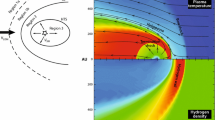
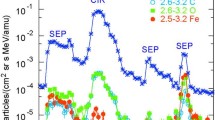
Abstract
The interaction of interstellar pickup ions with the solar wind termination shock is reviewed and assessed. The pickup ions mass and momentum load the wind and increase its pressure, effects which decrease the strength of the shock and its distance from the Sun. The pickup hydrogen may contribute substantially to the "reflected" ion population, which should provide most of the dissipation at the supercritical quasi-perpendicular shock. A fraction of the pickup ions impinging on the shock is "injected" into the process of diffusive shock acceleration to form the anomalous cosmic ray component. An injection mechanism which accounts for the apparent absence of solar wind ions in the anomalous component is "shock surfing", in which pickup ions which approach the shock slowly may be trapped between the upstream Lorentz force and the shock potential and accelerated in the motional electric field beyond the energy threshold for diffusive shock acceleration. However, the simplest interpretation of shock surfing would favor less massive pickup ion species, in contradiction with Voyager observations of anomalous component composition. A possible extension of the shock surfing mechanism is considered, as well as other injection mechanisms. Finally, the pressure of the anomalous component may modify the structure of the termination shock, which in turn may influence injection rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axford, W.I.: 1972, ‘The interaction of the solar wind with the interstellar medium’. Solar Wind, edited by C.P. Sonnet, P.J. Coleman, Jr., and J.M. Wilcox, NASA SP 308, p. 609.
Barnes, A.: 1993, ‘Motion of the heliospheric termination shock: A gas dynamic model’. J. Geophys. Res., 98, 15137.
Bogdan, T.J., M.A. Lee, and P. Schneider: 1991, ‘Coupled quasi-linear wave damping and stochastic acceleration of pickup ions in the solar wind’. J. Geophys. Res., 96, 161.
Chalov, S.V., H.J. Fahr, and V. Izmodenov: 1997, ‘Spectra of energized pick-up ions upstream of the two-dimensional heliospheric termination shock, II, Acceleration by Alfvénic and by large-scale solar wind turbulences’. Astron. Astrophys., 320, 659.
Chassefière, E., J.L. Bertaux, R. Lallement, and V.G. Kurt: 1986, ‘Atomic hydrogen and helium densities of the interstellar medium measured in the vicinity of the Sun’. Astron. Astrophys., 160, 229.
Cummings, A.C., and E.C. Stone: 1996, ‘Composition of anomalous cosmic rays and implications for the heliosphere’. Space Sci. Rev., 78, 117.
Decker, R.B.: 1993, ‘The role of magnetic loops in particle acceleration at nearly perpendicular shocks’. J. Geophys. Res., 98, 33.
Fisk, L.A., B. Kozlovsky, and R. Ramaty: 1974, ‘An interpretation of the observed oxygen and nitrogen enhancements in low-energy cosmic rays’. Astrophys. J., 190, L35.
Geiss, J., G. Gloeckler, and R. von Steiger: 1996, ‘Origin of C+ions in the heliosphere’. Space Sci. Rev., 78, 43.
Giacalone, J., and J.R. Jokipii: 1996, ‘Perpendicular transport in shock acceleration’. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 11.095.
Gloeckler, G.: 1996, ‘The abundance of atomic 1H, 4He and 3He in the local interstellar cloud from pickup ion observations with SWICS on Ulysses’. Space Sci. Rev., 78, 335.
Gloeckler, G., J. Geiss, E.C. Roelof, L.A. Fisk, F.M. Ipavich, K.W. Ogilvie, L.J. Lanzerotti, R. von Steiger, and B. Wilken: 1994, ‘Acceleration of interstellar pickup ions in the disturbed solar wind observed on Ulysses’. J. Geophys. Res., 99, 17,637.
Goodrich, C.C.: 1985, ‘Numerical simulations of quasi-perpendicular collisionless shocks’. in Collisionless Shocks in the Heliosphere: Reviews of Current Research, Geophys. Monogr. Ser., vol. 35, edited by B.T. Tsurutani and R.G. Stone, p. 153, AGU, Washington, D.C.
Holzer, T.E.: 1972, ‘Interaction of the solar wind with the neutral component of the interstellar gas’. J. Geophys. Res., 77, 5407.
Isenberg, P.A.: 1997, ‘A weaker solar wind termination shock’. Geophys. Res. Lett., 24, 623.
Jokipii, J.R.: 1982, ‘Particle drift, diffusion, and acceleration at shocks’. Astrophys. J., 255, 716.
Jokipii, J.R.: 1986, ‘Particle acceleration at a termination shock, I, Application to the solar wind and the anomalous component’. J. Geophys. Res., 91, 2929.
Jokipii, J.R.: 1990, ‘The anomalous component of cosmic rays', in Physics of the Outer Heliosphere, edited by S. Grzedzielski and D.E. Page, p. 169, Pergamon Press, Oxfrod.
Jokipii, J.R., and J. Giacalone: 1996, ‘The acceleration of pickup ions’. Space Sci. Rev., 78, 137.
Jokipii, J.R., and F.B. McDonald: 1995, ‘Quests for the limits of the heliosphere’. Scientific American, 272, 62.
Jokipii, J.R., E.H. Levy, and W.B. Hubbard: 1977, ‘Effects of particle drift on cosmic ray transport, 1, General properties, applications to solar modulation’. Astrophys. J., 213, 861.
Jones, F.C., M.G. Baring, and D.C. Ellison: 1998, ‘The acceleration of pick-up ions at the solar wind termination shock: A non-linear Monte Carlo calculation’. p. 278, in Klccker, B. et al., Anomalous cosmic rays, Space Sci. Rev., 83, 259.
Kennel, C.F., J.P. Edmiston, and T. Hada: 1985, ‘A quarter century of collisionless shock research’. in Collisionless Shocks in the Heliosphere: A Tutorial Review, Geophys. Monogr. Ser., vol. 34, edited by R.G. Stone and B.T. Tsurutani, p. 1, AGU, Washington, D.C.
Ko, C.-M., J.R. Jokipii, and G.M. Webb: 1988, ‘Cosmic-ray-modified stellar winds III. A numerical iterative approach’. Astrophys. J., 326, 761.
Lee, M.A.: 1996, ‘A perturbation calculation of the dynamical effects of cosmic rays and interstellar gas on the solar wind’. in Solar Wind Eight, edited by D. Winterhalter, J.T. Gosling, S.R. Habbal, W.S. Kurth, and M. Neugebauer, p. 658, AIP Conference Proceedings 382, AIP, Woodbury, New York.
Lee, M.A.: 1997, ‘Effects of cosmic rays and interstellar gas on the dynamics of a wind’. in Cosmic Winds and the Heliosphere, edited by J.R. Jokipii, C.P. Sonett, and M.S. Giampapa, p. 857, University of Arizona Press, Tucson.
Lee, M.A., and W.I. Axford: 1988, ‘Model structure of a cosmic-ray mediated stellar or solar wind’. Astron. Astrophys., 194, 297.
Lee, M.A., V.D. Shapiro, and R.Z. Sagdeev: 1996, ‘Pickup ion energization by shock surfing’. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 4777.
Lee, M.A., V.D. Shapiro, and K.B. Quest: 1997, ‘Shock surfing as the pre-energization mechanism at the astrophysical shocks’. Eos Trans. AGU, 78, Fall Meet. Suppl., 544.
Ie Roux, J.A., and H. Fichtner: 1997, ‘The influence of pickup, anomalous, and galactic cosmic-ray protons on the structure of the beliospheric shock: a self-consistent approach’. Astrophys. J., 477, L115.
Ie Roux, J.A., and V.S. Ptuskin: 1998, ‘Self-consistent stochastic preacceleration of interstellar pickup ions in the solar wind including the effects of wave coupling and damping’. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 4799.
Lipatov, A.S., G.P. Zank, and H.L. Pauls: 1997, ‘3D Hybrid simulation of heavy ion acceleration at the collisionless shocks’. Eos Trans. AGU, 78, Spring Meet. Suppl., 259.
Lipatov, A.S., G.P. Zank, and H.L. Pauls: 1998, ‘The acceleration of pickup ions at shock waves: Test particle-mesh simulations’. J. Geophys. Res., in press.
Parker, E.N.: 1963, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, Wiley-Interscience, New York, pp. 113-128.
Parker, E.N.: 1965, The passage of energetic charged particles through interplanetary space, Planet. Space Sci., 13, 9.
Paschmann, G., and N. Sckopke: 1983, ‘Ion reflection and heating at the earth's bow shock’. in Topics of Plasma-, Astro-, and Space Physics, edited by G. Haerendel and B. Battrick, p. 139, Max-Plack-Institut für Physik und Astrophysik, Garching, Federal Republic of Germany.
Pauls, H.L., and G.P. Zank: 1997, ‘Interaction of a nonuniform solar wind with the local interstellar medium. 2. A two-fluid model’. J. Geophys. Res, 102, 19779.
Pesses, M.E., J.R. Jokipii, and D. Eichler: 1981, ‘Cosmic ray drift, shock wave acceleration, and the anomalous component of cosmic rays’. Astrophys. J., 246, L85.
Quémerais, E., J.-L. Bertaux, B.R. Sandel, and R. Lallement: 1994, ‘A new measurement of the interplanetary hydrogen density with ALAE/ATLAS 1’. Astron. Astrophys., 290, 941.
Richardson, J.D., K.I. Paularena, A.J. Lazarus, and J.W. Belcher: 1995, ‘Radial evolution of the solar wind from IMP 8 to Voyager 2', Geophys. Res. Lett., 22, 325.
Sagdeev, R.Z.: 1966, ‘Cooperative phenomena and shock waves in collisionless plasmas’. in Reviews of Plasma Physics, 4, edited by M.A. Leontovich, p. 23, Consultants Bur., New York.
Stone, E.C., A.C. Cummings, and W.R. Webber: 1996, ‘The distance to the solar wind termination shock in 1993 and 1994 from observations of anomalous cosmic rays’. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 11,017.
Story, T.R., and G.P. Zank: 1995, ‘The response of a gasdynamic termination shock to interplanetary disturbances’. J. Geophys. Res., 100, 9489.
van Nes, P., R. Reinhard, T.R. Sanderson, K.-P. Wenzel, and R.D. Zwickl: 1984, ‘The energy spectrum of 35-to 1600-keV protons associated with interplanetary shocks’. J. Geophys. Res., 89, 2122.
Vasyliunas, V.M., and G.L. Siscoe: 1976, ‘On the flux and the energy spectrum of interstellar neutrals in the solar system’. J. Geophys. Res., 81, 1247.
Zank, G.P., H.L. Pauls, I.H. Cairns, and G.M. Webb: 1996, ‘Interstellar pickup ions and quasi-perpendicular shocks: Implications for the termination shock and interplanetary shocks', J. Geophys. Res., 101, 457.
Zilbersher, D., and M. Gedalin: 1997, ‘Pickup ion dynamics at the structured quasiperpendicular shock’. Planet. Space Sci., 45(6), 693.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.A. The Injection, Acceleration, and Dynamical Influence of Interstellar Pickup Ions at the Solar Wind Termination Shock. Astrophysics and Space Science 264, 497–508 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002468119228
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002468119228