Abstract
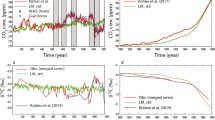
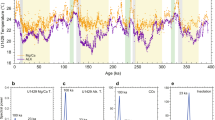
Changes of atmospheric CO2 concentration since 1958 are shown to be related to sea surface temperature changes. The largest contribution to changes arises from the Pacific equatorial upwelling region, with the Indian Ocean and Atlantic contributing only small fractions to the variance. It is hypothesized that the observed relationship is related to the nutrients that are brought up by upwelling cold water, with photosynthesis contributing to a lowering of the partial pressure of CO2 in the sea and thus to a greater tendency for a flux from the air to the sea.
Possible longer term variations of sea temperature and CO2 are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angell, J. K. andKorshover, J. (1975),Estimate of the global change in tropospheric temperature between 1958 and 1973, Mon. Wea. Rev.103, 1007–1012.
Bacastow, R. B. (1976),Modulation of atmospheric carbon dioxide by the southern oscillation, Nature261, 116–118.
Baes, C. F., Jr.,Goeller, H. E., Olson, J. S. andRotty, R. M. (1977),Carbon dioxide and climate: the uncontrolled experiment, Am. Sci.65, 310–320.
Bathen, K. H. (1970),Seasonal changes in the heat storage and depth of the mixed layer in the North Pacific Ocean, Rept. HIG-70-17, Hawaii Institute of Geophysics, University of Hawaii, 23 pp.
Broecker, W. S.,Chemical Oceanography (Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich, New York 1974), 214 pp.
Broecker, W. S. andPeng, T. H. (1974),Gas exchange rates between air and sea, Tellus26, 21–35.
Budyko, M. (1977),On present-day climatic changes, Tellus29, 193–204.
Bunt, A. B.,Primary Productivity of the Biosphere, Ecological Studies No. 14 (eds. H. Lieth and R. H. Whittaker), (Springer Verlag, New York 1975), pp. 169–183.
Climap (1976),The surface of the ice-age earth, Science191, 1131–1137.
Crutcher, H. L. andDavis, O. M.,Marine Climatic Atlas of the World, Vol. VIII (Naval Weather Service Command, 1969).
Essenwanger, O.,Applied Statistics in Atmospheric Science, Part A, Frequencies and Curve Fitting (Elsevier, Amsterdam 1976).
Junge, C. E. andCzeplak, G. (1968),Some aspects of the seasonal variation of carbon dioxide and ozone, Tellus20, 422–434.
Keeling, C. D. (1968),Carbon dioxide in surface ocean waters, 4. Global distribution, J. Geophys. Res.73, 4543–4553.
Liss, P. S. andSlater, P. G. (1974),Flux of gases across the air-sea interface, Nature,247, 181–184.
Mitchell, J. M., Jr.,A preliminary evaluation of atmospheric pollution as a cause of the global temperature fluctuation of the past century, inGlobal Effects of Environmental Pollution (S. F. Singer, ed.), (Springer-Verlag, New York 1970), pp. 139–155.
Newell, R. E. (1974),Changes in the poleward energy flux by the atmosphere and ocean as a possible cause for ice ages, Quat. Res.4, 117–127.
Newell, R. E. andWeare, B. C. (1976),Factors governing tropospheric mean temperature, Science194, 1413–1414.
Newell, R. E. andWeare, B. C. (1977),A relationship between atmospheric carbon dioxide and Pacific sea surface temperature, Geophys. Res. Letters4, 1–2.
Oeschger, H., Siegenthaler, V., Schotterer, V. andGugelmann, A. (1975),A box diffusion model to study the carbon dioxide exchange in nature, Tellus27, 168–192.
Street, F. A. andGrove, A. T. (1976),Environmental and climatic implications of late Quaternary lake-level fluctuations in Africa, Nature261, 385–390.
Walker, G. T. andBliss, E. W. (1932),World Weather V, Mem. Royal Meteor. Soc. 4: 36, 53–84.
Weare, B. C., Navato, A. R. andNewell, R. E. (1976),Empirical orthogonal analysis of Pacific sea surface temperatures, J. Phys. Oceanog.6, 671–678.
Weare, B. C. (1977),Empirical orthogonal analysis of Atlantic Ocean surface temperatures, Q. J. Roy. Met. Soc.103, 467–478.
Wright, P. B. (1975),An index of the Southern Oscillation, Report CRV RP4, Climatic Research Unit, University of Norwich, 19 pp.
Zuta, S. andUrquizo, W. (1972),Temperature promedio de la superficio del mar frente a la costa Peruana, periodo 1928–1969, Inst. del Mar del Peru, Boletin 2: 8, 459–520.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newell, R.E., Navato, A.R. & Hsiung, J. Long-term global sea surface temperature fluctuations and their possible influence on atmospheric CO2 concentrations. PAGEOPH 116, 351–371 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01636891
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01636891