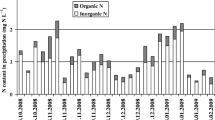
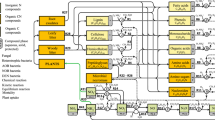
Abstract
Sulphate fluxes in bulk deposition, throughfall and soil solution were monitored during two years, and integrated within a model describing the cycling of S in a chalk grassland ecosystem. Throughfall fluxes were strongly determined by interceptive properties of the grassland canopy. Seasonal variation in Leaf Area Index resulted in dry deposition velocities for SO2 varying between 0.1 cm.s−1 (snow cover, almost no aerodynamic resistance) to 0.9–1.8 cm.s−1 in periods with a fully developed canopy. On an annual basis net canopy exchange (assimilation of SO2 minus foliar leaching) was estimated to be −15% of net throughfall. Simulated soil solution concentrations, being the result of throughfall input, leaching, adsorption, biomass uptake and mineralization, closely fitted actual values (r > 0.92; p > 0.001). Actual and simulated leaching were 1.74 ± 0.03 and 2.00 keq.-ha−1.yr−1, respectively. Sulphur budgets for the soil showed net accumulation from April to October and net losses from October to April. Annual budgets for the ecosystem showed atmospheric input (2.02keq.ha−1.yr−1) and actual output (2.05keq.ha−1.yr−1) to be almost balanced. Apart from increased soil solution concentrations, additional input of sulphate (3.55 keq.ha−1.yr−1) to experimental plots resulted in additional accumulation in the ecosystem of 0.62 keq.ha−1.yr−1
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adema EH, Heeres R & Hulskotte J (1986) On the dry deposition of NH3, SO2 and NO2 on wet surfaces in a small scale windtunnel. Proceedings 7th World Clean Air Congress, Sydney, 25–29 September 1986. Vol. 2: 1–18
Bache DH (1977) Sulphur dioxide uptake and the leaching of sulphates from a pine forest. Journal of Applied Ecology 14: 881–895
Baldocchi DD, Hicks BB & Meyers TP (1988) Measuring biosphere-atmosphere exchanges of biologically related gasses with micrometeorological methods. Ecology 69: 1331–1340
Bobbink R & Willems JH (1987) Increasing dominance of Brachypodium pinnatum (L.) Beauv. in chalk grasslands: a threat to a species-rich ecosystem. Biological Conservation 40: 301–314
Bobbink R, Bik L & Willems JH (1988) Effects of nitrogen fertilization on vegetation structure and dominance of Brachypodium pinnatum (L.) Beauv. in chalk grassland. Acta Botanica Neerlandica 37(2): 231–242
Breemen N van, Burrough PA, Velthorst EJ, van Dobben HF, Toke de Wit, Ridder TB & Reynders HFR (1982) Soil acidification from atmospheric ammonium sulphate in forest canopy throughfall. Nature 299: 548–550
Breemen N van, Visser WFJ & Pape Th (1988) Biogeochemistry of an oak-woodland ecosystem in the Netherlands affected by acid atmospheric deposition. Agricultural Research Reports 930. Pudoc, Wageningen
Bruin HAR de (1987) From Penman to Makkink. T.N.O. Committee on Hydrological Research, ‘Evaporation and Weather’, Proceedings and Informations 39: 5–31
Buysman E, Maas H & Asman W (1984) Een gedetailleerde ammoniakemissiekaart van Nederland. Institute for Meteorology and Oceanography, Utrecht University, The Netherlands. Report V-84-20, 124 pp.
Buysman E, Maas H & Asman W (1985) Ammonia in Europe, Summary report. Institute for Meteorology and Oceanography, Utrecht University, The Netherlands. Report R-85-2
Cape JN, Fowler D, Kinnaird JW, Nicholson IA & Paterson IS (1987) Modification of rainfall chemistry by a forest canopy. In: Coughtrey PJ, Martin PJ & Unsworth MM (Eds) Pollutant Transport and Fate in Ecosystems
Christophersen N & Wright RF (1981) Sulfate budget and a model for sulfate concentrations in stream water at Birkenes, a small forested catchment in southernmost Norway. Water Resources Research 17(2): 377–389
Coughenour MB (1980) Simulation of a grassland sulfur-cycle. Ecological Modelling 9: 179–213
Coughenour MB (1981) Relationships of SO2 dry deposition to a grassland sulfur cycle. Ecological Modelling 13: 1–16
Coughenour MB, Dodd JL, Coleman DC & Lauenroth WK (1979) Partitioning of carbon and SO2-sulfur in a native grassland. Oecologia (Berl.) 42; 229–240
Dam D van, Heil GW & Heijne B (1987) Throughfall chemistry of grassland vegetation; a new method with ion exchange resins. Functional Ecology 1: 423–427
Feddes RA (1987) Crop factors in relation to Makkink reference-crop evapotranspiration. T.N.O. Committee on Hydrological Research, ‘Evaporation and weather’, Proceedings and Informations 39: 33–45
Fowler D (1980) Removal of sulphur and nitrogen compounds from the atmosphere in rain and by dry deposition. In: Drabløs D & Tollan A (Eds) Ecological Impact of Acid Precipitation. SNSF-Project. Ås, Norway
Garten CT Jr, Bondietti EA & Lomax RD (1988) Contribution of foliar leaching and dry deposition to sulfate in net throughfall below deciduous trees. Atmospheric Environment 22(7): 1425–1432
Gilliam FS (1987) The chemistry of wet deposition for a tall-grass prairie ecosystem: inputs and interactions with plant canopies. Biogeochemistry 4: 203–217
Haines B (1983) Forest ecosystem sulfate sulfur input-output discrepancies and acid rain, are they related. Oikos 41(1): 139–143
Heil GW & van Dam D (1986) Vegetation structures and their roughness lengths with respect to atmospheric deposition. Proceedings of the Seventh World Clean Air Congress 1986. International Union of Air Pollution Prevention Associations (IUPPA) Sydney, Australia 25–29 August 1986. Vol. 5: 16–21
Heil GW & Diemont WH (1983) Raised nutrient levels change heathland into grassland. Vegetatio 53: 113–120
Heil GW, Werger MJA, de Mol W, van Dam D & Heijne B (1988) Capture of Atmospheric Ammonium by Grassland Canopies. Science 239: 764–765
Hilhorst MA (1984) A sensor for the determination of the complex permittivity of materials as a measure for the moisture content. Sensors and Actuators: 79–84. Kluwer Technical Books, Deventer, Holland
Johnson DW (1984) Sulphur cycling in forests. Biogeochemistry 1: 29–43
Johnson DW, Henderson GS, Huff DD, Lindberg SE, Richter DD, Shriner DS, Todd DE & Turner J (1982) Cycling of organic and inorganic sulphur in a chestnut oak forest. Oecologia 54: 141–148
Johnson DW, van Miegroet H, Cole DW & Kelly JM (1986) Sulfur cycling in five forest ecosystems. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 30: 965–979
KNMI (1972) Klimaatatlas van Nederland. Staatsuitgeverij, 's-Gravenhage
KNMI (1985–1988) Maandoverzicht van het weer in Nederland 82(10): 85(7): XXX-XXX
Likens GE, Borman FH, Pierce RS, Eaton JS & Johnson NM (1977) Biogeochemistry of a Forested Ecosystem. Springer Verlag, New York
Lindberg SE & Garten Jr CT (1988) Sources of sulphur in forest canopy throughfall. Nature 336: 148–151
Lovett GM & Lindberg SE (1984) Dry deposition and canopy exchange in a mixed-oak forest as determined by analysis of throughfall. Journal of Applied Ecology 21: 1013–1027
Matt DR, McMillen RT, Womack JD & Hicks BB (1987) A comparison of estimated and measured SO2 deposition velocities. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 36: 331–347
Mayer R & Ulrich B (1978) Input of atmospheric sulfur by dry and wet deposition to two Central European forest ecosystems. Atmospheric Environment 12: 375–377
McMahon TA & Denison PJ (1979) Empirical atmospheric deposition parameters — A survey. Atmospheric Environment 13: 571–585
Meiwes KJ & Khanna PK (1981) Distribution and cycling of sulphur in the vegetation of two forest ecosystems in an acid rain environment. Plant and Soil 60(3): 369–375
Parker GG (1983) Throughfall and stemflow in the forest nutrient cycle. Advances in Ecological Research 13: 58–120
Raybould CC, Unsworth MH & Gregory PJ (1977) Sources of sulphur in rain collected below a wheat canopy. Nature 267: 146–147
Reynders HFR, van Staden JJ & Griepink B (1979) Batchwise photometric determination of sulphate in water samples. Fresenius Zeitschrift für Analytische Chemie 298: 156–157
Richter DD, Johnson DW & Todd DE (1983) Atmospheric sulfur deposition, neutralization, and ion leaching in two deciduous forest ecosystems. Journal of Environmental Quality 12(2): 263–270
Schneider T & Bresser AHM (1988) Dutch priority Programm on acidification. National Institute for Public Health and Environmental Protection. Report No. 00-06
Seastedt TR (1985) Canopy interpretation of nitrogen in bulk precipitation by annually burned and unburned tallgrass prairie. Oecologia (Berlin) 66: 88–92
Stednick JD (1982) Sulfur cycling in Douglas-fir on a glacial outwash terrace. Journal of Environmental Quality 11(1): 43–45
Sterman JD (1984) Appropriate summary statistics for evaluating the historical fit of system dynamics models. Dynamica 10: 51–66
Strickland TC & Fitzgerald JW (1984) Formation and mineralization of organic sulfur in forest soils. Biogeochemistry 1: 79–95
Swift MJ, Heal OW & Anderson JM (1979) Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Studies in Biology, Vol. 5. Blackwell, Oxford, 372 pp
Ulrich B, Mayer R & Khanna RK (1979) Deposition von Luftverunreinigungen und ihre Auswirkung in Waldökosystemen in Solling. J.D. Sauerlander's Verlag, Frankfurt A.M.
Ulrich B, Mayer R, Khanna PK & Prenzel J (1987) Ausfilterung aus der Luft von Schwefelverbindungen durch einen Buchenbestand. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung and Bodenkunde 142: 329–335
Willems JH (1982) Phytosociological and geographical survey of Mesobromion communities in Western Europe. Vegetatio 48: 227–240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Dam, D., Heil, G.W., Heijne, B. et al. Atmospheric deposition and sulphur cycling in chalk grasslandA mechanistic model simulating field observations . Biogeochemistry 9, 19–38 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00002715
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00002715