Abstract.
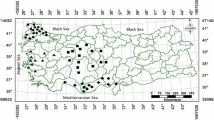
Persistent organochlorine residues such as hexachlorobenzene (HCB), hexachlorocyclohexane isomers (HCHs), chlorocyclodienes, and the DDT group (DDTs) were determined in fat and muscle samples of resident red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa) hunted in Spain. Chlorinated contamination pattern varied largely depending on geographical distribution. Birds collected from the northern part of Spain contained greater concentrations of lindane (34.4 ng/g fat basis) than those from central or southern Spain. In contrast, red-legged partridges collected in southern locations exhibited elevated levels of p,p′-DDE (62.3 ng/g fat basis) as compared with central (31.2 ng/g fat basis) and northern areas (5.6 ng/g fat basis). The only cyclodiene detected, dieldrin, showed higher amounts (3.4 ng/g fat basis) in partridges collected in central Spain. The sex differences in pollutant occurrence and concentrations were negligible. One-year-old birds accumulated greater concentrations of β-HCH, and dieldrin than older birds. Global comparison of organochlorine concentrations indicated that northern partridges are more contaminated by compounds of industrial origin, whereas southern birds contained greater amounts of agricultural chemicals. Estimates of hazards associated with organochlorine levels in resident red-legged partridges in Spain suggested that southern birds may be at risk from exposure to DDTs, and northern birds may be affected by excessive concentrations of lindane. The use of red-legged partridge as bioindicator for OCP contamination is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 January 1999/Accepted: 7 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera, A., Ariño, A., Conchello, M. et al. Red-Legged Partridges (Alectoris rufa) as Bioindicators for Persistent Chlorinated Chemicals in Spain. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 38, 114–120 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449910014
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449910014