Abstract
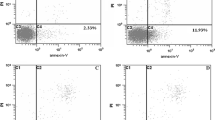
Liver cancer, one of the most common types of cancer in the world, is the second leading cause of death for cancer patients. For liver cancer, there is an urgent need for an effective treatment with no or less toxic side effects. Lactonic sophorolipids (LSL), as a potential anticancer drug, has attracted wide attention of pharmaceutical researchers with its good biological activities. The effects of LSL and cell death inhibitors were measured by MTT test on HepG2 cells. Meanwhile, the morphology of the cells was observed under a microscope. The apoptosis rate was detected by flow cytometry, and the expression levels of enzyme activity of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 were measured by detection kits. Meanwhile, mRNA levels of Apaf-1, Caspase-3, Bax, and Bcl-2 were measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR; protein levels of Caspase-3, Cleaved Caspase-3, Bax, and Bcl-2 were measured by western blot. LSL can inhibit the proliferation of cells, and it is possible to induce apoptosis in cells. The HepG2 cells with LSL co-culture exhibited typical apoptotic morphology, and the expression levels of enzyme activity of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 increased (P< 0.05). We also found that LSL increases cell apoptosis rate and regulates the expression of genes and proteins associated with apoptosis through the Caspase-3 pathway. These results indicate that LSL may be one of the potential drug candidates to inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells.
Key points
• LSL, which is of good biological activities such as anti-bacterium, virus elimination, and inflammatory response elimination, has been firstly used to intervene in vitro to investigate its effect on HepG2 cell proliferation.
• LSL can inhibit the proliferation of cells, and it is possible to induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells through the Caspase-3 pathway.
• The mechanism of LSL action on HepG2 cell proliferation was firstly also discussed, which provides a certain experimental reference for the clinical treatment of liver cancer.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Akiyode O, George D, Getti G, Boateng J (2016) Systematic comparison of the functional physico-chemical characteristics and biocidal activity of microbial derived biosurfactants on blood-derived and breast cancer cells. J Colloid Interface Sci 479:221–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.051
Banjerdpongchai R, Wudtiwai B, Pompimon W (2015) Enterocarpam-III induces human liver and breast cancer cell apoptosis via mitochondrial and Caspase-9 activation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16(5):1833–1837. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.5.1833
Borsanyiova M, Patil A, Mukherji R, Prabhune A, Bopegamage S (2016) Biological activity of sophorolipids and their possible use as antiviral agents. Folia Microbiol 61(1):85–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-015-0413-z
Bruix J, Han KH, Gores G, Llovet JM, Mazzaferro V (2015) Liver cancer: approaching a personalized care. J Hepatol 62(1 Suppl):S144–S156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.007
Callaghan B, Lydon H, Roelants SLKW, Van Bogaert INA, Marchant R, Banat IM, Mitchell CA (2016) Lactonic sophorolipids increase tumor burden in Apcmin+/- Mice. PLoS One 11(6):e0156845. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156845
Chen J, Song X, Zhang H, Qu YB, Miao JY (2006) Sophorolipid produced from the new yeast strain Wickerhamiella domercqiae induces apoptosis in H7402 human liver cancer cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(1):52–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0243-z
Cheng Z, Li XF, Ding J (2016) Characteristics of liver cancer stem cells and clinical correlations. Cancer Lett 379(2):230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.07.041
Colombo M, Maisonneuve P (2017) Controlling liver cancer mortality on a global scale: Still a long way to go. J Hepatol 67(2):216–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.05.004
Huang J, Wu LJ, Tashiro SI, Onodera S, Ikejima T (2005) The augmentation of TNFα-induced cell death in murine L929 fibrosarcoma by the pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-fmk through pre-mitochondrial and MAPK-dependent pathways. Acta Med Okayama 59(6):253–260. https://doi.org/10.18926/AMO/31959
Joshi-Navare K, Shiras A, Prabhune A (2011) Differentiation-inducing ability of sophorolipids of oleic and linoleic acids using a glioma cell line. Biotechnol J 6(5):509–512. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201000345
Kaczanowski S (2016) Apoptosis: its origin, history, maintenance and the medical implications for cancer and aging. Phys Biol 13(3):031001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1478-3975/13/3/031001
Kralovcova D, Pejchalova M, Rudolf E, Cervinka M (2008) Quantitative analysis of expression level of Bcl-2 and Bax genes in HepG2 and HL-60 cells after treatment with etoposide. Acta Med (Hradec Kralove) 51(3):191–195. https://doi.org/10.14712/18059694.2017.23
Li H, Ma XJ, Shao LJ, Shen J, Song X (2012) Enhancement of sophorolipid production of Wickerhamiella domercqiae var. sophorolipid CGMCC 1576 by low-energy ion beam implantation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167(3):510–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9664-1
Li H, Guo W, Ma XJ, Li JS, Song X (2017) In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of sophorolipids to human cervical cancer. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 181(4):1372–1387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2290-6
Liu CY, Chen KF, Chen PJ (2015) Treatment of liver cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 5(9):a021535. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a021535
Liu XG, Ma XJ, Yao RS, Pan CY, He HB (2016) Sophorolipids production from rice straw via SO3 micro-thermal explosion by Wickerhamiella domercqiae var. sophorolipid CGMCC 1576. AMB Express 6(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-016-0227-7
Liu ZF, Liu GD, Liu XW, Li SC (2017) The effects of hyperoside on apoptosis and the expression of Fas/Fasl and survivin in SW579 human thyroid squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Oncol Lett 14(2):2310–2314. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6453
Lydon HL, Baccile N, Callaghan B, Marchant R, Mitchell CA, Banat IM (2017) Adjuvant antibiotic activity of acidic sophorolipids with potential for facilitating wound healing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61(5):e02547–e02516. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02547-16
Ma XJ, Li H, Shao LJ, Shen J, Song X (2011) Effects of nitrogen sources on production and composition of sophorolipids by Wickerhamiella domercqiae var. sophorolipid CGMCC 1576. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(6):1623–1632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3327-y
Ma XJ, Li H, Song X (2012) Surface and biological activity of sophorolipid molecules produced by Wickerhamiella domercqiae var. sophorolipid CGMCC 1576. J Colloid Interface Sci 376(1):165–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.03.007
Naughton PJ, Marchant R, Naughton V, Banat IM (2019) Microbial biosurfactants: current trends and applications in agricultural and biomedical industries. J Appl Microbiol 127(1):12–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14243
Nawale L, Dubey P, Chaudhari B, Sarkar D, Prabhune A (2017) Anti-proliferative effect of novel primary cetyl alcohol derived sophorolipids against human cervical cancer cells HeLa. PLoS One 12(4):e0174241. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174241
Olechowska-Jarzab A, Ptak-Belowska A, Brzozowski T (2016) Terapeutic importance of apoptosis pathways in pancreatic cancer. Folia Med Cracov 56(1):61–70
Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C, Garufi A, D’Orazi G (2016) Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging (Albany NY) 8(4):603–619. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100934
Ribeiro IAC, Faustino CMC, Guerreiro PS, Frade RFM, Bronze MR, Castro MF, Ribeiro MHL (2015) Development of novel sophorolipids with improved cytotoxic activity toward MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J Mol Recognit 28(3):155–165. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2403
Ribeiro IAC, Bronze MR, Castro MF, Ribeiro MHL (2016) Selective recovery of acidic and lactonic sophorolipids from culture broths towards the improvement of their therapeutic potential. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39(12):1825–1837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1657-y
Schramm H, Jaramillo ML, Quadros TD, Zeni EC, Muller YMR, Ammar D, Nazari EM (2017) Effect of UVB radiation exposure in the expression of genes and proteins related to apoptosis in freshwater prawn embryos. Aquat Toxicol 191:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.07.014
Sia D, Villanueva A, Friedman SL, Llovet JM (2017) Liver cancer cell of origin, molecular class, and effects on patient prognosis. Gastroenterology 152(4):745–761. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.048
Sun KW, Ma YY, Guan TP, Xia YJ, Shao CM, Chen LG, Ren YJ, Yao HB, Yang Q, He XJ (2012) Oridonin induces apoptosis in gastric cancer through apaf-1, cytochrome c and Caspase-3 signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 18(48):7166–7174. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7166
Wang ZL, Cui RS, Wang K (2018) Effects of sevoflurane pretreatment on the apoptosis of rat H9c2 cardiomyocytes and the expression of GRP78. Exp Ther Med 15(3):2818–2823. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.5799
Xie DF, Yuan PW, Wang D, Jin H, Chen H (2017) Effects of naringin on the expression of miR-19b and cell apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett 14(2):1455–1459. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6278
You HY, Zhang WJ, Xie XM, Zheng ZH, Zhu HL, Jiang FZ (2016) Pitavastatin suppressed liver cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Onco Targets Ther 9:5383–5388. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S106906
Yue Y, Yang YM, Shi L, Wang ZR (2015) Suppression of human hepatocellular cancer cell proliferation by Brucea javanica oil-loaded liposomes via induction of apoptosis. Arch Med Sci 11(4):856–862. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2015.53306
Zhang JQ, Li YM, Liu T, He WT, Chen YT, Chen XH, Li X, Zhou WC, Yi JF, Ren ZJ (2010) Antitumor effect of matrine in human hepatoma G2 cells by inducing apoptosis and autophagy. World J Gastroenterol 16(34):4281–4290. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i34.4281
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the suggestion of manuscript revised by Associate Professor Hongfei Xing from the University of Science and Technology of China.
Funding
This study received support from the Anhui Province Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2017B230), the China Scholarship Council Visiting Scholar Project (Grant No. 201908340044), the key project of support program for top talents of colleges and universities of Anhui Province department of education (Grant No. gxgwfx2019027), the Natural science foundation of Anhui province of China (Grant No. 1808085MC71), and the Anhui University Natural Science Research Project (Grant No. KJ2020A0383).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiao Wang performed the experiments and analyzed the results and the manuscript. Na Xu, Qinglin Li, and Shengqi Chen helped in performing experiments. Hui Cheng, Mo Yang, and Ting Jiang assisted in statistical analysis. Xiaojing Ma, Dengke Yin, and Jun Chu designed and supervised the study, reviewed the paper, and provided technical support. All authors had final decision of report content, interpretation of data, and the decision to submit the report for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 761 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Xu, N., Li, Q. et al. Lactonic sophorolipid–induced apoptosis in human HepG2 cells through the Caspase-3 pathway. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 2033–2042 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11045-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11045-5