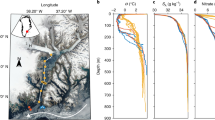
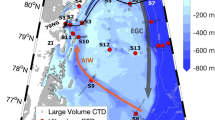
Abstract
Recent work has shown that glaciers are a globally significant source of the micronutrient Fe to the ocean. Polar regions are particularly susceptible to climate change and have been subject to pronounced warming in the past few decades. In response to this warming, the volume of glacial meltwater runoff from Greenland has increased. This meltwater has a relatively high particulate and dissolved Fe content. Seasonal Fe limitation of marine ecosystems has been found in parts of the North Atlantic, so it has been proposed that increasing fluxes of Fe rich meltwater from Greenland to the North Atlantic could alleviate this Fe limitation and thereby increase marine primary production. However, here we use a synthesis of biogeochemical and physical oceanography studies to suggest that the physical circulation around Greenland does not favour direct export of dissolved or particulate Fe from inshore to offshore waters. The Fe budget in surface waters of the North Atlantic may therefore be insensitive to increasing meltwater fluxes from Greenland.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achterberg EP, Moore CM, Henson SA, Steigenberger S, Stohl A, Eckhardt S, Avendano LC, Cassidy M, Hembury D, Klar JK, Lucas MI, Macey AI, Marsay CM, Ryan-Keogh TJ (2013) Natural iron fertilization by the Eyjafjallajokull volcanic eruption. Geophys Res Lett 40(5):921–926
Aguilar-Islas AM, Rember R, Nishino S, Kikuchi T, Itoh M (2013) Partitioning and lateral transport of iron to the Canada Basin. Polar Sci 7(2):82–99
Ardelan MV, Holm-Hansen O, Hewes CD, Reiss CS, Silva NS, Dulaiova H, Steinnes E, Sakshaug E (2010) Natural iron enrichment around the Antarctic Peninsula in the Southern Ocean. Biogeosciences 7(1):11–25
Arendt KE, Nielsen TG, Rysgaard S, Tonnesson K (2010) Differences in plankton community structure along the Godthabsfjord, from the Greenland Ice Sheet to offshore waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 401:49–62
Arendt KE, Dutz J, Jonasdottir SH, Jung-Madsen S, Mortensen J, Moller EF, Nielsen TG (2011) Effects of suspended sediments on copepods feeding in a glacial influenced sub-Arctic fjord. J Plankton Res 33(10):1526–1537
Arendt KE, Juul-Pedersen T, Mortensen J, Blicher ME, Rysgaard S (2013) A 5-year study of seasonal patterns in mesozooplankton community structure in a sub-Arctic fjord reveals dominance of Microsetella norvegica (Crustacea, Copepoda). J Plankton Res 35(1):105–120
Arnalds O, Olafsson H, Dagsson-Waldhauserova P (2014) Quantification of iron-rich volcanogenic dust emissions and deposition over the ocean from Icelandic dust sources. Biogeosciences 11(23):6623–6632
Bacon S, Marshall A, Holliday PN, Aksenov Y, Dye SR (2014) Seasonal variability of the East Greenland Coastal current. J Geophys Res: Oceans 119(6):3967–3987
Bamber J, van den Broeke M, Ettema J, Lenaerts J, Rignot E (2012) Recent large increases in freshwater fluxes from Greenland into the North Atlantic. Geophys Res Lett 39:L19501
Bhatia MP, Kujawinski EB, Das SB, Breier CF, Henderson PB, Charette MA (2013) Greenland meltwater as a significant and potentially bioavailable source of iron to the ocean. Nat Geosci 6(4):274–278
Borrione I, Aumont O, Nielsdottir MC, Schlitzer R (2014) Sedimentary and atmospheric sources of iron around South Georgia, Southern Ocean: a modelling perspective. Biogeosciences 11(7):1981–2001
Box JE, Colgan W (2013) Greenland Ice Sheet mass balance reconstruction. Part III: marine Ice loss and total mass balance (1840–2010). J Clim 26(18):6990–7002
Boyd PW, Watson AJ, Law CS, Abraham ER, Trull T, Murdoch R, Bakker DCE, Bowie AR, Buesseler KO, Chang H, Charette M, Croot P, Downing K, Frew R, Gall M, Hadfield M, Hall J, Harvey M, Jameson G, LaRoche J, Liddicoat M, Ling R, Maldonado MT, McKay RM, Nodder S, Pickmere S, Pridmore R, Rintoul S, Safi K, Sutton P, Strzepek R, Tanneberger K, Turner S, Waite A, Zeldis J (2000) A mesoscale phytoplankton bloom in the polar Southern Ocean stimulated by iron fertilization. Nature 407(6805):695–702
Boyle EA, Edmond JM, Sholkovitz ER (1977) Mechanism of iron removal in estuaries. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 41(9):1313–1324
Bucciarelli E, Blain S, Treguer P (2001) Iron and manganese in the wake of the Kerguelen Islands (Southern Ocean). Mar Chem 73(1):21–36
Buck KN, Sohst B, Sedwick PN (In Press) The organic complexation of dissolved iron along the U.S. GEOTRACES (GA03) North Atlantic Section. Deep Sea Res Part II: Top Stud Oceanogr
Buesseler KO, Doney SC, Karl DM, Boyd PW, Caldeira K, Chai F, Coale KH, de Baar HJW, Falkowski PG, Johnson KS, Lampitt RS, Michaels AF, Naqvi SWA, Smetacek V, Takeda S, Watson AJ (2008) Environment—Ocean iron fertilization—moving forward in a sea of uncertainty. Science 319(5860):162–170
Bullard JE (2013) Contemporary glacigenic inputs to the dust cycle. Earth Surf Proc Land 38(1):71–89
Calbet A, Riisgaard K, Saiz E, Zamora S, Stedmon C, Nielsen TG (2011) Phytoplankton growth and microzooplankton grazing along a sub-Arctic fjord (Godthabsfjord, west Greenland). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 442:11–22
Carrivick JL, Quincey DJ (2014) Progressive increase in number and volume of ice-marginal lakes on the western margin of the Greenland Ice Sheet. Global Planet Change 116:156–163
Chu VW, Smith LC, Rennermalm AK, Forster RR, Box JE (2012) Hydrologic controls on coastal suspended sediment plumes around the Greenland Ice Sheet. Cryosphere 6(1):1–19
Conway TM, John SG (2014) Quantification of dissolved iron sources to the North Atlantic Ocean. Nature 511(7508):212–215
Crusius J, Schroth AW, Gasso S, Moy CM, Levy RC, Gatica M (2011) Glacial flour dust storms in the Gulf of Alaska: hydrologic and meteorological controls and their importance as a source of bioavailable iron. Geophys Res Lett 38:L06602
Cullen JT, Chong M, Ianson D (2009) British Columbian continental shelf as a source of dissolved iron to the subarctic northeast Pacific Ocean. Global Biogeochem Cycles 23(4):GB4012
Dai MH, Martin JM (1995) First data on trace-metal level and behavior in 2 major Arctic river-estuarine systems (Ob and Yenisey) and in the adjacent Kara Sea, Russia. Earth Planet Sci Lett 131(3–4):127–141
de Baar HJW, de Jong JTM, Bakker DCE, Loscher BM, Veth C, Bathmann U, Smetacek V (1995) Importance of iron for plankton blooms and carbon dioxide drawdown in the Southern Ocean. Nature 373:412–415
de Jong J, Schoemann V, Lannuzel D, Croot P, de Baar H, Tison J-L (2012) Natural iron fertilization of the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean by continental shelf sources of the Antarctic Peninsula. J Geophys Res: Biogeosci 117:G01029
Dierssen HM, Smith RC, Vernet M (2002) Glacial meltwater dynamics in coastal waters west of the Antarctic peninsula. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(4):1790–1795
Duce RA, Liss PS, Merrill JT, Atlas EL, Buat-Menard P, Hicks BB, Miller JM, Prospero JM, Arimoto R, Church TM, Ellis W, Galloway JN, Hansen L, Jickells TD, Knap AH, Reinhardt KH, Schneider B, Soudine A, Tokos JJ, Tsunogai S, Wollast R, Zhou M (1991) The atmospheric input of trace species to the world ocean. Global Biogeochem Cycles 5:193–259
Dulaiova H, Ardelan MV, Henderson PB, Charette MA (2009) Shelf-derived iron inputs drive biological productivity in the southern Drake Passage. Global Biogeochem Cycles 23:GB4014
Dziallas C, Grossart HP, Tang KW, Nielsen TG (2013) Distinct communities of free-living and Copepod-associated microorganisms along a salinity gradient in Godthabsfjord, West Greenland. Arct Antarct Alp Res 45(4):471–480
Elrod VA, Berelson WM, Coale KH, Johnson KS (2004) The flux of iron from continental shelf sediments: a missing source for global budgets. Geophys Res Lett 31(12):L12307
Fellman JB, Spencer RGM, Hernes PJ, Edwards RT, D’Amore DV, Hood E (2010) The impact of glacier runoff on the biodegradability and biochemical composition of terrigenous dissolved organic matter in near-shore marine ecosystems. Mar Chem 121(1–4):112–122
Fitzwater SE, Johnson KS, Gordon RM, Coale KH, Smith WO (2000) Trace metal concentrations in the Ross Sea and their relationship with nutrients and phytoplankton growth. Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 47(15–16):3159–3179
Frajka-Williams E, Rhines PB (2010) Physical controls and interannual variability of the Labrador Sea spring phytoplankton bloom in distinct regions. Deep-Sea Res Part I-Oceanogr Res Pap 57(4):541–552
Frants M, Gille ST, Hatta M, Hiscock WT, Kahru M, Measures CI, Mitchell BG, Zhou M (2013) Analysis of horizontal and vertical processes contributing to natural iron supply in the mixed layer in southern Drake Passage. Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 90:68–76
Gerringa LJA, Alderkamp A-C, Laan P, Thuroczy C-E, de Baar HJW, Mills MM, van Dijken GL, van Haren H, Arrigo KR (2012) Iron from melting glaciers fuels the phytoplankton blooms in Amundsen Sea (Southern Ocean): iron biogeochemistry. Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 71–76:16–31
Gordon RM, Johnson KS, Coale KH (1998) The behaviour of iron and other trace elements during the IronEx-I and PlumEx experiments in the equatorial Pacific. Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 45(6):995–1041
Gustafsson O, Widerlund A, Andersson PS, Ingri J, Roos P, Ledin A (2000) Colloid dynamics and transport of major elements through a boreal river—brackish bay mixing zone. Mar Chem 71(1–2):1–21
Hanna E, Huybrechts P, Steffen K, Cappelen J, Huff R, Shuman C, Irvine-Fynn T, Wise S, Griffiths M (2008) Increased runoff from melt from the Greenland Ice Sheet: a response to global warming. J Clim 21(2):331–341
Harden BE, Straneo F, Sutherland DA (2014) Moored observations of synoptic and seasonal variability in the East Greenland Coastal current. J Geophys Res Oceans 119(12):8838–8857
Hawkings JR, Wadham JL, Tranter M, Raiswell R, Benning LG, Statham PJ, Tedstone A, Nienow P, Lee K, Telling J (2014) Ice sheets as a significant source of highly reactive nanoparticulate iron to the oceans. Nat Commun 5:3929
Holliday NP, Waniek JJ, Davidson R, Wilson D, Brown L, Sanders R, Pollard RT, Allen JT (2006) Large-scale physical controls on phytoplankton growth in the Irminger Sea Part I: hydrographic zones, mixing and stratification. J Mar Syst 59(3–4):201–218
Homoky WB, Severmann S, McManus J, Berelson WM, Riedel TE, Statham PJ, Mills RA (2012) Dissolved oxygen and suspended particles regulate the benthic flux of iron from continental margins. Mar Chem 134:59–70
Hong HS, Kester DR (1985) Chemical forms of iron in the Connecticut River estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 21(4):449–459
Hood E, Scott D (2008) Riverine organic matter and nutrients in southeast Alaska affected by glacial coverage. Nat Geosci 1(9):583–587
Hop H, Pearson T, Hegseth EN, Kovacs KM, Wiencke C, Kwasniewski S, Eiane K, Mehlum F, Gulliksen B, Wlodarska-Kowalczuk M, Lydersen C, Weslawski JM, Cochrane S, Gabrielsen GW, Leakey RJG, Lonne OJ, Zajaczkowski M, Falk-Petersen S, Kendall M, Wangberg SA, Bischof K, Voronkov AY, Kovaltchouk NA, Wiktor J, Poltermann M, di Prisco G, Papucci C, Gerland S (2002) The marine ecosystem of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Polar Res 21(1):167–208
Hopwood MJ, Statham PJ, Tranter M, Wadham J (2014) Glacial flours as a potential source of Fe(II) and Fe(III) to polar waters. Biogeochemistry 118(1):443–452
Hudson B, Overeem I, McGrath D, Syvitski JPM, Mikkelsen A, Hasholt B (2014) MODIS observed increase in duration and spatial extent of sediment plumes in Greenland fjords. Cryosphere 8(4):1161–1176
Hyacinthe C, Bonneville S, Van Cappellen P (2006) Reactive iron(III) in sediments: chemical versus microbial extractions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70(16):4166–4180
Jickells TD, Spokes LJ (2001) Atmospheric Iron Inputs to the Oceans. In: Turner DR, Hunter KA (eds) The biogeochemistry of iron in seawater. IUPAC series on analytical and physical chemistry of environmental systems. Wiley, Chichester, pp 85–121
Jickells TD, An ZS, Andersen KK, Baker AR, Bergametti G, Brooks N, Cao JJ, Boyd PW, Duce RA, Hunter KA, Kawahata H, Kubilay N, laRoche J, Liss PS, Mahowald N, Prospero JM, Ridgwell AJ, Tegen I, Torres R (2005) Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate. Science 308(5718):67–71
Johnson KS, Gordon RM, Coale KH (1997) What controls dissolved iron concentrations in the world ocean? Mar Chem 57(3–4):137–161
Juul-Pedersen T, Arendt KE, Mortensen J, Blicher ME, Søgaard DH, Rysgaard S (In Press) Seasonal and interannual phytoplankton production in a sub-arctic tidewater outlet glacier fjord, west Greenland. Mar Ecol Prog Ser
Kjeldsen KK, Mortensen J, Bendtsen J, Petersen D, Lennert K, Rysgaard S (2014) Ice-dammed lake drainage cools and raises surface salinities in a tidewater outlet glacier fjord, west Greenland. J Geophys Res-Earth Surf 119(6):1310–1321
Klunder MB, Bauch D, Laan P, de Baar HJW, van Heuven S, Ober S (2012) Dissolved iron in the Arctic shelf seas and surface waters of the central Arctic Ocean: impact of Arctic river water and ice-melt. J Geophys Res: Oceans 117(C1):C01027
Lam PJ, Bishop JKB (2008) The continental margin is a key source of iron to the HNLC North Pacific Ocean. Geophys Res Lett 35(7):L07608
Lawson EC, Bhatia MP, Wadham JL, Kujawinski EB (2014) Continuous summer export of nitrogen-rich organic matter from the Greenland ice sheet inferred by ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 48(24):14248–14257
Le Moigne FAC, Moore CM, Sanders RJ, Villa-Alfageme M, Steigenberger S, Achterberg EP (2014) Sequestration efficiency in the iron-limited North Atlantic: implications for iron supply mode to fertilized blooms. Geophys Res Lett 41(13):4619–4627
Lippiatt SM, Lohan MC, Bruland KW (2010) The distribution of reactive iron in northern Gulf of Alaska coastal waters. Mar Chem 121(1–4):187–199
Martin JH, Fitzwater SE (1988) Iron deficiency limits phytoplankton growth in the north-east Pacific subarctic. Nature 331:341–343
Martin JH, Fitzwater SE, Gordon RM (1990a) Iron deficiency limits phytoplankton growth in Antarctic waters. Global Biogeochem Cycles 4(1):5–12
Martin JH, Gordon RM, Fitzwater SE (1990b) Iron in Antarctic waters. Nature 345:156–158
Mayer LM (1982a) Aggregation of colloidal iron during estuarine mixing—kinetics, mechanism, and seasonality. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46(12):2527–2535
Mayer LM (1982b) Retention of riverine iron in estuaries. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46(6):1003–1009
Measures CI, Brown MT, Selph KE, Apprill A, Zhou M, Hatta M, Hiscock WT (2013) The influence of shelf processes in delivering dissolved iron to the HNLC waters of the Drake Passage, Antarctica. Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 90:77–88
Mernild SH, Liston GE, Hasholt B, Knudsen NT (2006) Snow distribution and melt modeling for Mittivakkat Glacier, Ammassalik Island, southeast Greenland. J Hydrometeorol 7(4):808–824
Mortensen J, Lennert K, Bendtsen J, Rysgaard S (2011) Heat sources for glacial melt in a sub-Arctic fjord (Godthabsfjord) in contact with the Greenland Ice Sheet. J Geophys Res-Oceans 116:C01013
Mortensen J, Bendtsen J, Motyka RJ, Lennert K, Truffer M, Fahnestock M, Rysgaard S (2013) On the seasonal freshwater stratification in the proximity of fast-flowing tidewater outlet glaciers in a sub-Arctic sill fjord. J Geophys Res-Oceans 118(3):1382–1395
Myers PG, Donnelly C, Ribergaard MH (2009) Structure and variability of the West Greenland current in summer derived from 6 repeat standard sections. Prog Oceanogr 80(1–2):93–112
Nedelec F, Statham PJ, Mowlem M (2007) Processes influencing dissolved iron distributions below the surface at the Atlantic Ocean-Celtic Sea shelf edge. Mar Chem 104(3–4):156–170
Nielsdottir MC, Moore CM, Sanders R, Hinz DJ, Achterberg EP (2009) Iron limitation of the postbloom phytoplankton communities in the Iceland Basin. Global Biogeochem Cycles 23(3):GB3001
Nielsdottir MC, Bibby TS, Moore CM, Hinz DJ, Sanders R, Whitehouse M, Korb R, Achterberg EP (2012) Seasonal and spatial dynamics of iron availability in the Scotia Sea. Mar Chem 130:62–72
Painter SC, Henson SA, Forryan A, Steigenberger S, Klar J, Stinchcombe MC, Rogan N, Baker AR, Achterberg EP, Moore CM (2014) An assessment of the vertical diffusive flux of iron and other nutrients to the surface waters of the subpolar North Atlantic Ocean. Biogeosciences 11(8):2113–2130
Planquette H, Statham PJ, Fones GR, Charette MA, Moore CM, Salter I, Nedelec FH, Taylor SL, French M, Baker AR, Mahowald N, Jickells TD (2007) Dissolved iron in the vicinity of the Crozet Islands, Southern Ocean. Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 54(18–20):1999–2019
Planquette H, Sanders RR, Statham PJ, Morris PJ, Fones GR (2011) Fluxes of particulate iron from the upper ocean around the Crozet Islands: A naturally iron-fertilized environment in the Southern Ocean. Global Biogeochem Cycles 25(2):GB2011
Planquette H, Sherrell RM, Stammerjohn S, Field MP (2013) Particulate iron delivery to the water column of the Amundsen Sea, Antarctica. Mar Chem 153:15–30
Prospero JM, Bullard JE, Hodgkins R (2012) High-latitude dust over the North Atlantic: inputs from icelandic proglacial dust storms. Science 335(6072):1078–1082
Quigg A, Nunnally CC, McInnes AS, Gay S, Rowe GT, Dellapenna TM, Davis RW (2013) Hydrographic and biological controls in two subarctic fjords: an environmental case study of how climate change could impact phytoplankton communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 480:21–37
Raiswell R (2011) Iceberg-hosted nanoparticulate Fe in the Southern Ocean: mineralogy, origin, dissolution kinetics and source of bioavailable Fe. Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 58(11–12):1364–1375
Raiswell R, Canfield DE (2012) The iron biogeochemical cycle past and present. Geochem Perspect 1(1):1–220
Raiswell R, Tranter M, Benning LG, Siegert M, De’ath R, Huybrechts P, Payne T (2006) Contributions from glacially derived sediment to the global iron (oxyhydr)oxide cycle: implications for iron delivery to the oceans. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70(11):2765–2780
Raiswell R, Benning LG, Tranter M, Tulaczyk S (2008) Bioavailable iron in the Southern Ocean: the significance of the iceberg conveyor belt. Geochem Trans 9(7):9
Rijkenberg MJA, Middag R, Laan P, Gerringa LJA, van Aken HM, Schoemann V, de Jong JTM, de Baar HJW (2014) The distribution of dissolved iron in the west atlantic ocean. PLoS One 9(6):e101323–e101323
Ryan-Keogh TJ, Macey AI, Nielsdottir MC, Lucas MI, Steigenberger SS, Stinchcombe MC, Achterberg EP, Bibby TS, Moore CM (2013) Spatial and temporal development of phytoplankton iron stress in relation to bloom dynamics in the high-latitude North Atlantic Ocean. Limnol Oceanogr 58(2):533–545
Rysgaard S, Vang T, Stjernholm M, Rasmussen B, Windelin A, Kiilsholm S (2003) Physical conditions, carbon transport, and climate change impacts in a northeast Greenland fjord. Arct Antarct Alp Res 35(3):301–312
Schroth AW, Crusius J, Sholkovitz ER, Bostick BC (2009) Iron solubility driven by speciation in dust sources to the ocean. Nat Geosci 2(5):337–340
Schroth AW, Crusius J, Campbell RW, Hoyer I (2014) Estuarine removal of glacial iron and implications for iron fluxes to the ocean. Geophys Res Lett 41(11):3951–3958
Severmann S, McManus J, Berelson WM, Hammond DE (2010) The continental shelf benthic iron flux and its isotope composition. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74(14):3984–4004
Shaw TJ, Raiswell R, Hexel CR, Vu HP, Moore WS, Dudgeon R, Smith KL Jr (2011) Input, composition, and potential impact of terrigenous material from free-drifting icebergs in the Weddell Sea. Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 58(11–12):1376–1383
Sholkovitz ER (1978) The flocculation of dissolved Fe, Mn, Al, Cu, Ni, Co and Cd during estuarine mixing. Earth Planet Sci Lett 41(1):77–86
Sholkovitz ER, Boyle EA, Price NB (1978) The removal of dissolved humic acids and iron during estuarine mixing. Earth Planet Sci Lett 40:130–136
Siedlecki SA, Mahadevan A, Archer DE (2012) Mechanism for export of sediment-derived iron in an upwelling regime. Geophys Res Lett 39(3):L03601
Smetacek V, Klaas C, Strass VH, Assmy P, Montresor M, Cisewski B, Savoye N, Webb A, d’Ovidio F, Arrieta JM, Bathmann U, Bellerby R, Berg GM, Croot P, Gonzalez S, Henjes J, Herndl GJ, Hoffmann LJ, Leach H, Losch M, Mills MM, Neill C, Peeken I, Roettgers R, Sachs O, Sauter E, Schmidt MM, Schwarz J, Terbrueggen A, Wolf-Gladrow D (2012) Deep carbon export from a Southern Ocean iron-fertilized diatom bloom. Nature 487(7407):313–319
Statham PJ, Skidmore M, Tranter M (2008) Inputs of glacially derived dissolved and colloidal iron to the coastal ocean and implications for primary productivity. Global Biogeochem Cycles 22(3):GB3013
Straneo F, Heimbach P (2013) North Atlantic warming and the retreat of Greenland’s outlet glaciers. Nature 504(7478):36–43
Straneo F, Hamilton GS, Sutherland DA, Stearns LA, Davidson F, Hammill MO, Stenson GB, Rosing-Asvid A (2010) Rapid circulation of warm subtropical waters in a major glacial fjord in East Greenland. Nat Geosci 3(3):182–186
Sutherland DA, Pickart RS, Jones EP, Azetsu-Scott K, Eert AJ, Olafsson J (2009) Freshwater composition of the waters off southeast Greenland and their link to the Arctic Ocean. J Geophys Res-Oceans 114:C05020
Tang KW, Nielsen TG, Munk P, Mortensen J, Moller EF, Arendt KE, Tonnesson K, Juul-Pedersen T (2011) Metazooplankton community structure, feeding rate estimates, and hydrography in a meltwater-influenced Greenlandic fjord. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 434:77–90
Thuroczy C-E, Alderkamp A-C, Laan P, Gerringa LJA, Mills MM, Van Dijken GL, de Baar HJW, Arrigo KR (2012) Key role of organic complexation of iron in sustaining phytoplankton blooms in the Pine Island and Amundsen Polynyas (Southern Ocean). Deep-Sea Res Part II-Top Stud Oceanogr 71–76:49–60
Treguer PJ (2014) The Southern Ocean silica cycle. CR Geosci 346(11–12):279–286
van der Merwe P, Bowie AR, Quéroué F, Armand L, Blain S, Chever F, Davies D, Dehairs F, Planchon F, Sarthou G, Townsend AT, Trull TW (2015) Sourcing the iron in the naturally fertilised bloom around the Kerguelen Plateau: particulate trace metal dynamics. Biogeosciences 12(3):739–755
Wadley MR, Jickells TD, Heywood KJ (2014) The role of iron sources and transport for Southern Ocean productivity. Deep-Sea Res Part I-Oceanogr Res Pap 87:82–94
Waniek JJ, Holliday NP, Davidson R, Brown L, Henson SA (2005) Freshwater control of onset and species composition of Greenland shelf spring bloom. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 288:45–57
Wu J, Luther GW III (1996) Spatial and temporal distribution of iron in the surface water of the northwestern Atlantic Ocean. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60(15):2729–2741
Acknowledgments
The authors thank two reviewers for constructive comments on the manuscript, the Danish Meteorological Institute for providing satellite images and Kate Davis (Southampton) for Fig. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: R. Kelman Wieder.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hopwood, M.J., Bacon, S., Arendt, K. et al. Glacial meltwater from Greenland is not likely to be an important source of Fe to the North Atlantic. Biogeochemistry 124, 1–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-015-0091-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-015-0091-6