Abstract
Purpose
We investigated in vivo-colon targetability and therapeutic properties of DS against experimental rat colitis.
Methods
The systemic absorption and colonic delivery of D after oral administration of DS was analyzed by examining the concentration of drugs in the GI tract, plasma, urine and feces. Therapeutic activity of DS was determined using a TNBS-induced rat colitis model. Adrenal suppression by DS administration was evaluated by monitoring the concentration of ACTH and corticosterone in the plasma.
Results
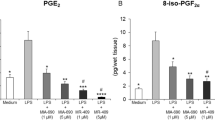
DS administered orally was delivered efficiently to the large intestine resulting in D accumulation at the target site. In addition, DS was not detectable in the plasma and was detected very low in the urine after DS administration. The fecal and urinary recovery of D (after DS administration) was much greater and less than that after D administration, suggesting that DS should exhibit enhanced therapeutic activity and reduced systemic side effects. Consistent with this notion, DS was more effective than D in healing rat colitis. Moreover, oral administration of either D or DS reduced the plasma corticosterone and ACTH levels from the normal levels, which is significantly greater for D.
Conclusion
DS is a promising colon specific prodrug that improves therapeutic properties of D







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- CD:
-
Crohn’s disease
- D:
-
Dexamathasone
- DS:
-
Dexamathasone 21-sulfate or sulfate conjugated dexamathasone
- DSI:
-
Distal small intestine
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- PSI:
-
Proximal small intestine
- TNBS:
-
2,4,6-Trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid
References
D. K. Podolsky. Inflammatory bowel disease (1). N. Engl. J. Med. 325:928–37 (1991).
D. K. Podolsky. Inflammatory bowel disease (2). N. Engl. J. Med. 325:1008–16 (1991).
R. J. Xavier, and D. K. Podolsky. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448:427–34 (2007) doi:10.1038/nature06005.
B. Crotty, and D. P. Jewell. Drug therapy of ulcerative colitis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 34:189–98 (1992).
M. Robinson. Medical therapy of inflammatory bowel disease for the 21st century. Eur. J. Surg. Suppl. 582:90–8 (1998) doi:10.1080/11024159850191517.
E. Domenech. Inflammatory bowel disease: current therapeutic options. Digestion. 73(Suppl 1):67–76 (2006) doi:10.1159/000089781.
D. R. Friend, and G. W. Chang. Drug glycosides: potential prodrugs for colon-specific drug delivery. J. Med. Chem. 28:51–7 (1985) doi:10.1021/jm00379a012.
A. D. McLeod, L. Tolentino, and T. N. Tozer. Glucocorticoid-dextran conjugates as potential prodrugs for colon-specific delivery: steady-state pharmacokinetics in the rat. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 15:151–61 (1994) doi:10.1002/bdd.2510150207.
H. Yano, F. Hirayama, H. Arima, and K. Uekama. Preparation of prednisolone-appended alpha-, beta- and gamma-cyclodextrins: substitution at secondary hydroxyl groups and in vitro hydrolysis behavior. J. Pharm. Sci. 90:493–503 (2001) doi:10.1002/1520-6017(200104)90:4<493::AID-JPS1007>3.0.CO;2-W.
Y. J. Jung, M. J. Doh, I. H. Kim, H. S. Kong, J. S. Lee, and Y. M. Kim. Prednisolone 21-sulfate sodium: a colon-specific pro-drug of prednisolone. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 55:1075–82 (2003) doi:10.1211/0022357021413.
I. H. Kim, H. S. Kong, B. I. Choi, Y. S. Kim, H. J. Kim, Y. W. Yang, Y. J. Jung, and Y. M. Kim. Synthesis and in vitro properties of dexamethasone 21-sulfate sodium as a colon-specific prodrug of dexamethasone. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 32:389–97 (2006) doi:10.1080/03639040500519441.
V. R. Sinha, and R. Kumria. Colonic drug delivery: prodrug approach. Pharm. Res. 18:557–64 (2001) doi:10.1023/A:1011033121528.
A. Rubinstein. Microbially controlled drug delivery to the colon. Biopharm. Drug. Dispos. 11:465–75 (1990) doi:10.1002/bdd.2510110602.
H. Yano, F. Hirayama, M. Kamada, H. Arima, and K. Uekama. Colon-specific delivery of prednisolone-appended alpha-cyclodextrin conjugate: alleviation of systemic side effect after oral administration. J. Control Release. 79:103–12 (2002) doi:10.1016/S0168-3659(01)00532-6.
G. P. Morris, P. L. Beck, M. S. Herridge, W. T. Depew, M. R. Szewczuk, and J. L. Wallace. Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology. 96:795–803 (1989).
M. W. Son, J. I. Ko, H. M. Doh, W. B. Kim, T. S. Park, M. J. Shim, and B. K. Kim. Protective effect of taurine on TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 21:531–6 (1998).
S. Y. Zhou, D. Fleisher, L. H. Pao, C. Li, B. Winward, and E. M. Zimmermann. Intestinal metabolism and transport of 5-aminosalicylate. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27:479–85 (1999).
D. R. Friend. Review article: issues in oral administration of locally acting glucocorticosteroids for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 12:591–603 (1998) doi:10.1046/j.1365-2036.1998.00348.x.
U. Fagerholm, A. Lindahl, and H. Lennernas. Regional intestinal permeability in rats of compounds with different physicochemical properties and transport mechanisms. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 49:687–90 (1997).
L. Kagan, and A. Hoffman. Systems for region selective drug delivery in the gastrointestinal tract: biopharmaceutical considerations. Expert Opin. Drug. Deliv. 5:681–692 (2008) doi:10.1517/17425247.5.6.681.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, I., Kong, H., Lee, Y. et al. Dexamethasone 21-Sulfate Improves the Therapeutic Properties of Dexamethasone Against Experimental Rat Colitis by Specifically Delivering the Steroid to the Large Intestine. Pharm Res 26, 415–421 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9758-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9758-1