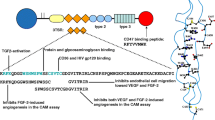
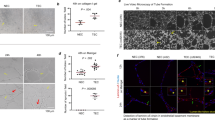
Abstract
Angiogenesis is essential for the growth and metastasis of solid tumors. The balance of endothelial cell (EC) proliferation and apoptosis is a major determinant in tumor angiogenesis. Recently, several studies demonstrated that numerous angiogenic factors not only induce angiogenesis but also function as EC survival factors. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a potent angiogenic factor, is also an EC survival factor in embryonic vasculogenesis and tumor angiogenesis. VEGF activates specific intracellular survival pathways in ECs including Bcl-2, A1, IAP, Akt, and Erk. Integrins may function as EC survival factors by preventing anoikis by enhancing binding to the extracellular matrix. In addition, integrins may function in concert with VEGF to promote EC survival. Angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) has recently been shown to stabilize EC networks by binding to the EC-specific tyrosine kinase receptor Tie-2. Pericytes also function as EC survival factors, by cell-cell contact, secretion of survival factors, or both. Targeting any of the above mechanisms for EC survival may provide novel antineoplastic strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 1971; 285: 1182–1186.
Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1995; 1: 27–31.
Battegay EJ. Angiogenesis: mechanistic insights, neovascular diseases, and therapeutic prospects. J Mol Med 1995; 73: 333–346.
Keck PJ, Hauser SD, Krivi G, et al. Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science 1989; 246: 1309–1312.
Takahashi Y, Cleary KR, Mai M, et al. Significance of vessel count and vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor (KDR) in intestinal-type gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1996; 2: 1679–1684.
Toi M, Kashitani J, Tominaga T. Tumor angiogenesis is an independent prognostic indicator in primary breast carcinoma. Int J Cancer 1993; 55: 371–374.
Macchiarini P, Fontanini G, Hardin MJ, Squartini F, Angeletti CA. Relation of neovascularisation to metastasis of non-smallcell lung cancer. Lancet 1992; 340: 145–146.
Weidner N, Carroll PR, Flax J, Blumenfeld W, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol 1993; 143: 401–409.
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary KR, Ellis LM. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 3964–3968.
Takahashi Y, Tucker SL, Kitadai Y, et al. Vessel counts and VEGF expression as prognostic factors in node-negative colon cancer. Arch Surg 1997; 132: 541–546.
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 1989; 246: 1306–1309.
Plouet J, Schilling J, Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and characterization of a newly identified endothelial cell mitogen produced by AtT-20 cells. EMBO J 1989; 8: 3801–3806.
Berse B, Brown LF, Van de Water L, Dvorak HF, Senger DR. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol Biol Cell 1992; 3: 211–220.
Houck KA, Ferrara N, Winer J, Cachianes G, Li B, LeungDW. The vascular endothelial growth factor family: Identification of a fourth molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol Endocrinol 1991; 5: 1806–1814.
Tischer E, Mitchell R, Hartman T, et al. The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor. Multiple protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 11947–11954.
Connolly DT, Heuvelman DM, Nelson R, et al. Tumor vascular permeability factor stimulates endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 1989; 84: 1470–1478.
Wilting J, Christ B, Bokeloh M, Weich HA. In vivo effects of vascular endothelial growth factor on the chicken chorioallantoic membrane. Cell Tissue Res 1993; 274: 163–172.
Alon T, Hemo I, Itin A, Pe'er J, Stone J, Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat Med 1995; 1: 1024–1028.
Benjamin LE, Keshet E. Conditional switching of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in tumors: Induction of endothelial cell shedding and regression of hemangioblastoma-like vessels by VEGF withdrawal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 8761–8766.
Gerber HP, Dixit V, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and A1 in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 13313–13316.
Gerber HP, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 30-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 30336–30343.
Shaheen RM, Davis DW, LiuW, et al. Antiangiogenic therapy targeting the tyrosine kinase receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibits the growth of colon cancer liver metastasis and induces tumor and endothelial cell apoptosis. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 5412–5416.
Bruns CJ, Liu W, Shaheen RM, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is an in vivo survival factor for tumor endothelium in a murine model of colorectal liver metastases. Cancer 2000; 89: 488–499.
Gupta K, Kshirsagar S, Li W, et al. VEGF prevents apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells via opposing effects on MAPK/ERK and SAPK/JNK signaling. Exp Cell Res 1999; 247: 495–504.
Watanabe Y, Dvorak HF. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits anchorage-disruptioninduced apoptosis in microvessel endothelial cells by inducing W. Liu et al. scaffold formation. Exp Cell Res 1997; 233: 340–349.
LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG, MacKenzie AE. The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene 1998; 17: 3247–3259.
Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteins—suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 239–252.
Tran J, Rak J, Sheehan C, et al. Marked induction of the IAP family antiapoptotic proteins survivin and XIAP by VEGF in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 264: 781–788.
Horrevoets AJ, Fontijn RD, van Zonneveld AJ, de Vries CJ, ten Cate JW, Pannekoek H. Vascular endothelial genes that are responsive to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in vitro are expressed in atherosclerotic lesions, including inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1, stannin, and two novel genes. Blood 1999; 93: 3418–3431.
O'Connor DS, Schechner JS, Adida C, et al. Control of apoptosis during angiogenesis by survivin expression in endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 2000; 156: 393–398.
Leenders WP. Targetting VEGF in anti-angiogenic and antitumour therapy: where are we now? Int J Exp Pathol 1998; 79: 339–346.
Rosen L. Antiagiogenic strategies and agents in clinical trials. The Oncologist 2000; 5(suppl 1): 20–27.
Nor JE, Polverini PJ. Role of endothelial cell survival and death signals in angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 1999; 3: 101–116.
Fong TA, Shawver LK, Sun L, et al. SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types. Can Res 1999; 59: 99–106.
Partanen J, Armstrong E, Makela TP, et al. A novel endothelial cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase with extracellular epidermal growth factor homology domains. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12: 1698–1707.
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, et al. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 1996; 87: 1171–180.
Kwak HJ, So J-N, Lee SJ, Kim I, Koh GY. Angiopoietin-1 is an apoptosis survival factor for endothelial cells. FEBS Lett 1999; 448: 249–53.
Papapetropoulos A, Garcia-Cardena G, Dengler TJ, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD, Sessa WC. Direct actions of angiopoietin-1 on human endothelium: Evidence for network stabilization, cell survival, and interaction with other angiogenic growth factors. Lab Invest 1999; 79: 213–223.
Papapetropoulos A, Fulton D, Mahboubi K, et al. Angiopoietin-1 inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis via the Akt/survivin pathway. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 9102–9105.
Holash J, Maisonpierre PC, Compton D, et al. Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Science 1999; 284: 1994–1998.
Lin P, Polverini P, Dewhirst M, Shan S, Rao PS, Peters K. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis using a soluble receptor establishes a role for Tie2 in pathologic vascular growth. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 2072–2078.
Lin P, Buxton JA, Acheson A, et al. Antiangiogenic gene therapy targeting the endothelium-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 8829–8834.
Hynes RO. Integrins: Versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 1992; 69: 11–15.
Meredith JE, Jr, Fazeli B, Schwartz MA. The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol Biol Cell 1993; 4: 953–961.
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M, et al. Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 1994; 79: 1157–1164.
Frisch SM, Francis H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1994; 124: 619–626.
Brooks PC, Stromblad S, Klemke R, Visscher D, Sarkar FH, Cheresh DA. Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 1815–1822.
Stromblad S, Becker JC, Yebra M, Brooks PC, Cheresh DA. Suppression of p53 activity and p21WAF1/CIP1 expression by vascular cell integrin alphaVbeta3 during angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 1996; 98: 426–433.
Petitclerc E, Stromblad S, von Schalscha TL, et al. Integrin alpha(v)beta3 promotes M21 melanoma growth in human skin by regulating tumor cell survival. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2724–2730.
Eliceiri BP, Cheresh DA. The role of alphav integrins during angiogenesis: insights into potential mechanisms of action and clinical development. J Clin Invest 1999; 103: 1227–1230.
Benjamin LE, Hemo I, Keshet E. A plasticity window for blood vessel remodelling is defined by pericyte coverage of the preformed endothelial network and is regulated by PDGF-B and VEGF. Development 1998; 125: 1591–1598.
Thomas WE. Brain macrophages: On the role of pericytes and perivascular cells. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 1999; 31: 42–57.
Hirschi KK, D'Amore PA. Pericytes in the microvasculature. Cardiovas Res 1996; 32: 687–698.
Nehls V, Denzer K, Drenckhahn D. Pericyte involvement in capillary sprouting during angiogenesis in situ. Cell Tissue Res 1992; 270: 469–474.
Nicosia RF, Villaschi S. Rat aortic smooth muscle cells become pericytes during angiogenesis in vitro. Lab Invest 1995; 73: 658–666.
D'Amore PA. Capillary growth: A two-cell system. Sem Cancer Biol 1992; 3: 49–56.
Hirschi KK, Rohovsky SA, D'Amore PA. PDGF, TGF-beta, and heterotypic cell-cell interactions mediate endothelial cellinduced recruitment of 10T1/2 cells and their differentiation to a smooth muscle fate. J Cell Biol 1998; 141: 805–814. [Published erratum appears in J Cell Biol 1998; 141: 12871]
Lindahl P, Johansson BR, Leveen P, Betsholtz C. Pericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice. Science 1997; 277: 242–245.
Hellstrom M, Kal n M, Lindahl P, Abramsson A, Betsholtz C. Role of PDGF-B and PDGFR-beta in recruitment of vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes during embryonic blood vessel formation in the mouse. Development 1999; 126: 3047–3055.
Eberhard A, Kahlert S, Goede V, Hemmerlein B, Plate KH, Augustin HG. Heterogeneity of angiogenesis and blood vessel maturation in human tumors: Implications for antiangiogenic tumor therapies. Can Res 2000; 60: 1388–1393.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Ahmad, S.A., Reinmuth, N. et al. Endothelial cell survival and apoptosis in the tumor vasculature. Apoptosis 5, 323–328 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009679307513
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009679307513