Abstract
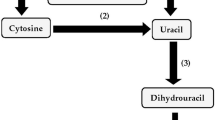
Pyrimidine base and ribonucleoside utilization was investigated in the two type strains of thePseudomonas alcaligenes group. As sole sources of nitrogen, the pyrimidine bases uracil, thymine and cytosine as well as the dihydropyrimidine bases dihydrouracil and dihydrothymine supported the growth ofPseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes ATCC 17440 but neither these bases nor pyrimidine nucleosides supportedPseudomonas alcaligenes ATCC 14909 growth. Ribose, deoxyribose, pyrimidine and dihydropyrimidine bases as well as pyrimidine nucleosides failed to be utilized by eitherP. pseudoalcaligenes orP. alcaligenes as sole carbon sources. The activities of the pyrimidine salvage enzymes nucleoside hydrolase, cytosine deaminase, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase and dihydropyrimidinase were detected in cell-free extracts ofP. pseudoalcaligenes andP. alcaligenes. InP. pseudoalcaligenes, the levels of cytosine deaminase, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase and dihydropyrimidinase could be affected by the nitrogen source present in the culture medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen L, Kilstrup M & Neuhard J (1989) Pyrimidine, purine and nitrogen control of cytosine deaminase synthesis inEscherichia coli K12. Involvement of theglnLG andpurR genes in the regulation ofcodA expression. Arch. Microbiol. 152: 115–118
Ban J, Vitale L & Kos E (1972) Thymine and uracil catabolism inEscherichia coli. J. Gen. Microbiol. 73: 267–272
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of dye-binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254
Chu C-P & West TP (1990) Pyrimidine ribonucleoside catabolism inPseudomonas fluorescens biotype A. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 57: 253–257
Fink K, Cline RE & Fink RM (1963) Paper chromatography of several classes of compounds: correlated Rf values in a variety of solvent systems. Anal. Chem. 35: 389–398
Hunninghake D & Grisolia S (1965) Uracil and thymine reductases. Methods Enzymol. 12A: 50–59
Kelln RA & Warren RAJ (1974) Pyrimidine metabolism inPseudomonas acidovorans. Can. J. Microbiol. 20: 427–433
Kim JM, Shimizu S & Yamada H (1987) Cytosine deaminase that hydrolyzes creatinine to N-methylhydantoin in various cytosine deaminase-forming microorganisms. Arch. Microbiol. 147: 58–63
Kramer J & Kaltwasser H (1969) Verwertung von pyrimidinderivaten durchHydrogenomonas facilis. II. Abbau von thymin und uracil durch wildstamm und mutanten. Arch. Mikrobiol. 69: 138–148
Morin A, Hummel W & Kula M-R (1986) Production of hydantoinase fromPseudomonas fluorescens strain DSM 84. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25: 91–96
O'Donovan GA & Neuhard J (1970) Pyrimidine metabolism in microorganisms. Bacteriol. Rev. 34: 278–343
Ralston-Barrett E, Palleroni NJ & Doudoroff M (1976) Phenotypic characterization and deoxyribonucleic acid homologies of the ‘Pseudomonas alcaligenes’ group. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 26: 421–426
Sakai T, Watanabe T & Chibata I (1968) Metabolism of pyrimidine nucleotides in bacteria. J. Ferment. Technol. 46: 202–213
Sakai T, Yu T & Omata S (1976) Distribution of enzymes related to cytidine degradation in bacteria. Agric. Biol. Chem. 40: 1893–1895
Stanier RY, Palleroni NJ & Doudoroff M (1966) The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J. Gen. Microbiol. 43: 159–271
Vogels GD & van derDrift C (1976) Degradation of purines and pyrimidines by microorganisms. Bacteriol. Rev. 40: 403–468
West TP & O'Donovan GA (1982) Repression of cytosine deaminase by pyrimidines inSalmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 149: 1171–1174
West TP, Shanley MS & O'Donovan GA (1982) Improved colorimetric procedure for quantitating N-carbamoyl-β-alanine with minimum dihydrouracil interference. Anal. Biochem. 122: 345–347
West TP, Traut TW, Shanley MS & O'Donovan GA (1985) ASalmonella typhimurium strain defective in uracil catabolism and β-alanine synthesis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131: 1083–1090
West TP (1989) Isolation and characterization of thymidylate synthetase mutants ofXanthomonas maltophilia. Arch. Microbiol. 151: 220–222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
West, T.P. Pyrimidine base and ribonucleoside utilization by thePseudomonas alcaligenes group. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 59, 263–268 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583679
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00583679