Abstract
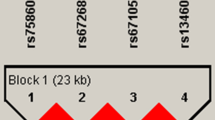
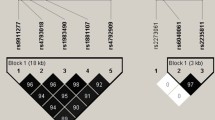
Osteoporosis is a common health problem in Mexico, so it is essential to investigate the status of different gene polymorphisms that could serve as genetic susceptibility markers in the Mexican population. Genes with a role in bone metabolism are excellent candidates for association studies. In this study were determined the allelic and genotypic frequencies of four polymorphic markers (C/T rs3736228, G/A rs4988321, T/C rs627174 and T/C rs901824) in the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene (LRP5) and their association with osteoporosis in 100 pos-menopausal osteoporotic Mexican women and their controls, using real time-PCR and TaqMan probes. Only the G/A polymorphism (rs4988321, Val667Met) showed significant differences (p = 0.039) when genotype frequencies were compared. However, when the haplotypes of these four polymorphisms were analyzed, interesting associations became evident. The CGTT haplotype showed significant association with low risk of osteoporosis (OR 0.629; p = 0.007; [95 % CI, 0.448–0.884]), whereas the TACT haplotype was significantly associated with a higher risk of osteoporosis (OR 7.965; p = 0.006; [95 % CI, 1.557–54.775]). Our results supported the association of LRP5 with osteoporosis and showed the potential value of LRP5 haplotypes to identify risk of osteoporosis in Mexican population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gong Y, Slee RB, Fukai N, Rawadi G, Roman-Roman S, Reginato AM, Wang H, Cundy T, Glorieux FH, Lev D et al (2001) LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell 107:513–523
Kato M, Patel MS, Levasseur R, Lobov I, Chang BH, Glass DA II, Hartmann C, Li L, Hwang TH, Brayton CF et al (2002) Cbfa1-independent decrease in osteoblast proliferation, osteopenia, and persistent embryonic eye vascularization in mice deficient in LRP5, a Wnt coreceptor. J Cell Biol 157:303–314
Boyden LM, Mao J, Belsky J, Mitzner L, Farhi A, Mitnick MA, Wu D, Insogna K, Lifton RP (2002) High bone density due to a mutation in LDL-receptor-related protein 5. N Engl J Med 346:1513–1521
Little RD, Carulli JP, Del Mastro RG, Dupuis J, Osborne M, Folz C, Manning SP, Swain PM, Zhao SC, Eustace B et al (2002) A mutation in the LDL receptor-related protein 5 gene results in the autosomal dominant high-bone-mass trait. Am J Hum Genet 70:11–19
Van Wesenbeeck L, Cleiren E, Gram J, Beals RK, Bénichou O, Scopelliti D, Key L, Renton T, Bartels C, Gong Y et al (2003) Six novel missense mutations in the LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) gene in different conditions with an increased bone density. Am J Hum Genet 72:763–771
Ferrari SL, Deutsch S, Baudoin C, Cohen-Solal M, Ostertag A, Antonarakis SE, Rizzoli R, de Vernejoul MC (2005) LRP5 gene polymorphisms and idiopathic osteoporosis in men. Bone 37:770–775
Grundberg E, Lau EM, Lorentzson M, Karlsson M, Holmberg A, Groop L, Mellström D, Orwoll E, Mallmin H, Ohlsson CM et al (2008) Large-scale association study between two coding LRP5 gene polymorphisms and bone phenotypes and fractures in men. Osteoporos Int 19:829–837
Bollerslev J, Wilson SG, Dick IM, Islam FM, Ueland T, Palmer L, Devine A, Prince RL (2005) LRP5 gene polymorphisms predict bone mass and incident fractures in elderly Australian women. Bone 36:599–606
Ezura Y, Nakajima T, Urano T, Sudo Y, Kajita M, Yoshida H, Suzuki T, Hosoi T, Inoue S, Shiraki M et al (2007) Association of a single-nucleotide variation (A1330V) in the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene (LRP5) with bone mineral density in adult Japanese women. Bone 40:997–1005
van Meurs JB, Rivadeneira F, Jhamai M, Hugens W, Hofman A, van Leeuwen JP, Pols HA, Uitterlinden AG (2006) Common genetic variation of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 and 6 genes determines fracture risk in elderly white men. J Bone Miner Res 21:141–150
van Meurs JB, Trikalinos TA, Ralston SH, Balcells S, Brandi ML, Brixen K, Kiel DP, Langdahl BL, Lips P, Ljunggren O et al (2008) Large-scale analysis of association between LRP5 and LRP6 variants and osteoporosis. JAMA 299:1277–1290
Richards JB, Rivadeneira F, Inouye M, Pastinen TM, Soranzo N, Wilson SG, Andrew T, Falchi M, Gwilliam R, Ahmadi KR et al (2008) Bone mineral density, osteoporosis, and osteoporotic fractures: a genome-wide association study. Lancet 371:1505–1512
Richards JB, Kavvoura FK, Rivadeneira F, Styrkársdóttir U, Estrada K, Halldórsson BV, Hsu YH, Zillikens MC, Wilson SG, Mullin BH et al (2009) Collaborative meta-analysis: associations of 150 candidate genes with osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture. Ann Intern Med 151:528–537
Stathopoulou MG, Dedoussis GV, Trovas G, Katsalira A, Hammond N, Deloukas P, Lyritis GP (2010) Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 polymorphisms are associated with bone mineral density in Greek postmenopausal women: an interaction with calcium intake. J Am Diet Assoc 110:1078–1083
Liu JM, Zhang MJ, Zhao L, Cui B, Li ZB, Zhao HY, Sun LH, Tao B, Li M, Ning G (2010) Analysis of recently identified osteoporosis susceptibility genes in Han Chinese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:E112–E120
Riancho JA, Olmos JM, Pineda B, García-Ibarbia C, Pérez-Núñez MI, Nan DN, Velasco J, Cano A, García-Pérez MA, Zarrabeitia MT et al (2011) Wnt receptors, bone mass, and fractures: gene-wide association analysis of LRP5 and LRP6 polymorphisms with replication. Eur J Endocrinol 164:123–131
Giroux S, Elfassihi L, Cardinal G, Laflamme N, Rousseau F (2007) LRP5 coding polymorphisms influence the variation of peak bone mass in a normal population of French-Canadian women. Bone 40:1299–1307
Koay MA, Woon PY, Zhang Y, Miles LJ, Duncan EL, Ralston SH, Compston JE, Cooper C, Keen R, Langdahl BL et al (2004) Influence of LRP5 polymorphisms on normal variation in BMD. J Bone Miner Res 19:1619–1627
Koh JM, Jung MH, Hong JS, Park HJ, Chang JS, Shin HD, Kim SY, Kim GS (2004) Association between bone mineral density and LDL receptor-related protein 5 gene polymorphisms in young Korean men. J Korean Med Sci 19:407–412
Tran BN, Nguyen ND, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV (2008) Association between LRP5 polymorphism and bone mineral density: a Bayesian meta-analysis. BMC Med Genet 9:55–67
Clark P (2009) Osteoorosis in Mexico: “the challenge”. Salud Pública Mex 51(Suppl 1):S2–S3
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Isolation of high molecular weight DNA from mammalian cells. In: Ford N, Nolan C, Ferguson M (eds) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, pp 9.14–9.19
Reed TE, Schull WJ (1968) A general maximum likelihood estimation program. Am J Hum Genet 20:579–580
Excoffier L, Slatkin M (1995) Maximum-likelihood estimation of molecular haplotype frequencies in a diploid population. Mol Biol Evol 12:921–927
Tevfik D (2009) Statistical analysis in HLA and disease association studies. http://www.dorak.info/hla/stat.html. Accessed 20 Feb 2011
Sham PC (1998) Statistics in human genetics. Arnold applications of statistics series. A Hodder Arnold Publication, London
Zhang ZL, Qin YJ, He JW, Huang QR, Li M, Hu YQ, Liu YJ (2005) Association of polymorphisms in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene with bone mineral density in postmenopausal Chinese women. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:1111–1116
Saarinen A, Välimäki VV, Välimäki MJ, Löyttyniemi E, Auro K, Uusen P, Kuris M, Lehesjoki AE, Mäkitie O (2007) The A1330V polymorphism of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene (LRP5) associates with low peak bone mass in young healthy men. Bone 40:1006–1012
Mizuguchi T, Furuta I, Watanabe Y, Tsukamoto K, Tomita H, Tsujihata M, Ohta T, Kishino T, Matsumoto N, Minakami H et al (2004) LRP5, low-density-lipoprotein-receptor-related protein 5, is a determinant for bone mineral density. J Hum Genet 49:80–86
Funakoshi Y, Omori H, Yada H, Katoh T (2010) Relationship between changes of bone mineral density over seven years and A1330V polymorphism of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene or lifestyle factors in Japanese female workers. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 19:534–539
Funakoshi Y, Omori H, Yada H, Katoh T (2011) A1330V polymorphism of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene and bone mineral density in Japanese male workers. Environ Health Prev Med 16:106–112
Koller DL, Ichikawa S, Johnson ML, Lai D, Xuei X, Edenberg HJ, Conneally PM, Hui SL, Johnston CC, Peacock M et al (2005) Contribution of the LRP5 gene to normal variation in peak BMD in women. J Bone Miner Res 20:75–80
Gómez R, Magaña JJ, Cisneros B, Pérez-Salazar E, Faugeron S, Véliz D, Castro C, Rubio J, Casas L, Valdés-Flores M (2007) Association of the Estrogen receptor alfa gene polymorphism with osteoporosis in the Mexican population. Clin Genet 72:574–581
Magaña JJ, Gómez R, Cisneros B, Casas L, Castorena F, Miranda A, Diez P, Castro C, Rubio J, Valdés M (2006) Association of the CT gene (CA) polymorphism with BMD in osteoporotic Mexican women. Clin Genet 70:402–408
Falcón-Ramírez E, Casas-Avila L, Miranda A, Diez P, Castro C, Rubio J, Gómez R, Valdés-Flores M (2011) Sp1 polymorphism in collagen I alpha1 gene is associated with osteoporosis in lumbar spine of Mexican women. Mol Biol Rep 38:2987–2992
Magaña JJ, Gómez R, Cisneros B, Casas L, Valdés-Flores M (2008) Association of interleukin-6 gene polymorphism with bone mineral density in Mexican women. Arch Med Res 39:618–624
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología SALUD-2007-C01-69706.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Leonora Casas-Avila and Edith Falcón-Ramírez contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falcón-Ramírez, E., Casas-Avila, L., Cerda-Flores, R.M. et al. Association of LRP5 haplotypes with osteoporosis in Mexican women. Mol Biol Rep 40, 2705–2710 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2357-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2357-6