski, S., 1985. Habitat requirements and bioindicator value of the main communities of aquatic vegetation in north-east Poland. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 32: 7–29.
Kohler, A., R. Brinkmeier & H. Vollrath, 1974. Verbreitung und Indikatorwert des submersen Makrophyten in Fleissgewässern der Frieberger Au. An. Ber. Bot. Ges. 45: 5–36.
Kohler, A., 1975. Makrophytische Wasserpflanzen als Bioindikatoren für Belastungen von Fliessgewässer-Ökosystemen. Verhandlungen der Umweltschutz Sonderrheihe Umwelttagung 31: 127–139.
Kohler, A., 1982. Wasserpflanzen als Belastungsindikatoren. Dechenia-beihefte (Bonn) 26: 31–42.
Konold, W., O. Schäfer & A. Kohler, 1990. Wasserpflanzen als Bioindikatoren, dargestellt am Beispiel kleinerer Stillgewässer Oberschwabens und der Franche-Comité. Ökologie und Naturschutz 3: 167–180.
Kussmaul, H. & D. Mühlhausen, 1979. Hydrologische und hydrochemische Untersuchungen zur Uferfiltration, Teil III: Veränderungen der Wasserbeschaffenheit durch Uferfiltration und Trinkwasseraufbereitung. Gwf-Wasser/Abwasser 120: 320–329.
Lafont, M. & A. Durbec, 1991. Essai de description biolgique des interactions entre eau de surface et eau souterraine: vulnérabilité d'un aquifère à la pollution d'un fleuve. Annls Limn. 26: 119–126.
Laszlo, F. 1989. Qualität bei der Gewinnung von uferfiltriertem Grundwasser in Ungarn. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 17: 453–463.
Lehotsky, J., 1986. Variations de la qualité des eaux du Danube pendant l'infiltration riveraine. Etude et rapports d'hydrologie. ‘Pollution et protection des aquifères’, ed. UNESCO: 406–419.
Le Roux, E., A. Fehri, J. M. Dorioz & P. Blanc, 1987. Contribution à l'étude des échanges de phosphore entre l'eau et les sédiments dans un système fluvio-lacustre. Sciences de l'eau 6: 97–106.
Lowrance, R. R., R. L. Todd & L. E. Asmussen, 1983. Waterborne nutrient budgets for the riparian zone of an agricultural watershed. Agric. Ecosystem. envir. 10: 371–384.
Manning, P. G., 1989. Iron, phosphorus and lead relationships in suspended sediments from Lake St Clair and the Detroit river. Can. Mineral. 27: 247–255.
Migayrou, J., 1990. Quelques aspects des échanges napperivière dans la plaine d'Alsace. Bull. Soc. Ind. Mulhouse 817: 55–60.
Moeller R. E., J. M. Burkholder & R. G. Wetzel, 1988. Significance of sedimentary phosphorus to a rooted submersed macrophyte (Najas flexilis (Wild.) Rostk. and Schmidt) and its algal epiphytes. Aquat. Bot. 32: 261–281.
Muller, S., 1990. Une séquence de groupements végétaux bioindicateurs d'eutrophisation croissante des cours d'eau faiblement minéralisés des Basses Bosges gréseuses du Nord. C.R. acad. Sci. Paris. 310: 509–514.
Penka, M., M. Vyskot, E. Klimo & F. Vasicek, 1991. Floodplain forest ecosystem. II. After water management measures. Developments in agricultural and managed-forest ecology, 15B, Elsevier ed., 629 p.
Pilleboue E. & J. M. Dorioz, 1986. Mass-balance and transfer mechanisms of phosphorus in a rural watershed of Lac Léman, France. In P. G. Sly (ed.), Sediments and interactions. Springer Verlag: 91–102.
Redshaw, C. J., C. F. Mason, C. R. Hayes & R. D. Roberts, 1990. Factors influencing phosphate exchange across the sediment-water interface of eutrophic reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 192: 233–245.
Roeck, U., M. Trémolières, A. Exinger & R. Carbiener, 1991. Utilisation des mousses aquatiques dans une étude sur le transfert du mercure en tant que descripteur du fonctionnement hydrologique (échanges cours d'eau-nappe) en plaine d'Alsace, Bull. d'Hydroécol. 12: 95–109.
Roweck, H., K. Weiss & A. Kohler, 1986. Zur Verbreitung und Biologie von Potamogeton coloratus und P. polygonifolius in Bayern und Baden-Württemberg. Ber. Bayer. Bot. Ges. 57: 17–52.
Sanchez-Perez, J. M., M. Trémolières & R. Carbiener, 1991a. Une station d'épuration naturelle phosphates et nitrates apportés par les eaux de débordement du Rhin: la forêt alluviale à Frêne et Orme. C. R. Acad. Sc., 312, série III: 395–402.
Sanchez-Perez, J. M., M. Trémolières, A. Schnitzler & R. Carbiener, 1991b. Evolution de le qualité physico-chimique des eaux de la frange superficielle de la nappe phréatique en fonction du cycle saisonnier et des stades de succession des forêts alluviales rhénanes (Querco-Ulmetum). Acta Oecol. 12: 581–601.
Trémolières, M., I. Eglin, U. Roeck & R. Carbiener, 1993. The exchange process between river and groundwater on the central Alsace floodplain (easter France). I. The case of the canalised river Rhine. Hydrobiologia 254: 133–148.
Von Gunten, H. R. & T. P. Kull, 1986. Infiltration of inorganic compounds from the Glatt river, Switzerland, into a groundwater aquifer. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 29: 333–346.
Von Gunten, H. R., G. Karametaxas, U. Krähenbühl, M. Kuslys, R. Giovanoli, E. Hoehn & R. Keil, 1991. Seasonal biogeochemical cycles in river-borne groundwater. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 55: 3597–3609.
Wiegleb, G., 1978. Der soziologische Konnex der 47 häufigsten Makrophyten der Gewässer Mitteleuropas. Vegetatio 38: 165–174.
Wiegleb, G., 1984. A study of habitat conditions of the macrophytic vegetation in selected river systems in western lower Saxony (Fed. Rep. of Germany). Aquat. Bot. 18: 313–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trémolières, M., Roeck, U., Klein, J.P. et al. The exchange process between river and groundwater on the central Alsace floodplain (Eastern France): II. The case of a river with functional floodplain. Hydrobiologia 273, 19–36 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126766
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126766