Abstract
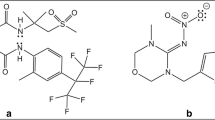
The decomposition of the amidinohydrazone-type insecticide Hydramethylnon (HMN) by soil fungi has been investigated. A simple spectrophotometric method was developed for the estimation of HMN in soil and fungal culture media. HMN was found to be degraded in soil with a half life of 14 to 25 days.
Degradation of HMN by the lignolytic fungus,Phanerochaete chrysosporium yielded two major breakdown products;p-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamic acid (TFCA) andp-(trifluoromethyl)-benzoic acid (TFBA). TFCA was converted to TFBA which was subsequently metabolised via themeta-fission pathway. Fluoride release from HMN could not be detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BzDAc:
-
benzene, dioxane, acetic acid (60: 36: 4)
- DCM:
-
dichloroethane
- DNPH:
-
2,4-dinitro-phenylhydrazine
- HMN:
-
Hydramethylnon
- TDAc:
-
toluene, dioxane, acetic acid (90: 30: 1)
- TFCA:
-
p-(trifluoromethyl)-cinnamic acid
- TFBA:
-
p-(trifluoromethyl)-benzoic acid
- TFP:
-
1,5-bis(trifluoro-p-tolyl)-1,4-pentadien-3-one
- VA:
-
veratryl alcohol
References
Ageorges A, Pelter A & Ward RS (1991) Enzyme catalysed oxidation of non-phenolic aromatic compounds. Phytochem. 30: 121–126
Aitken MD, Venkatadri R & Irvine RL (1989) Oxidation of phenolic pollutants by a lignin degrading enzyme from the white-rot fungusP. chrysosporium. Water Res. 23: 443–450
Aust SD (1990) Degradation of environmental pollutants byP. chrysosporium. Microb. Ecol. 20: 197–209
Bumpus JA, Tien M, Wright D & Aust SD (1985) Oxidation of persistent environmental pollutants by a white rot fungus,P. chrysosporium. Science 228: 1434–1436
Bumpus JA (1989) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons byP. chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 154–158
Bumpus JA & Aust SD (1987) Biodegradation of DDT [1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane] by the white rot fungusP. chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 2001–2008
—— (1990) Biodegradation of environmental pollutants by the white rot fungusP. chrysosporium: involvement of the lignin degrading system. Bioassays 6: 166–170
Bumpus JA & Brock BJ (1988) Biodegradation of crystal violet by the white rot fungusP. chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Micobiol. 54: 1143–1150
Cripps C, Bumpus JA & Aust SD (1990) Biodegradation of azo and heterocyclic dyes byP. chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 1114–1118
Dagley S (1971) Catabolism of aromatic compounds by microorganisms. Adv. Microbiol. Physiol. 6: 1–42
Dosoretz CG, Dass SB, Reddey CA & Grethlein HE (1990) Protease-mediated degradation of lignin in liquid cultures ofP. chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 3429–3434
Dosoretz CG & Grethlein HE (1991) Physiological aspects of the regulation of extracellular enzymes ofP. chrysosporium. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 28: 253–265
Eggling L (1983) Lignin — an exceptional biopolymer ... and a rich resource? Trends in Biotech. 1: 123–127
Fernado T, Aust SD & Bumpus JA (1989) Effects of culture parameters on DDT [1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chloro-phenyl) ethane] biodegradation byP. chrysosporium. Chemosphere 19: 1387–1398
Glenn JK & Gold MH (1983) Decolourization of several polymeric dyes by the lignin-degrading basidiomyceteP. chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45: 1741–1747
Hardman DJ (1991) Biotransformation of halogenated compound. Critical Reviews in Biotechnol. 11: 1–40
Harvey PJ (1986) Recent developments in the understanding of lignin biodegradation. J. Biol. Education 20: 169–174
Hollingshaus JG & Little RJ (1984b) Toxicity, penetration and metabolism of AC 217,300 (AMDRO) in the tobacco budworm (Heliothis virescens) by various methods of application. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 22: 329–336
Kennedy DW, Aust SD & Bumpus JA (1990) Comparative biodegradation of alkyl halide insecticides by the white rot fungusP. chrysosporium (BKM-F-1767). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 2347–2353
Kirk T, Schultz E, Connors WJ, Lorenz LF & Zeikus JG (1978) Influence of culture parameters on lignin metabolism byP. chrysosporium. Arch. Microbiol. 177: 277–285
Kohler A, Jager A, Willershausen H & Graf H (1988) Extracellular ligninase ofP. chrysosporium Burdsall has no role in the degradation of DDT. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech. 29: 618–620
Lamar RT, Glaser JA & Kirk TK (1990a) Fate of pentachlorophenol (PCP) in sterile soils innoculated with the white rot basidiomyceteP. chrysosporium: minerilisation, volatilisation and depletion of PCP. Soil Biol. Biochem. 22: 433–440
Lamar RT, Larsen MS & Kirk TK (1990b) Sensitivity to and degradation of pentachlorophenol byPhanerochaete spp. App. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 3519–3526
Lovell (1979) Proc. 1979 British Crop Protection Conf. Pests and Diseases, pp 572–582
Mallipudi NM, Stout SJ, Lee A & Orloski EJ (1986) Photolysis of Amdro fire ant insecticide active ingredient Hydramethylnon (AC217,300) in distilled water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 34: 1050–1057
Momohara I, Matsumoto Y & Ishizu A (1991) Degradation of a quinone-type model compound byP. chrysosporium and its lignin peroxidase. Mokuzia Gakkaishi. 37: 63–68
Paszcynski A, Pasti MB, Goszczyski S, Crawford DL & Crawford RL (1991) New approach to improve degradation of recalcitrant azo dyes byStreptomyces spp andP. chrysosporium. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 13: 378–384
Pellinen J, Joyce TW & Chang H-M (1988) Dechlorination of high-molecular weight chlorolignin by the white rot fungusP. chrysosporium. TAPPI. 71: 191–194
Platt MW, Hader Y & Chet I (1985) The decolourisation of the polymeric dye Poly-blue (polyvinalamine sulfonate anthroquinone) by lignin degrading fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech. 21: 394–396
Ryan TP & Bumpus JA (1989) Biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid in liquid culture and in soil by the white rot fungusP. chrysosporium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech. 31: 302–307
Smith MR (1991) The biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. Biodegradation 1: 191–206
Spurr EB (1991) Wasp control by poison baiting: experimental use of hydramethylnon in canned sardine bait. Proc. 44th NZ Weed and Pest Control Conference 1991, pp 42–46
Tien M & Kirk TK (1984) Lignin-degrading enzyme fromP. chrysosporium: purification, characterisation and catalytic properties of a unique H2O2 requiring oxygenase. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 2280–2284
Vander-Meer RK, Williams DF & Lofgren CS (1982) Degradation of the toxicant AC 217300 in Amdro imported fire ant bait under field conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 30: 1045–1048
Walker JRL & Bong CL (1981) Metabolism of fluoroacetate by a soilPseudomonas sp andFusarium solani. Soil Biol. Biochem. 13: 231–235
Walker JRL & Taylor BG (1983) Metabolism of phloroglucinol byFusarium solani. Arch. Microbiol. 134: 123–126
Wayne R, Cardaciotto S, Thomson M, Stockton G, Millen W, Conley J, Davis L, Rajan S, Lopata R, Maniara G, Jones M & Wilson L (1988) Physiochemical properties, stability and minor components of Hydramethylnon. Iyakuhin Kenkyu. 19: 966–983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abernethy, G.A., Walker, J.R.L. Degradation of the insecticide Hydramethylnon byPhanerochaete chrysosporium . Biodegradation 4, 131–139 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702330
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702330