Abstract
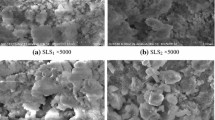
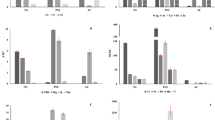
This study aimed at evaluating and comparing the removal of arsenic from solutions by a low-cost waste-based sorbent, produced by pyrolysing sewage sludge under appropriate conditions, and by a commercially activated carbon. Batch sorption experiments were performed under isothermal conditions (20°C), in order to evaluate the effect of pH on the arsenic sorption kinetics and on the equilibrium sorption capacity of the materials under study. Kinetic data revealed that the arsenic sorption was faster onto the activated carbon than onto the pyrolysed sludge. The sorption process was well described by both the pseudo-first and pseudo-second-order kinetics equations for both materials. Changes in the initial solution pH have distinct effects on the removal of arsenic onto pyrolysed sludge and activated carbon. While for pyrolysed sludge, pH affects essentially the equilibrium time, for activated carbon it affects the sorption capacity. Equilibrium results were well described by both Freundlich and Langmuir isotherm models, although fittings corresponding to the Langmuir isotherm were slightly better. The Langmuir maximum sorption capacity determined for the pyrolysed sludge was 71 μg g−1, while for activated carbon was 229 μg g−1. Despite the relative lower capacity of the pyrolysed sludge, the considerable lower cost and the valorisation of the sludge may justify further research on its use for water decontamination.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, M. N., Kaneco, S., Kitagawa, T., Begum, A., Katsumata, H., Suzuki, T., & Ohta, K. (2006). Removal of arsenic in aqueous solutions by adsorption onto waste rice husk. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 45, 8105–8110.
Budinova, T., Petrov, N., Razvigorova, M., Parra, J., & Galiatsatou, P. (2006). Removal of arsenic(III) from aqueous solution by activated carbons prepared from solvent extracted olive pulp and olive stones. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 45, 1896–1901.
Budinova, T., Savova, D., Tsyntsarski, B., Ania, C. O., Cabal, B., Parra, J. B., & Petrov, N. (2009). Biomass waste-derived activated carbon for the removal of arsenic and manganese ions from aqueous solutions. Applied Surface Science, 255, 4650–4657.
Diário da República—I SÉRIE-A (1998 )Decreto-Lei n.o 236/98, in: DR 176/98 SÉRIE I-A de 1998-08-01. pp. 47.
Diário da República—I SÉRIE-A (2007) Decreto-Lei n.o 306/07, in: DR 164/07 SÉRIE I-A de 2007-08-27. pp. 19.
EPA (2000) Arsenic occurrence in public drinking water supplies. pp. 1–138.
Freundlich, H. (1906). Concerning adsorption in solutions. Zeitschrift Fur Physikalische Chemie—Stochiometrie Und Verwandtschaftslehre, 57, 385–470.
Gupta, V. K., Carrott, P. J. M., & Carrott, M. (2009). Suhas, low-cost adsorbents: growing approach to wastewater treatmenta review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 783–842.
Hasan, S. H., Ranjan, D., & Talat, M. (2009). “Rice Polish” for the removal of arsenic from aqueous solution: optimization of process variables. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 48, 4194–4201.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34, 451–465.
Holl, W. H. (2010). Mechanisms of arsenic removal from water. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32, 287–290.
Kamala, C. T., Chu, K. H., Chary, N. S., Pandey, P. K., Ramesh, S. L., Sastry, A. R. K., et al. (2005). Removal of arsenic(III) from aqueous solutions using fresh and immobilized plant biomass. Water Research, 39, 2815–2826
Khan, M. A., & Ho, Y. S. (2011). Arsenic in drinking water: a review on toxicological effects, mechanism of accumulation and remediation. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 23, 1889–1901.
Lagergren, S. (1898). Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöter stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens, Handlingar, 24, 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I: solids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 38, 2221–2295.
Lopes, C. B., Otero, M., Lin, Z., Silva, C. M., Pereira, E., Rocha, J., & Duarte, A. C. (2010). Effect of pH and temperature on Hg2+ water decontamination using ETS-4 titanosilicate. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 175, 439–444.
Malik, A. H., Khan, Z. M., Mahmood, Q., Nasreen, S., & Bhatti, Z. A. (2009). Perspectives of low cost arsenic remediation of drinking water in Pakistan and other countries. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 1–12.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta, 58, 201–235.
Mohan, D., & Pittman, C. U. (2007). Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 142, 1–53.
Mohan, D., Gupta, V. K., Srivastava, S. K., & Chander, S. (2001). Kinetics of mercury adsorption from wastewater using activated carbon derived from fertilizer waste. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 177, 169–181.
Oke, I. A., Olarinoye, N. O., & Adewusi, S. R. A. (2008). Adsorption kinetics for arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by untreated powdered eggshell. Adsorption-Journal of The International Adsorption Society, 14, 73–83.
Oliveira, D. Q. L., Goncalves, M., Oliveira, L. C. A., & Guilherme, L. R. G. (2008). Removal of As(V) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using solid waste from leather industry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 151, 280–284.
Pandey, P. K., Choubey, S., Verma, Y., Pandey, M., & Chandrashekhar, K. (2009). Biosorptive removal of arsenic from drinking water. Bioresource Technology, 100, 634–637.
Rahaman, M. S., Basu, A., & Islam, M. R. (2008). The removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solutions by waste materials. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2815–2823.
Ranjan, D., Talat, M., & Hasan, S. H. (2009). Biosorption of arsenic from aqueous solution using agricultural residue ‘rice polish’. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1050–1059.
Sharma, V. K., & Sohn, M. (2009). Aquatic arsenic: toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environmental International, 35, 743–759.
Smith, K. M., Fowler, G. D., Pullket, S., & Graham, N. J. D. (2009). Sewage sludge-based adsorbents: a review of their production, properties and use in water treatment applications. Water Research, 43, 2569–2594.
Sullivan, C., Tyrer, M., Cheeseman, C. R., & Graham, N. J. D. (2010). Disposal of water treatment wastes containing arsenic—a review. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 1770–1778.
Zhang, F. S., Nriagu, J. O., & Itoh, H. (2005). Mercury removal from water using activated carbons derived from organic sewage sludge. Water Research, 39, 389–395.
Acknowledgements
We thank Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia-FCT. This research was supported by FCT Post-Doctoral grants funding C.B. Lopes (SFRH/BPD/45156/2008) and J.P. Coelho (SFRH/BPD/48449/2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tavares, D.S., Lopes, C.B., Coelho, J.P. et al. Removal of Arsenic from Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Sewage Sludge-Based Sorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 2311–2321 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1025-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1025-0