Abstract
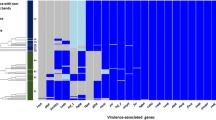
Pasteurella multocida is a leading cause of respiratory disease in pigs worldwide. In this study, we determined the genetic characteristics of 115 P. multocida isolates from the lungs of pigs with respiratory disease in China in 2015 using capsular typing, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) genotyping, and virulence genotyping based on the detection of virulence-associated genes. The results showed that the isolates belonged to three capsular types: A (49.6%), D (46.1%), and nontypable (4.3%); and two LPS genotypes: L3 (22.6%) and L6 (77.4%). When combining the capsular types with the LPS genotypes, a genotype group D: L6 (46.1%) was the most prevalent among the strains. Among the 23 virulence-associated genes detected in this study, a small number of them displayed a certain level of “genotype-preference”. We found that pfhA, hgbA, and hgbB had a close association with P. multocida LPS genotypes, while tadD was more associated with P. multocida capsular types. In addition, multilocus sequence typing (MLST) on 40 P. multocida isolates identified four sequence types: ST3, ST10, ST11, and ST16, and the distribution of ST11 was significantly higher than the other MLST genotypes. Interestingly, all of the ST11 isolates detected in this study were genotype D: L6 strains and they were 100% positive for hgbB. Our data suggest that a capsule/LPS/MLST genotype D/L6/ST11 is likely to be strongly associated with respiratory clinical manifestation of the disease in pigs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bethe A, Wieler LH, Selbitz H-J, Ewers C (2009) Genetic diversity of porcine Pasteurella multocida strains from the respiratory tract of healthy and diseased swine. Vet Microbiol 139:97–105
Choi C, Kim B, Cho W, Kim J, Kwon D, Cheon D, Chae C (2001) Capsular serotype, toxA gene, and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Pasteurella multocida isolated from pigs with pneumonia in Korea. Vet Rec 149:210–212
Davies RL, MacCorquodale R, Baillie S, Caffrey B (2003) Characterization and comparison of Pasteurella multocida strains associated with porcine pneumonia and atrophic rhinitis. J Med Microbiol 52:59–67
Ewers C, Lübke-Becker A, Bethe A, Kießling S, Filter M, Wieler LH (2006) Virulence genotype of Pasteurella multocida strains isolated from different hosts with various disease status. Vet Microbiol 114:304–317
Ferreira TSP et al (2012) Virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Pasteurella multocida strains isolated from rabbits in Brazil. Sci World J 2012:685028
Furian TQ et al (2016) Virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance of Pasteurella multocida isolated from poultry and swine. Braz J Microb 47:210–216
Fussing V, Nielsen J, Bisgaard M, Meyling A (1999) Development of a typing system for epidemiological studies of porcine toxin-producing Pasteurella multocida ssp. multocida in Denmark. Vet Microbiol 65:61–74
García N, Fernández-Garayzábal J, Goyache J, Domínguez L, Vela A (2011) Associations between biovar and virulence factor genes in Pasteurella multocida isolates from pigs in Spain. Vet Rec Engl Ed 169:362
García-Alvarez A, Chaves F, Fernández A, Sanz C, Borobia M, Cid D (2015) An ST11 clone of Pasteurella multocida, widely spread among farmed rabbits in the Iberian Peninsula, demonstrates respiratory niche association infection. Genet Evol 34:81–87
García-Alvarez A, Vela AI, San Martín E, Chaves F, Fernández-Garayzábal JF, Lucas D, Cid D (2017) Characterization of Pasteurella multocida associated with ovine pneumonia using multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) and virulence-associated gene profile analysis and comparison with porcine isolates. Vet Microbiol 204:180–187
Guo D, Zheng M, Pan S (1980) Serological identification of capsular antigens of Pasteurella multocida in China. Collect Pap Vet Res 6:25–36
Harper M, Boyce JD, Adler B (2006) Pasteurella multocida pathogenesis: 125 years after Pasteur. FEMS Microbiol Lett 265:1–10
Harper M et al (2013) Pasteurella multocida Heddleston serovar 3 and 4 strains share a common lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis locus but display both inter-and intrastrain lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity. J Bacteriol 195:4854–4864
Harper M et al (2014) Structural analysis of lipopolysaccharide produced by Heddleston serovars 10, 11, 12 and 15 and the identification of a new Pasteurella multocida lipopolysaccharide outer core biosynthesis locus, L6. Glycobiology 24:649–659
Harper M et al (2015) Development of a rapid multiplex PCR to genotype Pasteurella multocida strains using the lipopolysaccharide outer core biosynthesis locus. J Clin Microbiol 53(2):477–485
Hatfaludi T, Al-Hasani K, Boyce JD, Adler B (2010) Outer membrane proteins of Pasteurella multocida. Vet Microbiol 144:1–17
Heddleston K, Gallagher J, Rebers P (1972) Fowl cholera: gel diffusion precipitin test for serotyping Pasteurella multocida from avian species. Avian Dis 16:925–936
Hotchkiss EJ, Hodgson JC, Lainson FA, Zadoks RN (2011) Multilocus sequence typing of a global collection of Pasteurella multocida isolates from cattle and other host species demonstrates niche association. BMC Microbiol 11:115
James Versalovic KCC, Funke Guido, Jorgensen James H, Landry Marie Louise, Warnock David W (2011) Manual of clinical microbiology, 10th edn. ASM press, Washington DC
Katsuda K, Hoshinoo K, Ueno Y, Kohmoto M, Mikami O (2013) Virulence genes and antimicrobial susceptibility in Pasteurella multocida isolates from calves. Vet Microbiol 167:737–741
Khamesipour F, Momtaz H, Mamoreh MA (2014) Occurrence of virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance in Pasteurella multocida strains isolated from slaughter cattle in Iran. Front Microbiol 5
Kubatzky KF (2012) Pasteurella multocida and immune cells. In: Pasteurella multocida. Springer, pp 53–72
Liang W, Peng Z, Liu W, Xu Z, Chen H, Wu B (2014) Complete genome sequence of P. multocida serotype A strain HB03, isolated from swine. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IPVS congress. Cancun, Mexico: IPVS, p 30
Liu W et al (2012) Complete genome sequence of Pasteurella multocida HN06, a toxigenic strain of serogroup D. J Bacteriol 194:3292–3293
Liu H, Zhao Z, Xi X, Xue Q, Long T, Xue Y (2017) Occurrence of Pasteurella multocida among pigs with respiratory disease in China between 2011 and 2015. Ir Vet J 70:2
Magyar T, Donkó T, Repa I, Kovács M (2013) Regeneration of toxigenic Pasteurella multocida induced severe turbinate atrophy in pigs detected by computed tomography. BMC Vet Res 9:222
May BJ, Zhang Q, Li LL, Paustian ML, Whittam TS, Kapur V (2001) Complete genomic sequence of Pasteurella multocida, Pm70. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:3460–3465
Peng Z et al (2016a) Genomic characterization of Pasteurella multocida HB01, a serotype A bovine isolate from China. Gene 581:85–93
Peng Z, Liang W, Wu B (2016b) Molecular typing methods for Pasteurella multocida-A review. Acta Microbiologica Sinica 56(10):1521–1529
Peng Z et al (2017) Experimental pathogenicity and complete genome characterization of a pig origin Pasteurella multocida serogroup F isolate HN07. Vet Microbiol 198:23–33
Pors SE, Hansen MS, Christensen H, Jensen HE, Petersen A, Bisgaard M (2011) Genetic diversity and associated pathology of Pasteurella multocida isolated from porcine pneumonia. Vet Microbiol 150:354–361
Register K, Brockmeier S, de Jong M, Pijoan C (2012) Pasteurellosis. In: Zimmerman JJ, Karriker AL, Ramirez A, Schwartz JK, Stevenson WG (eds) Diseases of swine, 10th edn. Wiley, West Sussex, pp 2924–2975
Sarangi LN et al (2015) Virulence gene profiling and antibiotic resistance pattern of Indian isolates of Pasteurella multocida of small ruminant origin. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 38:33–39
Tang X, Zhao Z, Hu J, Wu B, Cai X, He Q, Chen H (2009) Isolation, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence genes of Pasteurella multocida strains from swine in China. J Clin Microbiol 47:951–958
Townsend KM, Boyce JD, Chung JY, Frost AJ, Adler B (2001) Genetic organization of Pasteurella multocida cap loci and development of a multiplex capsular PCR typing system. J Clin Microbiol 39:924–929
Wang L, Sun J, Guo D, Cao P, Liu J, Liu C, Liu D, Qu L (2016) Identification of capsule serotype and genotype of Pasteurella multocida in some areas of China. Chinese J Prev Vet Med 38(2):116–119
Wilkie I, Harper M, Boyce J, Adler B (2012) Pasteurella multocida: diseases and pathogenesis. In: Pasteurella multocida. Springer, pp 1–22
Wilson BA, Ho M (2013) Pasteurella multocida: from zoonosis to cellular microbiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 26:631–655
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Special Public Welfare Industry (Agriculture) Research Program Grant 201403054 from the Ministry of Agriculture of China; the National Sci-Tech Support Plan Grant 2015BAD12B04 from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Z., Wang, H., Liang, W. et al. A capsule/lipopolysaccharide/MLST genotype D/L6/ST11 of Pasteurella multocida is likely to be strongly associated with swine respiratory disease in China. Arch Microbiol 200, 107–118 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1421-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1421-y