Abstract
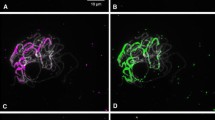
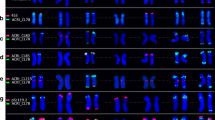
Among cultivated rye, Secale cereale L., collected in Japan, we found an extra heterochromatin on the long-arm interstitial region of chromosome 2R. This extra heterochromatin was polymorphic in the population. The plants with the extra heterochromatin showed a specific DNA fragment of 1.2 kb in digests prepared with the restriction enzyme DraI. The fragment was cloned and used as a probe for fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH). The clone, pScJNK1, showed a hybridization signal at the extra heterochromatic region. The segregation of the number of signals corresponded to the number of the extra heterochromatin of the 2R chromosome, indicating that the sequence might construct the heterochromatin. Southern hybridization using the clone as a probe showed a ladder pattern, suggesting that the sequence was a tandem repeat. Three sequences homologous to pScJNK1 were isolated; these were 1192–1232 bp, 44.7–45.9% in GC content, highly homologous (>93%) with each other, and did not show any significant homology to other sequences in a DNA database. Slot blot hybridization using pScJNK1 as a probe indicated that there were about 4000 copies of the sequence in the haploid genome carrying the extra heterochromatin, whereas less than 20 copies existed in the genome without the heterochromatin. Southern hybridization using MspI and HapII indicated that all of the second cytosine nucleotides in CCGG sites in the sequence were methylated in the extra heterochromatin.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Appels R, Moran LB (1986) Rye heterochromatin. I. Studies on clusters of the major repeating sequence and the identification of a new dispersed repetitive sequence element. Can J Genet Cytol 28: 645-657.
Appels R, Driscoll C, Peacock WJ (1978) Heterochromatin and highly repeated DNA sequences in rye (Secale cereale). Chromosoma 70: 67-89.
Bedbrook JR, Jones J, O'Dell M, Thompson RD, Flavell RB (1980) A molecular description of telomeric heterochromatin in Secale species. Cell 19: 411-419.
Bennett MD, Smith JB (1976) Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 274: 227-274.
Friebe B, Mukai Y, Gill BS (1992) C-banding polymorphisms in several accessions of Triticum tauschii (Aegilops squarrosa). Genome 35: 192-199.
Gill BS, Kimber G (1974) The Giemsa C-banded karyotypes of rye. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71: 1247-1249.
Hansen JC, Ausio J (1992) Chromatin dynamics and the modulation of genetic activity. Trends Biochem Sci 17: 187-191.
Holmquist G (1979) The mechanism of C-banding: depurination and b-elimination. Chromosoma 72: 203-224.
Koo HS, Crothers DM (1988) Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 1763-1767.
Kunze B, Weichenhan D, Virks P, Traut W, Winking H (1996) Copy numbers of a clustered long-range repeat determine C-band staining. Cytogenet Cell Genet 73: 86-91.
McIntyre CL, Pereira S, Moran LB, Appels R (1990) New Secale cereale (rye) DNA derivatives for the detection of rye chromosome segments in wheat. Genome 33: 317-323.
Mukai Y (1996) In situ hybridization. In: Fukui K, Nakayama S, eds. Plant Chromosomes: Laboratory Method. CRC Press, pp. 155-170.
Mukai Y, Friebe B, Gill BS (1992) Comparison of C-banding patterns and in situ hybridization sites using highly repetitive and total genomic rye DNA probes of ‘Imperial’ rye chromosomes added to ‘Chinese Spring’ wheat. Jpn J Genet 67: 71-83.
Murray HG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8: 4321-4325.
Nagaki K, Tsujimoto H, Sasakuma T (1998) Dynamics of tandem repetitive Afa-family sequences in triticeae, wheat-related species. J Mol Evol 38: 479-486.
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1986) Isolation of D-genome specific repeated DNA sequence from Aegilops squarrosa. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4: 102-109.
Rieger R, Michaelis A, Gree MM (1976) Glossary of Genetics and Cytogenetics, Classical and Molecular. Springer-Verlag.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Sandery MJ, Forster EF, Blundern R, Jones RN (1990) Identification of a family of repeated sequence on the rye B chromosome. Genome 33: 908-913.
Sumner AT (1990) Chromosome Banding. London: Unwin Hyman Inc.
Tsujimoto H, Niwa K (1992) DNA structure of the B chromosome of rye revealed by in situ hybridization using repetitive sequences. Jpn J Genet 67: 233-241.
Vershinin AV, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) The large-scale genomic organization of repetitive DNA families at the telomeres of rye chromosomes. Pl J 7: 1823-1833.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagaki, K., Tsujimoto, H. & Sasakuma, T. A novel repetitive sequence, termed the JNK repeat family, located on an extra heterochromatic region of chromosome 2R of Japanese rye. Chromosome Res 7, 95–102 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009226612818
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009226612818