Abstract
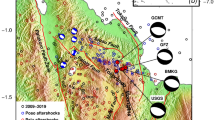
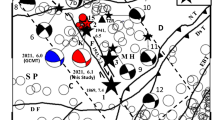
TheM s =6.9 Gonghe, China, earthquake of April 26, 1990 is the largest earthquake to have been documented historically as well as recorded instrumentally in the northeastern Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) plateau. The source process of this earthquake and the tectonic stress field in the northeastern Qinghai-Xizang plateau are investigated using geodetic and seismic data. The leveling data are used to invert the focal mechanism, the shape of the slipped region and the slip distribution on the fault plane. It is obtained through inversion of the leveling data that this earthquake was caused by a mainly reverse dip-slipping buried fault with strike 102°, dip 46° to SSW, rake 86° and a seismic moment of 9,4×1018 Nm. The stress drop, strain and energy released for this earthquake are estimated to be 4.9 MPa, 7.4×10−5 and 7.0×1014 J, respectively. The slip distributes in a region slightly deep from NWW to SEE, with two nuclei, i.e., knots with highly concentrated slip, located in a shallower depth in the NWW and a deeper depth in the SEE, respectively.
Broadband body waves data recorded by the China Digital Seismograph Network (CDSN) for the Gonghe earthquake are used to retrieve the source process of the earthquakes. It is found through moment-tensor inversion that theM s =6.9 main shock is a complex rupture process dominated by shear faulting with scalar seismic moment of the best double-couple of 9.4×1018 Nm, which is identical to the seismic moment determined from leveling data. The moment rate tensor functions reveal that this earthquake consists of three consecutive events. The first event, with a scalar seismic moment of 4.7×1018 Nm, occurred between 0–12 s, and has a focal mechanism similar to that inverted from leveling data. The second event, with a smaller seismic moment of 2.1×1018 Nm, occurred between 12–31 s, and has a variable focal mechanism. The third event, with a sealar seismic moment of 2.5×1018 Nm, occurred between 31–41 s, and has a focal mechanism similar to that inverted from leveling data. The strike of the 1990 Gonghe earthquake, and the significantly reverse dip-slip with minor left-lateral strike-slip motion suggest that the pressure axis of the tectonic stress field in the northeastern Qinghai-Xizang plateau is close to horizontal and oriented NNE to SSW, consistent with the relative collision motion between the Indian and Eurasian plates. The predominant thrust mechanism and the complexity in the tempo-spatial rupture process of the Gonghe earthquake, as revealed by the geodetic and seismic data, is generally consistent with the overall distribution of isoseismals, aftershock seismicity and the geometry of intersecting faults structure in the Gonghe basin of the northeastern Qinghai-Xizang plateau.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avouac, J. P., andTapponnier, P. (1993),Kinematic Model of Active Deformation in Central Asia, Geophys. Res. Lett.20, 895–898.
Chen, Y. T., Lin, B. H., Lin, Z. Y., andLi, Z. Y. (1975),The Focal Mechanism of the 1966 Hsingtai Earthquake as Inferred from the Ground Deformation Observations, Acta Geophysica Sinica18, 164–182 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen, Y. T., Lin, B. H., Wang, X. H., Huang, L. R., andLiu, M. L. (1979),A Dislocation Model of the Tangshan Earthquake of 1976 from the Inversion of Geodetic Data, Acta Geophysica Sinica22, 201–217 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Dreger, D. S. (1994),Investigation of the Rupture Process of the 28th June 1992 Landers Earthquake Utilizing TERRA Scope Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.84, 713–724.
Dziewonski, A. M., Ekström, G., Woodhouse, J. H., andZwart, G. (1991),Centroid-moment Tensor Solutions for April–June in 1990, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter.66, 133–143.
Gong, S. W., andGuo, F. Y. (1992),Vertical Ground Deformation in the Earthquake of Gonghe, Qinghai Province, Acta Seismological Sinica (Chinese edition)14, (Supplement), 725–727 (in Chinese).
Gong, S. W., Wang, Q. L., andLin, J. H. (1993),Study of Dislocation Model and Evolution Characteristics of Vertical Displacement Field of Gonghe M S =6.9 Earthquake, Acta Seismologica Sinica (English edition)6, (3), 641–648.
Hartzell, S., andIida, M. (1990),Source Complexity of the 1987 Whittier Narrows, California, Earthquake from the Inversion of Strong Motion Records, J. Geophys. Res.98, (B12), 22123–22134.
Institute of Geology, State Seismological Bureau (ed.),Seismotectonic Map of Asia and Europe (China Cartography Press, Beijing 1981) (in Chinese).
Kanamori, H., andAnderson, D. L. (1975),Theoretical Basis of Some Empirical Relations in Seismology, Bull Seismol. Soc. Am.65, 1073–1095.
Kennett, B. L. N.,Seismic Wave Propagation in Stratified Media (Cambridge University Press, 1983), 342 pp.
Mansinha, L., andSmylie, D. E. (1971),The Displacement Fields of Inclined Faults, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.61, 1433–1400.
Ma, X. Y. (ed.),Outlines of Lithospheric Dynamics of China (Seismological Press, Beijing, 1987) (in Chinese).
Person, W. J. (1991),Seismological Notes—March–April 1990, Bull. Seismol. Soc. am.81, 297–302.
Tu, D. L. (1990),Geological Structure Background of Gonghe Earthquake M S =6.9, on April 26, 1990, Plateau Earthq. Res.2 (3), 15–20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Velasco, A. A., Ammon, C. J., andLay, T. (1994),Empirical Green Function Deconvolution of Broadband Surface Waves: Rupture Directivity of the 1992 Landers, California (M w =7.3) Earthquake, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.84 (3), 735–750.
Ward, S. N., andBarrientos, S. (1986),An Inversion for Slip Distribution and Fault Shape from Geodetic Observations of the 1983, Borah Peak, Idaho, Earthquake, J. Geophys. Res.,91, 4909–4919.
Xu, Z. H., Wang, S. Y., Huang, Y. R., andGao, A. J. (1992),Tectonic Stress Field of China Inferred from a Large Number of Small Earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res.97, (B8), 11867–11877.
Zhao, M., Chen, Y. T., Gong, S. W., andWang, Q. L. (1993),Inversion of focal mechanism of the Gonghe, China, Earthquake of April 26, 1990, using leveling data. InContinental Earthquakes (eds. Ding, G. Y. and Chen Z. L.) IASPEI Publication Series for the IDNDR3, 246–252.
Zeng, Q. S. (1990),Survey of the Earthquake M s 6.9 between Gonghe and Xinghai on April 26, 1990, Plateau Earthq. Res. 2 (3), 3–12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng, R. S. (1991),Seismicity and Earthquake Disaster of Qinghai Province, Plateau Earthq. Res.3, (1), 1–11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng, Q. S. (1995),Earthquake Resistance and Disaster Reduction and Short-impending Prediction of Qinghai Province, Plateau Earthq. Res.7, (1), 42–51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng, R. S., Zhu, J. S., Zhou, B., Ding, Z. F., He Z. Q., Zhu, L. R., Luo, X., andSun, W. G. (1993),Three-dimensional Seismic Velocity Structure of the Tibetan Plateau and its Eastern Neighboring Areas with Implications to the Model of Collision between Continents, Acta Seismologica Sinica (English edition)6, (2), 251–260.
Zeng, R. S., andSun, W. G. (1993),Seismicity and Focal Mechanism in Tibetan Plateau and its Implications to Lithospheric Flow, Acta Seismologica Sinica, (English edition)6, (2), 261–287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 96 B0006 Institute of Geophysics, State Seismological Bureau, Beijing, China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y.T., Xu, L.S., Li, X. et al. Source process of the 1990 Gonghe, China, earthquake and tectonic stress field in the northeastern Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) plateau. PAGEOPH 146, 697–715 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00874741
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00874741