Abstract
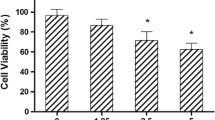
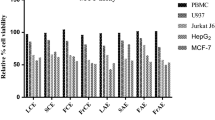
We demonstrated that an extract from Pylaiella littoralis, collected from the Federate States of Micronesia (FSM), could inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells. P. littoralis extract (PLE) showed anti-proliferative activities in the tumorigenic cells tested, ranging from 20.2% to 67.9%. The highest inhibitory activity, in HT-29 cells, was selected for further experiments. PLE showed no cytotoxic effect in normal cells and inhibited the growth of HT-29 cells depending on concentration and incubation time. PLE-treated HT-29 cells showed the typical morphological characteristics of apoptosis, such as apoptotic body formation and DNA fragmentation. PLE also induced mitochondrial membrane potential depolarization and resulted in increased mitochondrial membrane permeability, compared with untreated cells. PLE decreased Bcl-2 protein and increased Bax protein expression, activating caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) expression via the caspase pathway. PLE also increased the phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and it reduced cell viability in treatment cells with specific inhibitors such as PD98059 (a specific inhibitor of ERK), SP600125 (a specific inbibitor of JNK), and SB 203580 (a specific inbibitor of p38 MAPK). via the the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) pathway. These results suggest that PLE inhibits the proliferation of HT-29 cells by affecting the caspase and MAPK pathways involved in the induction of apoptosis. Thus, we suggest that P. littoralis extract might be potential candidate agents for the treatment of human colorectal cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Cory S (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science 281(5381):1322–1326
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: Signaling and modulation. Science 281(5381):1305–1308
Athukorala Y, Kim KN, Jeon YJ (2006) Antiproliferative and antioxidant properties of an enzymatic hydrolysate from brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Food Chem Toxicol 44(7):1065–1074
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Munro MHG, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR (2006) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 23:26–78
Boatright KM, Salvesen GS (2003) Mechanisms of caspase activation. Curr Opon Cell Biol 15(6):725–731
Chang L, Karin M (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signaling cascades. Nature 410(6824):37–40
Chen KC, Chang LS (2009) Arachidonic acid-induced apoptosis of human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells is mediated through mitochondrial alteration elicited by ROS and Ca (2+)-evoked activation of p38 alpha MAPK and JNK1. Toxicology 262(3): 199–206
Chen YR, Meyer CF, Tan TH (1996) Persistent activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in gamma radiationinduced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 271(2):631–634
Chinnaiyan AM, Orth K, O’Rourke K, Duan H, Poirier GG, Dixit VM (1996) Molecular ordering of the cell death pathway: Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL function upstream of the Ced-3 like apoptotic proteases. J Biol Chem 271(9):4573–4576
Cho SG, Choi EJ (2002) Apoptotic signaling pathways: Caspases and stress-activated protein kinases. J Biochem Mol Biol 35(1): 24–27
Choi BY, Kim HY, Lee KH, Cho YH, Kong G (1999) Clofilium, a potassium channel blocker, induces apoptosis of human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells via Bcl-2-insensitive activation of aspase-3. Cancer Lett 147(1–2):85–93
Dlugosz PJ, Billen LP, Annis MG, Zhu W, Zhang Z, Lin J, Leber B, Andrews DW (2006) Bcl-2 changes conformation to inhibit Bax oligomerization. EMBO J 25(11):2287–2296
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281(5381):1309–1312
Gschwind M, Huber G (1995) Apoptotic cell death induced by β-Amyloid 1–42Peptide is cell type dependent. J Neurochem 65(1):292–300
Heidelberg KB, Sebens KP, Purcell JE (2004) Composition and sources of near reef zooplankton on a Jamaican forereef along with implications for coral feeding. Coral Reefs 23(2):263–276
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407(6805):770–776
Heo SJ, Kim KN, Yoon WJ, Oh C, Choi YU, Affan A, Lee YJ, Lee HS, Kang DH (2011) Chromene induces apoptosis via caspase-3 activation in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 49(9):1988–2004
Jeong JW, Jin CY, Park C, Hong SH, Kim GY, Jeong YK, Lee JD, Yoo YH, Choi YH (2011) Induction of apoptosis by cordycepin via reactive oxygen species generation in human leukemia cells. Toxicol In Vitro 25(4):817–824
Jin Z, El-Deiry WS (2005) Overview of cell death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther 4(2):139–163
Johannes RE, Coles SL, Kuenzel NT (1970) The role of zooplankton in the nutrition of some scleractinian corals. Limnol Oceanogr 15(4):579–586
Kim AD, Kang KA, Zhang R, Lim CM, Kim HS, Kim DH, Jeon YJ, Lee CH, Chang WY, Hyun JW (2010a) Ginseng saponin metabolite induces apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells through the modulation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Pharmacology 30(2):134–140
Kim KN, Heo SJ, Kang SM, Ahn G, Jeon YJ (2010b) Fucoxanthin induces apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells through a ROS-mediated Bcl-xL pathway. Toxicol In Vitro 24(6):1648–1654
Kim KN, Heo SJ, Yoon WJ, Kang SM, Ahn G, Yi TH, Jeon YJ (2010c) Fucoxanthin inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the activation of NF-kB and MAPKs in lipopolysaccharideinduced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol 649(1–3):369–375
Kong CS, Kim JA, Yoon NY, Kim SK (2009) Induction of apoptosis by phloroglucinol derivative from Ecklonia Cava in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol 47(7):1653–1658
Kroemer G, Reed JC (2000) Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat Med 6(5):513–519
Kroemer G, Zamzami N, Susin, SA (1997) Mitochondrial control of apoptosis. Immunol Today 18(1):44–51
Kwon HJ, Bae SY, Kim KH, Han CH, Cho SH, Nam SW Choi YH, Kim BW (2007) Induction of apoptosis in HeLa cells by ethanolic extract of Corallin pilulifera. Food Chem 104(1): 196–201
Li Y, Qian ZJ, Ryu BM, Lee SH, Kim MM, Kim SK (2009) Chemical components and its antioxidant properties in vitro: An edible marine brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Bioorgan Med Chem 17(5):1963–1973
Lu KH, Lue KH, Liao HH, Lin KL, Chung JG, 2005. Induction of caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells by paclitaxel. Clin Chim Acta 357(1):65–73
Mabeau S, Fleurence J (1993) Seaweed in food products: Biochemical and nutritional aspects. Trends Food Sci Tech 4(4):103–107
Nechushtan A, Smith CL, Lamensdorf I, Yoon SH, Youle RJ (2001) Bax and Bak coalesce into novel mitochondria-associated clusters during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 153(6):1265–1276
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C (1991) A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by Propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 139(2):271–279
Nwosu F, Morris J, Lund VA, Stewart D, Ross HA, McDougall GJ (2011) Anti-proliferative and potential anti-diabetic effects of phenolic-rich extracts from edible marine algae. Food Chem 126(3):1006–1012
Okada H, Mak TW (2004) Pathways of apoptotic and nonapoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer 4(8):592–603
Park C, Jin CY, Kwon HJ, Hwang HJ, Kim GY, Choi IW, Kwon TK, Kim BW, Kim WJ, Choi YH (2010) Induction of apoptosis by esculetin in human leukemia U937 cells: role of Bcl-2 and extracellular-regulated kinase signaling. Toxicol In Vitro 24(2): 486–494
Persons DL, Yazlovitskaya EM, Cui W, Pelling JC (1999) Cisplatin-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in ovarian carcinoma cells: Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity increases sensitivity to cisplatin. Clin Cancer Res 5(5): 1007–1014
Ren G, Zhao YP, Yang L, Fu CX (2008) Anti-proliferative effect of clitocine from the mushroom Leucopaxillus giganteus on human cervical cancer HeLa cells by inducing apoptosis. Cancer Lett 262(2):190–200
Rodríguez-Bernaldo de Quirós A, Lage-Yusty MA, López-Hernández J (2010) Determination of phenolic compounds in macroalgae for human consumption. Food Chem 121(2):634–638
Rosenkranz AR, Schmaldienst S, Stuhlmeier KM, Chen W, Knapp W, Zlabinger GJ (1992) A microplate assay for the detection of oxidative products using 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin-deacetae. J Immunol Methods 156(1):39–45
Sahu RP, Zhang R, Batra S, Shi Y, Srivastava SK (2009) Benzyl isothiocyanate-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species causes cell cycle arrest and induces apoptosis via activation of MAPK in human pancreatic cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 30(10): 1744–1753
Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS (1998) Properties of the caspases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1387(1–2):17–31
Thees S, Hubbard GB, Winckler J, Schultz C, Rami A (2005) Specific alteration of the Bax/Bcl2 ratio and cytochrome c without execution of apoptosis in the hippocampus of aged baboons. Restor Neurol neurosci 23(1):1–9
Troiano RP (2007) Large-scale applications of accelerometers: new frontiers and new questions. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39(9):1501
Wang X, Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2000) Requirement for ERK activation in cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 275(50):39435–39443
Yang J, Lee K, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrade AM, Cai J, Peng PI, Jones DP, Wang X (1997) Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 275(5303):1129–1132
Ye BR, Jang J, Kwon YK, Jeon SM, Jeong JY, Kang DH, Oh CH, Kim JH, Affan Abu, Hyun JH (2012) Antioxidant effect of tropical seaweed Pylaiella littoralis extracts collected from chuuk lagoon in Federated States of Micronesia. Ocean and Polar Res 34(3):297–304
Ye H, Wang K, Zhou C, Liu J, Zeng X (2008) Purification, antitumor and antioxidant activities in vitro of polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Sargassum pallidum. Food Chem 111(2):428–432
Yuan, YV, Carrington MF, Walsh NA (2005) Extracts from dulse (Palmaria palmate) are effective antioxidants and inhibitors of cell proliferation in vitro. Food Chem Toxicol 43(7):1073–1081
Zhao Y, You H, Yang Y, Wei L, Zhang X, Yao L, Fan D, Yo Q (2004) Distinctive Regulation and Function of PI 3K/Akt and MAPKs in Doxorubicin-Induced Apoptosis of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. J Cell Biochem 91(3):621–632
Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, Lutschg A, Wang X (1997) Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell 90(3): 405–413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, BR., Kim, J., Kim, MS. et al. Induction of apoptosis by the tropical seaweed Pylaiella littoralis in HT-29 cells via the mitochondrial and MAPK pathways. Ocean Sci. J. 48, 339–348 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-013-0032-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-013-0032-z