Summary
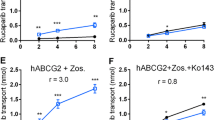
Introduction Palbociclib is a cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor with nanomolar potency and was recently approved for treatment of breast cancer. The drug may also be useful in glioblastoma (GBM) and diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPG), which often have an activated CDK4/6-retinoblastoma signaling pathway. However, GBM and DIPG spread widely into the surrounding brain, which calls for a CDK4/6 inhibitor with sufficient blood–brain barrier penetration. Methods We first performed in vitro transwell assays and demonstrate that palbociclib is a substrate of both P-gp and BCRP. Next, we conducted pharmacokinetic studies using wildtype, Abcg2−/−, Abcb1a/b−/− and Abcg2; Abcb1a/b−/− mice. Results The plasma levels were about 3000 and 500 nM and similar in all genotypes at 1 and 4 h after i.v. administration of 10 mg/kg. At 4 h the brain-to-plasma ratios were 0.3 in WT and Abcg2−/− mice versus 5.5 and 15 in Abcb1a/b−/− and Abcg2; Abcb1a/b−/− mice, respectively. The oral bioavailability of palbociclib was high (63 %) in WT mice and increased only modestly and non-significantly in Abcg2; Abcb1a/b−/− mice. The plasma level after oral dosing of 150 mg/kg was already much higher than observed in patients (200–400 nM) and exceeded 2500 nM for up to 24 h. This latter dose is commonly used in preclinical studies, which calls into question their predictive value as they were conducted at dose levels causing a clinically non-relevant systemic drug exposure. Conclusion Thus, the brain penetration of palbociclib is restricted by P-gp and BCRP, which may restrict the efficacy against GBM and DIPG. Moreover, preclinical studies with this agent should be conducted at a more clinically relevant dose level.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL, Meade M, Trachet E, Albassam M, Zheng X, Leopold WR, Pryer NK, Toogood PL (2004) Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by Pd 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 3(11):1427–1438
Baughn LB, Di Liberto M, Wu K, Toogood PL, Louie T, Gottschalk R, Niesvizky R, Cho H, Ely S, Moore MA, Chen-Kiang S (2006) A novel orally active small molecule potently induces G1 arrest in primary myeloma cells and prevents tumor growth by specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6. Cancer Res 66(15):7661–7667. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-1098
Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, Kalous O, Cohen DJ, Desai AJ, Ginther C, Atefi M, Chen I, Fowst C, Los G, Slamon DJ (2009) Pd 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res 11(5):R77. doi:10.1186/Bcr2419
Michaud K, Da S, Oermann E, Kim JS, Zhong WZ, Prados MD, Ozawa T, James CD, Waldman T (2010) Pharmacologic inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 arrests the growth of glioblastoma multiforme intracranial xenografts. Cancer Res 70(8):3228–3238. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-09-4559
Barton KL, Misuraca K, Cordero F, Dobrikova E, Min HD, Gromeier M, Kirsch DG, Becher OJ (2013) Pd-0332991, a Cdk4/6 inhibitor, significantly prolongs survival in a genetically engineered mouse model of brainstem glioma. PLoS ONE 8(10):E77639. doi:10.1371/Journal.Pone.0077639
Dhillon S (2015) Palbociclib: first global approval. Drugs 75(5):543–551. doi:10.1007/S40265-015-0379-9
Stupp R, Mason W, Van Den Bent M, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn M, Belanger K, Brandes A, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer R, Ludwin S, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross J, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff R, European Organisation for R, Treatment of Cancer Brain T Radiotherapy G, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials G (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996. doi:10.1056/Nejmoa043330
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2008) Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 455(7216):1061–1068. doi:10.1038/Nature07385
Brennan CW, Verhaak RG, Mckenna A, Campos B, Noushmehr H, Salama SR, Zheng S, Chakravarty D, Sanborn JZ, Berman SH, Beroukhim R, Bernard B, Wu CJ, Genovese G, Shmulevich I, Barnholtz-Sloan J, Zou L, Vegesna R, Shukla SA, Ciriello G, Yung WK, Zhang W, Sougnez C, Mikkelsen T, Aldape K, Bigner DD, Van Meir EG, Prados M, Sloan A, Black KL, Eschbacher J, Finocchiaro G, Friedman W, Andrews DW, Guha A, Iacocca M, Bp O’n, Foltz G, Myers J, Weisenberger DJ, Penny R, Kucherlapati R, Perou CM, Hayes DN, Gibbs R, Marra M, Mills GB, Lander E, Spellman P, Wilson R, Sander C, Weinstein J, Meyerson M, Gabriel S, Laird PW, Haussler D, Getz G, Chin L, Network TR (2013) The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 155(2):462–477. doi:10.1016/J.Cell.2013.09.034
Paugh BS, Broniscer A, Qu C, Miller CP, Zhang J, Tatevossian RG, Olson JM, Geyer JR, Chi SN, da Silva NS, Onar-Thomas A, Baker JN, Gajjar A, Ellison DW, Baker SJ (2011) Genome-wide analyses identify recurrent amplifications of receptor tyrosine kinases and cell-cycle regulatory genes in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J Clin Oncol 29(30):3999–4006. doi:10.1200/Jco.2011.35.5677
Wu G, Diaz A, Paugh B, Rankin S, Ju B, Li Y, Zhu X, Qu C, Chen X, Zhang J, Easton J, Edmonson M, Ma X, Lu C, Nagahawatte P, Hedlund E, Rusch M, Pounds S, Lin T, Onar-Thomas A, Huether R, Kriwacki R, Parker M, Gupta P, Becksfort J, Wei L, Mulder H, Boggs K, Vadodaria B, Yergeau D, Russell J, Ochoa K, Fulton R, Fulton L, Jones C, Boop F, Broniscer A, Wetmore C, Gajjar A, Ding L, Mardis E, Wilson R, Taylor MR, Downing JR, Ellison D, Zhang J, Baker SJ, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital-Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome P (2014) The genomic landscape of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma and pediatric non-brainstem high-grade glioma. Nat Genet 46(5):444–450. doi:10.1038/Ng.2938
Van Tellingen O, Yetkin-Arik B, de Gooijer MC, Wesseling P, Wurdinger T, de Vries HE (2015) Overcoming the blood–brain tumor barrier for effective glioblastoma treatment. Drug Resist Updat 19:1–12. doi:10.1016/J.Drup.2015.02.002
Lin F, de Gooijer MC, Hanekamp D, Brandsma D, Beijnen J, Van Tellingen O (2013) Targeting core (mutated) pathways of high-grade gliomas: challenges of intrinsic resistance and drug efflux. CNS Oncol 2(3):271–288. doi:10.2217/Cns.13.15
Sparreboom A, Van Asperen J, Mayer U, Schinkel A, Smit JW, Meijer DK, Borst P, Nooijen WJ, Beijnen J, van Tellingen O (1997) Limited oral bioavailability and active epithelial excretion of paclitaxel (taxol) caused by P-glycoprotein in the intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(5):2031–2035
Lin F, Buil L, Sherris D, Beijnen J, Van Tellingen O (2013) Dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor palomid 529 penetrates the blood–brain barrier without restriction by Abcb1 and Abcg2. Int J Cancer 133(5):1222–1233. doi:10.1002/Ijc.28126
Zhang Y, Huo M, Zhou J, Xie S (2010) Pksolver: an Add-in program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis in microsoft excel. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 99(3):306–314. doi:10.1016/J.Cmpb.2010.01.007
Shukla S, Ohnuma S, Ambudkar SV (2011) Improving cancer chemotherapy with modulators of Abc drug transporters. Curr Drug Targets 12(5):621–630
Oostendorp RL, Beijnen J, Schellens J (2009) The biological and clinical role of drug transporters at the intestinal barrier. Cancer Treat Rev 35(2):137–147. doi:10.1016/J.Ctrv.2008.09.004
Na DV, Beijnen J, Boogerd W, Van Tellingen O (2006) Blood–brain barrier and chemotherapeutic treatment of brain tumors. Expert Rev Neurother 6(8):1199–1209. doi:10.1586/14737175.6.8.1199
Dahan A, Miller JM, Amidon GL (2009) Prediction of solubility and permeability class membership: provisional Bcs classification of the world’s top oral drugs. AAPS J 11(4):740–746. doi:10.1208/S12248-009-9144-X
Flaherty K, Lorusso PM, Demichele A, Abramson VG, Courtney R, Randolph SS, Shaik MN, Wilner KD, O'Dwyer PJ, Schwartz GK (2012) Phase I, dose-escalation trial of the oral cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor Pd 0332991, administered using a 21-day schedule in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18(2):568–576. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-11-0509
Niesvizky R, Badros Az, Costa Lj, Ely Sa, Singhal Sb, Stadtmauer Ea, Haideri Na, Yacoub A, Hess G, Lentzsch S, Spicka I, Chanan-Khan Aa, Raab Ms, Tarantolo S, Vij R, Zonder Ja, Huang X, Jayabalan D, Diliberto M, Huang X, Jiang Y, Kim St, Randolph S, Chen-Kiang S (2015) Phase 1/2 Study Of Cdk4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (Pd-0332991) With bortezomib and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma1–21. Doi:10.3109/10428194.2015.1030641
Schwartz GK, LoRusso PM, Dickson MA, Randolph SS, Shaik MN, Wilner KD, Courtney R, O'Dwyer PJ (2011) Phase I study of Pd 0332991, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, administered in 3-week cycles (schedule 2/1). Br J Cancer 104(12):1862–1868. doi:10.1038/Bjc.2011.177
Parrish KE, Pokorny JL, Mittapalli RK, Bakken K, Sarkaria JN, Elmquist WF (2013) Abstract C81: Bbb efflux pump activity limits brain penetration of palbociclib (Pd0332991) in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther 12(11 Supplement):C81. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.Targ-13-C81
Kemper EM, Leenders W, Kusters B, Lyons S, Buckle T, Heerschap A, Boogerd W, Beijnen J, Van Tellingen O (2006) Development of luciferase tagged brain tumour models in mice for chemotherapy intervention studies. Eur J Cancer 42(18):3294–3303. doi:10.1016/J.Ejca.2006.07.013
Mcconville P, Hambardzumyan D, Moody JB, Leopold WR, Kreger AR, Woolliscroft MJ, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD, Holland EC (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging determination of tumor grade and early response to temozolomide in a genetically engineered mouse model of glioma. Clin Cancer Res 13(10):2897–2904. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-06-3058
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a research grant from the foundation Stophersentumoren.nl (O.v.T.). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Gooijer, M.C., Zhang, P., Thota, N. et al. P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein restrict the brain penetration of the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib. Invest New Drugs 33, 1012–1019 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0266-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0266-y