Abstract
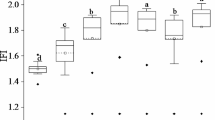
Data from 32 years of a rotation-fertility experiment were analyzed to determine the average P and K application rates required for maximum yield and for optimum yield. A four-year rotation of corn, soybean, wheat, hay was used for the first 10 years and then changed to corn-1, soybean, wheat, corn-2. Rates of P application per 4-year rotation ranged from 0 to 196 kg ha−1 and for K from 0 to 558 kg ha−1. Multiple regression equations were fitted to the mean yields per 4-year rotation for the response of each crop to P and K applications. The range in P application rates in kg of P per 4-year rotation required to get maximum yields of corn was 118 to 172, for soybeans was 134 to 150, and for wheat was 116 to 138. The range in K application rates in kg K per 4-year rotation to get maximum yields of corn was 378 to 411, for soybeans was 324 and 476, and for wheat was 11 to 323. For rates of application where P and K added exceeded crop removals, soil test P and K increased linearly with the cumulative positive balance of P and K. Where crop removal exceeded application rate, no relation was found between crop removal and soil test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber SA (1958) Relation of fertilizer placement to nutrient uptake and crop yield. I. Interaction of row phosphorus and the soil level of phosphorus. Agron J 50: 535–539
Barber SA (1979) Soil phosphorus after 25 years of cropping with five rates of phosphorus application. Com in Soil Sci and Pl Anal 10(11): 1459–1468
Barber SA (1980) Twenty-five years of P and K fertilization of a crop rotation. Fert Res 1: 29–36
Colwell JD (1978) Computations for studies of soil fertility and fertilizer requirements. Commonwealth Agric Bur: Slough, England/CSIRO: Australia
Cope JT (1984) Long-term fertility experiments on cotton, corn, soybean, sorghum and peanuts. Bulletin 561, Alabama
Draycott AP, Durrant MT and Webb DJ (1977) Long-term effects of fertilizers at Broom's Barn, 1971–76. Rothamsted Experimental Station Report for 1977, Part 2: 15–30
Dyke GV, George BJ, Johnston AE, Poulton PR and Todd AD The Broadbalk Wheat Experiment 1968–78. Yield and plant nutrients in crops grown continuously and in rotation. Rothamsted Report for 1982, Part 2: 5–43
Knudsen D (1980) Recommended phosphorus tests. p. 14–16, in: Recommended chemical soil test procedures for the North central region. Bulletin No. 499 (Revised), North Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station, North Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station, North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND
Last PJ, Webb RB, Buff RB, Bean MR, Durrant MJ and Jaggard KW (1984) Long-term effects of fertilizers at Broom's Barn, 1965–82
Odell RT, Walter WM, Boone LV and Oldham MG (1984) The Morrow Plots. Bulletin 775. Agricultural Experiment Station, College of Agriculture, University of Illinois, Urbana, IL
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Journal paper No. 10, 915 Purdue University Agric. Exp. Stn., West Lafayette, IN 47907. Contribution from the Department of Agronomy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, RG., Barber, S. Effect of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on crop response and soil fertility in a long-term experiment. Fertilizer Research 15, 123–136 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01050674
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01050674