Abstract
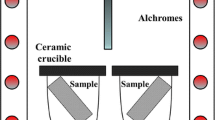
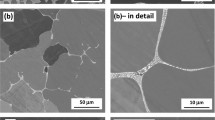
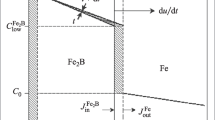
Isothermal oxidation resistance of Fe40 (at.%) Al-based atomized and deposited intermetallic alloys has been evaluated. The alloys included Fe40Al, Fe40Al + 0.1B, and Fe40Al + 0.1B + 10Al2O3 at 800, 900, 1000, and 1100 °C. The tests lasted approximately 100 h, although in most cases there was scale spalling. At 800 and 900 °C, the Fe40Al + 0.1B alloy had the lowest weight gain, whereas the Fe40Al alloy had the highest weight gain at 800 °C (0.10 mg/cm2) and the Fe40Al + 0.1B + 10Al2O3 alloy was the least oxidation resistant at 900 °C with 0.20 mg/cm2. At 1000 °C, the Fe40Al + 0.1B alloy showed the highest weight gain with 0.12 mg/cm2 and the Fe40Al alloy the lowest. At 1100 °C, again, as at 900 °C, the Fe40Al alloy was the least resistant, whereas the Fe40Al + 0.1B alloy performed the best, but the three alloys exhibited a paralinear bahavior on the weight-gain curves, indicating the spalling, breaking down, and rehealing of the oxides. This spalling was related to voids formed at the metal-oxide interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Sykes and J. Bampfylde: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1934, vol. 130, pp. 389–418.
G. Webband and A. Lefort: Symp. Proc. Fatigue and Fracture of Ordered Intermetallic Materials: I, TMS, Warrandale, PA, 1994, p. 103.
J.L. Smialek, J. Doychak, and D.J. Gaydosh; in Oxidation of High-Temperature Intermetallics, T. Grobstein and J. Doychak, eds., TMS, Warrandale, PA, 1989, p. 83.
J.H. Schneibel: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1992, vol. A153, p. 684.
S. Zeng, X.R. Nutt, and E.J. Lavernia: Metall. Mater. Trans., 1994, vol. A26, p. 817.
R.G. Baligidad, U. Prakash, and A. Radha Krishna: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1997, vol. A230, p. 188.
B.A. Pint, P.F. Tortorellli, and I.G. Wright: Mater. Corr., 1996, vol. 47, pp. 663–74.
B.A. Pint, P.F. Tortorellli, and I.G. Wright: Mater. High Temp., 1997, vol. 15, p. 613.
L. Martinez, O. Florez, M. Amaya, A. Duncan, S. Viswanathan, and D. Lawrynowics: J. Mater. Synth. Processing, 1997, vol. 5, p. 65.
M. Sakiyama, P. Tomasewicz, and G.R. Wallwork: Oxid. Met., 1979, vol. 13, pp. 573–77.
B.A. Pint: in Fundamental Aspects of High Temperature Corrosion, D.A. Shores, R.A. Rapp, and P.Y. Hou, eds., The Electrochemical Society, Pennington, NJ, 1997, pp. 74–85.
R.A. Perkins, G.H. Meier, and K.T. Chiang: Paper presented at the Workshop on Oxidation of High Temperature Intermetallics, sponsored by NASA Lewis Research Center, Case Western Reserve University, and the Cleveland Chapter of AIME, Cleveland, OH, Sept. 22–23, 1988.
P.F. Tortorelli and K. Natesan: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1998, vol. A258, pp. 115–25.
P.Y. You: in Microscopy of Oxidation, S.B. Newcomb and J.A. Little, eds., Institute of Materials, London, 1997, pp. 140–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espinosa-Medina, M.A., Casales, M., Martinez-Villafañe, A. et al. Oxidation behavior of atomized Fe40Al intermetallics doped with boron and reinforced with alumina fibers. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 9, 638–642 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994900770345494
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105994900770345494