Abstract
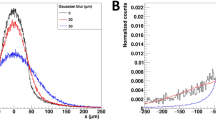
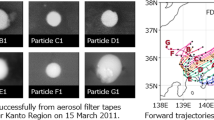
A nondestructive analytical method based on autoradiography and gamma spectrometry was developed to perform activity distribution analysis for particulate samples. This was applied to aerosols collected in Fukushima Japan, 40 km north of the Daiichi nuclear power plant for a 6 week period beginning shortly after the March 2011 tsunami. For an activity distribution of 990 “hot particles” from a small filter area, the hottest particle was nearly one Bq 137+134Cs but most of the activity in the filter was produced by particles having <50 mBq each. 134Cs/137Cs activity ratios corrected to March 20, 2011 ranged from 0.68 (u c = 28 %) to 1.3 (u c = 15 %). The average ratio for a large quantity of particles was 0.92 (u c = 4 %). Virtually all activity collected was beta and not alpha, suggesting little if any direct fuel debris was present at this site and time. These findings are expected to assist with separate efforts to better understand the emission events, radionuclide transport and potential environmental or biological uptake. The methods should be applicable to general environmental, radiotoxicological and similar studies for which activity distribution and particle chemistry are of importance.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Certain commercial equipment, instruments or materials are identified to specify experimental procedures. Such identification does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, nor does it imply that the materials or equipment identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.
References
Nuclear Energy Agency (2001) http://www.oecd-nea.org/press/2011/NEWS-04.html. Accessed 24 Aug 2011
Nikkinen M et al (2011) CTBTO science and technology 201,#JS-09, Vienna, Austria, 8–10 June 2011
Williams M (2011) IDG News Service http://www.arnnet.com.au/article/384238/ us_roboticists_complete_mission_japan_tsunami-hit_coast. Accessed 10 Feb 2012
Lindstrom RM (1994) Biol Trace Elem Res 43–45:597–603
Pollanen R et al (2011) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 248:623–627
Fichet P et al (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291:869–875
Zeissler CJ (2009) Log 315. MARC VIII, Kona
Zeissler CJ, Lindstrom AP, Davis J (2011) NUCL-33. American Chemical Society, Denver
Zeissler CJ, Lindstrom AP (2010) Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res A 624:92–100
Amemiya Y, Miyahara J (1988) Nature 336:89–90
Ohuchi H, Yamadera A (2002) Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res A 490:573–582
Vidonodo B et al (1997) Limnol Oceanogr 42:184–192
Changlai SP et al (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291:859–863
Tagami K et al (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 292:243–247
Manolopoulou M et al (2012) J Radioan Nucl Chem 292:155–159
Jinglong Wang et al (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 292:1297–1301
Sartandel S et al (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 292:995–998
Akio Iwanade et al (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 293:703–709
Stanley FE et al (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-012-1927-3
Fichet P et al (2012) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291:869–875
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeissler, C.J., Forsley, L.P.G., Lindstrom, R.M. et al. Radio-microanalytical particle measurements method and application to Fukushima aerosols collected in Japan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 296, 1079–1084 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2135-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-2135-x