Abstract
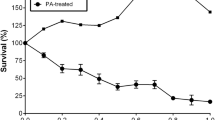
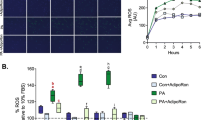
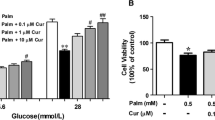
Fatty acid-induced cytotoxicity is believed to recapitulate lipotoxicity seen in obese type-2 diabetes, and, thus, contribute to beta cell loss in the disease. These studies were initiated to determine whether the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway was involved in palmitate-induced beta cell death. Treatment of INS-1 beta cells with palmitate enhanced interaction between TLR and myeloid differentiation factor88 (MyD88). Concomitant with TLR/MyD88 interaction, the level of phospho-C-Jun N-terminal kinase (phospho-JNK) showed an increase; however, the level of inhibitory factor kappa B alpha (IκBα) showed a decrease. Gene knockdown of TLR4 prevented palmitate-induced INS-1 cell death, while knockdown of TLR2 did not. In addition, gene knockdown of TLR4 prevented palmitate-induced increase of phospho-JNK and decrease of IκBα. JNK inhibitor SP60125 significantly protected against palmitate-induced INS-1 cell death, while IκB kinase (IKK) inhibitor acetylsalicylate did not. These data suggest involvement of JNK activation through the TLR4 signaling pathway in palmitate-induced INS-1 beta cell death.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petersen KF, Shulman GI (2002) Pathogenesis of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol 90(5A):11G–18G
Funaki M (2009) Saturated fatty acids and insulin resistance. J Med Invest 56:88–92
Newsholme P, Keane D, Welters HJ, Morgan NG (2007) Life and death decisions of the pancreatic beta-cell: the role of fatty acids. Clin Sci (Lond) 112:27–42
Lupi R, Dotta F, Marselli L, Del Guerra S, Masini M, Santangelo C, Patane G, Boggi U, Piro S, Anello M, Bergamini E, Mosca F, Di Mario U, Del Prato S, Marchetti P (2002) Prolonged exposure to free fatty acids has cytostatic and pro-apoptotic effects on human pancreatic islets: evidence that beta-cell death is caspase mediated, partially dependent on ceramide pathway, and Bcl-2 regulated. Diabetes 51:1437–1442
El-Assaad W, Buteau J, Peyot ML, Nolan C, Roduit R, Hardy S, Joly E, Dbaibo G, Rosenberg L, Prentki M (2003) Saturated fatty acids synergize with elevated glucose to cause pancreatic beta-cell death. Endocrinology 144:4154–4163
Marchetti P, Del Prato S, Lupi R, Del Guerra S (2006) The pancreatic beta-cell in human type 2 diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 16(Suppl. 1):S3–S6
Cnop M, Hannaert JC, Hoorens A, Eizirik DL, Pipeleers DG (2001) Inverse relationship between cytotoxicity of free fatty acids in pancreatic islet cells and cellular triglyceride accumulation. Diabetes 50:1771–1777
Maedler K, Oberholzer J, Bucher P, Spinas GA, Donath MY (2003) Monounsaturated fatty acids prevent the deleterious effects of palmitate and high glucose on human pancreatic beta-cell turnover and function. Diabetes 52:726–733
Kaneto H, Matsuoka TA, Katakami N, Kawamori D, Miyatsuka T, Yoshiuchi K, Yasuda T, Sakamoto K, Yamasaki Y, Matsuhisa M (2007) Oxidative stress and the JNK pathway are involved in the development of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Curr Mol Med 7:674–686
Cunha DA, Hekerman P, Ladrière L, Bazarra-Castro A, Ortis F, Wakeham MC, Moore F, Rasschaert J, Cardozo AK, Bellomo E, Overbergh L, Mathieu C, Lupi R, Hai T, Herchuelz A, Marchetti P, Rutter GA, Eizirik DL, Cnop M (2008) Initiation and execution of lipotoxic ER stress in pancreatic beta-cells. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 14):2308–2318
Rakatzi I, Mueller H, Ritzeler O, Tennagels N, Eckel J (2004) Adiponectin counteracts cytokine- and fatty acid-induced apoptosis in the pancreatic beta-cell line INS-1. Diabetologia 47:249–258
Fan M, Chambers TC (2001) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the response of tumor cells to chemotherapy. Drug Resist Updat 4:253–267
Wang XT, Pei DS, Xu J, Guan QH, Sun YF, Liu XM (2007) Opposing effects of Bad phosphorylation at two distinct sites by Akt1 and JNK1/2 on ischemic brain injury. Cell Signal 19:1844–1856
Madesh M, Antonsson B, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Hajnóczky G (2002) Rapid kinetics of tBid-induced cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO release and mitochondrial depolarization. J Biol Chem 277:5651–5659
Dutta J, Fan Y, Gupta N, Fan G, Gélinas C (2006) Current insights into the regulation of programmed cell death by NF-kappaB. Oncogene 25:6800–6816
Sekine N, Ishikawa T, Okazaki T, Hayashi M, Wollheim CB, Fujita T (2000) Synergistic activation of NF-kappab and inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase induction by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in INS-1 cells. J Cell Physiol 184:46–57
Beeharry N, Chambers JA, Green IC (2004) Fatty acid protection from palmitic acid-induced apoptosis is lost following PI3-kinase inhibition. Apoptosis 9:599–607
Choi SE, Kim HE, Shin HC, Jang HJ, Lee KW, Kim Y, Kang SS, Chun J, Kang Y (2007) Involvement of Ca2+-mediated apoptotic signals in palmitate-induced MIN6N8a beta cell death. Mol Cell Endocrinol 272:50–62
Pasare C, Medzhitov R (2005) Toll-like receptors: linking innate and adaptive immunity. Adv Exp Med Biol 560:11–18
Lee JY, Zhao L, Hwang DH (2010) Modulation of pattern recognition receptor-mediated inflammation and risk of chronic diseases by dietary fatty acids. Nutr Rev 68:38–61
Shi H, Kokoeva MV, Inouye K, Tzameli I, Yin H, Flier JS (2006) TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116:3015–3025
Lee JY, Plakidas A, Lee WH, Heikkinen A, Chanmugam P, Bray G, Hwang DH (2003) Differential modulation of Toll-like receptors by fatty acids: preferential inhibition by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Lipid Res 44:479–486
Lee JY, Zhao L, Youn HS, Weatherill AR, Tapping R, Feng L, Lee WH, Fitzgerald KA, Hwang DH (2004) Saturated fatty acid activates but polyunsaturated fatty acid inhibits Toll-like receptor 2 dimerized with Toll-like receptor 6 or 1. J Biol Chem 279:16971–16979
Senn JJ (2006) Toll-like receptor-2 is essential for the development of palmitate-induced insulin resistance in myotubes. J Biol Chem 281:26865–26875
Lee JY, Sohn KH, Rhee SH, Hwang D (2001) Saturated fatty acids, but not unsaturated fatty acids, induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mediated through Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem 276:16683–16689
Kiely A, Robinson A, McClenaghan NH, Flatt PR, Newsholme P (2009) Toll-like receptor agonist induced changes in clonal rat BRIN-BD11 beta-cell insulin secretion and signal transduction. J Endocrinol 202:365–373
Vives-Pi M, Somoza N, Fernández-Alvarez J, Vargas F, Caro P, Alba A, Gomis R, Labeta MO, Pujol-Borrell R (2003) Evidence of expression of endotoxin receptors CD14, toll-like receptors TLR4 and TLR2 and associated molecule MD-2 and of sensitivity to endotoxin (LPS) in islet beta cells. Clin Exp Immunol 133:208–218
Böni-Schnetzler M, Boller S, Debray S, Bouzakri K, Meier DT, Prazak R, Kerr-Conte J, Pattou F, Ehses JA, Schuit FC, Donath MY (2009) Free fatty acids induce a proinflammatory response in islets via the abundantly expressed interleukin-1 receptor I. Endocrinology 150:5218–5229
Choi SE, Lee SM, Lee YJ, Li LJ, Lee SJ, Lee JH, Kim Y, Jun HS, Lee KW, Kang Y (2009) Protective role of autophagy in palmitate-induced INS-1 beta-cell death. Endocrinology 150:126–134
Wen L, Peng J, Li Z, Wong FS (2004) The effect of innate immunity on autoimmune diabetes and the expression of Toll-like receptors on pancreatic islets. J Immunol 172:3173–3180
Kang YJ, Kusler B, Otsuka M, Hughes M, Suzuki N, Suzuki S, Yeh WC, Akira S, Han J, Jones PP (2007) Calcineurin negatively regulates TLR-mediated activation pathways. J Immunol 179:4598–4607
Erridge C, Samani NJ (2009) Saturated fatty acids do not directly stimulate Toll-like receptor signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1944–1949
Gill R, Tsung A, Billiar T (2010) Linking oxidative stress to inflammation: toll-like receptors. Free Radic Biol Med 48(9):1121–1132 Epub 2010 Jan 18
Ohashi K, Burkart V, Flohé S, Kolb H (2000) Cutting edge: heat shock protein 60 is a putative endogenous ligand of the toll-like receptor-4 complex. J Immunol 164:558–561
Wong SW, Kwon MJ, Choi AM, Kim HP, Nakahira K, Hwang DH (2009) Fatty acids modulate Toll-like receptor 4 activation through regulation of receptor dimerization and recruitment into lipid rafts in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 284:27384–27392
Reyna SM, Ghosh S, Tantiwong P, Meka CS, Eagan P, Jenkinson CP, Cersosimo E, Defronzo RA, Coletta DK, Sriwijitkamol A, Musi N (2008) Elevated toll-like receptor 4 expression and signaling in muscle from insulin-resistant subjects. Diabetes 57:2595–2602
Coll T, Palomer X, Blanco-Vaca F, Escolà-Gil JC, Sánchez RM, Laguna JC, Vázquez-Carrera M (2010) Cyclooxygenase 2 inhibition exacerbates palmitate-induced inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology 151:537–548
Marsh B, Stevens SL, Packard AE, Gopalan B, Hunter B, Leung PY, Harrington CA, Stenzel-Poore MP (2009) Systemic lipopolysaccharide protects the brain from ischemic injury by reprogramming the response of the brain to stroke: a critical role for IRF3. J Neurosci 29:9839–9849
Pradillo JM, Fernández-López D, García-Yébenes I, Sobrado M, Hurtado O, Moro MA, Lizasoain I (2009) Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in neuroprotection afforded by ischemic preconditioning. J Neurochem 109:287–294
Hua F, Wang J, Sayeed I, Ishrat T, Atif F, Stein DG (2009) The TRIF-dependent signaling pathway is not required for acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390:678–683
Taylor T, Kim YJ, Ou X, Derbigny W, Broxmeyer HE (2010) Toll-like receptor 2 mediates proliferation, survival, NF-kappaB translocation, and cytokine mRNA expression in LIF-maintained mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 19:1333–1341
Horng T, Barton GM, Flavell RA, Medzhitov R (2002) The adaptor molecule TIRAP provides signalling specificity for Toll-like receptors. Nature 420:329–333
Messlik A, Schmechel S, Kisling S, Bereswill S, Heimesaat MM, Fischer A, Göbel U, Haller DJ (2009) Loss of Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 leads to differential induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and proapoptotic responses in the intestinal epithelium under conditions of chronic inflammation. Proteome Res 8:4406–4417
Nishiya T, DeFranco AL (2004) Ligand-regulated chimeric receptor approach reveals distinctive subcellular localization and signaling properties of the Toll-like receptors. J Biol Chem 279:19008–19017
Jung DY, Lee H, Jung BY, Ock J, Lee MS, Lee WH, Suk K (2005) TLR4, but not TLR2, signals autoregulatory apoptosis of cultured microglia: a critical role of IFN-beta as a decision maker. J Immunol 174(10):6467–6476
Melloul D (2008) Role of NF-kappaB in beta-cell death. Biochem Soc Trans 36:334–339
Kharroubi I, Ladriere L, Cardozo AK, Dogusan Z, Cnop M, Eizirik DL (2004) Free fatty acids and cytokines induce pancreatic β-cell apoptosis by different mechanisms: role of nuclear factor-κB and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrinology 145:5087–5096
Pfaffenbach KT, Gentile CL, Nivala AM, Wang D, Wei Y, Pagliassotti MJ (2010) Linking endoplasmic reticulum stress to cell death in hepatocytes: roles of C/EBP homologous protein and chemical chaperones in palmitate-mediated cell death. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 298:E1027–E1035
Jung TW, Lee YJ, Lee MW, Kim SM, Jung TW (2009) Full-length adiponectin protects hepatocytes from palmitate-induced apoptosis via inhibition of c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase. FEBS J 276:2278–2284
Pagliassotti MJ, Wei Y, Wang D (2007) Insulin protects liver cells from saturated fatty acid-induced apoptosis via inhibition of c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase activity. Endocrinology 148:3338–3345
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Korea Research Foundation (KRF 2009-0072584) and Gyunggi Regional Research Center (GRRC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sung-Mi Lee, Sung-E Choi and Ji-Hyun Lee are contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SM., Choi, SE., Lee, JH. et al. Involvement of the TLR4 (Toll-like receptor4) signaling pathway in palmitate-induced INS-1 beta cell death. Mol Cell Biochem 354, 207–217 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0820-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0820-7